In this post, we are going to provide numericals on electricity for class 10 with solutions. These numericals on electricity are important and are always asked in the Class 10 CBSE, RBSE, and other board examinations.
Numerical Problems based on Ohm’s law
To solve the numericals on electricity
based on Ohm’s law , we will use the following formulas
V=IR
`R=V/I`
`I=V/R`
Where
V = Voltage (Potential difference) = volt
R = Resistance – Ohm (Ω)
I = Electric current – Ampere
1. When
a cell of 1.5 volts is applied in a circuit, a current of 0.5 ampere flows
through it. Calculate the resistance of the circuit.
Given values
Voltage (V) = 1.5
volt
Current (I) = 0.5 A
Resistance (R)
= ?
Solution
`R=frac\{V}{I}`
Put the values in the formula of resistance
`R=frac\{1.5}{0.5}`=3 Ohm
2. How
much current will an electric bulb draw from a 220-volt source. If the resistance
of the filament is 1200 ohm?
Given values
Voltage (V) = 220 volt
Resistance (R) = 1200 Ohm
Current (I) = ?
Solution
`I=frac\{V}{R}`
3. What
is the potential difference between the ends of a conductor of 15 Ohm
resistance when a current of 2 ampere flows through it.
Given values
Resistance (R)
= 15 Ohm
Electric current (I ) = 2 A
Potential difference (V) =?
Solution
V=IR
V=2 ×15=30 volt
4. A heater draws a current of 5 A when it is connected to 110 volts. What current will the heater draw when it is connected to 220 volts.
Given values
Current (I1) = 5 A
Voltage (V1) = 110 volts
Voltage (V2) = 220 volts
Current (I2) =?
Solution
According to Ohm’s law
V=IR
`R=frac\{110}{5}`=22 Ohm
When the voltage is 220 volt
The current will be
`I_2=frac\{220}{22}`=10 A
5. Calculate the potential difference required across a conductor of resistance 6 ohm to make a current of 2.5 A flow through it.
Given values
Resistance (R) = 6 ohm
Current (I) = 2.5 A
Potential difference (V) =?
Solution
V=IR
V=2.5× 6=15 volt
Numerical Problems Based on Resistance and Resistivity
We will use the following formulas to solve the numericals on electricity based on resistance and resistivity
`R=ρ frac\{l}{A}`
Where
R = Resistance -Ohm
ρ = Resistivity -Ohm m
l = length – m
A = area of cross-section -`m^2`
6. Calculate
the resistance of a copper wire of length 30 cm and the area of cross-section 3× 10-4
m2. The resistivity of copper is 1.7 × 10-8 ohm ×m.
Given values
Length of wire (l) = 30 cm = 0.3m
Area of cross-section (A) = 3× 10-4 m2
Resistivity of copper (p) = 1.7 × 10-8 ohm
×m.
Resistance (R ) =?
Solution
`R=ρ frac\{l}{A}`
`R=1.7 × 10^-8 × frac\{0.3}{3× 10^-4 }`
`R=(0.51× 10^(-8))/(3 × 10^(-4) )`
`R=(0.17× 10^(-8))/( 10^(-4) )`
`R=0.17×10^(-8)×10^4`
`R=0.17×10^(-4)` Ohm
7. Calculate
the resistivity of wire having length 1 m and area of cross section 1.20 × 10-6
m2, if its resistance is 0.013 ohm.
Given values
Area of cross-section (A) = 1.20 × 10-6 m2
Length (l) = 1m
Resistance (R) =0.013 ohm
Resistivity (ρ ) =?
Solution
`R=ρ frac\{l}{A}`
Now put the values in the formula
`0.013=ρ frac{1}{1.20 × 10^-6}`
`ρ= 0.013×frac\{1.20 ×10^-6}{1}`
`ρ=1.56 × 10^-8` ohm m
8. Calculate
the area of cross section of a wire of 1 m and resistance 25 ohm, if the resistivity
of material of the wire is 1.84 ×10-6 ohm m.
Given values
Length (l) = 1m
Resistance (R) = 25 ohm
Resistivity (ρ ) = 1.84 ×10-6 ohm m
Area of cross-section (A) =?
Solution
`R=ρ frac\{l}{A}`
`25=1.84×10^-6×frac\{1}{A}`
`A=1.84×10^(-6)×frac\{1}{25 }`
`A=7.36 × 10^-8 m^2`
9.1 m long wire with resistance 0.85 ohm and diameter 0.2 mm, what will be the resistivity of the metal at 20℃.
Given values
Length (l) =1m
Resistance (R)= 0.85 ohm
Diameter (d) =0.2 mm= 2 ×10-4m
Radius (r) = d/2 =
1 ×10-4m
Area of cross-section (A) =? (`πr^2`)
Solution
`R=ρ frac\{l}{A}`
`R=ρ frac\{l}{πr^2} `
`0.85=ρfrac\{ 7}{22×(1 × 10^(-4))^2 }`
`ρ= frac\{0.85×22}{7×10^-8}`
`ρ= 2.67×10^-8` ohm m
Numerical Problems based on the Combination of Resistances
Now we will solve the numericals based on a combination of resistance. The following formulas can be used to find the equivalent or total resistance of the combination.
`R= R_(1 )+ R_2+R_3+⋯R_n`
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3 +⋯1/R_n `
Where
`R_(1 ) ,R_2,R_3` and `R_n` are different resistances
R = total resistance of the combination
10. Three
resistances of 5 ohm,10 ohm, and 15 ohm are connected in series, find the total
resistance.
Given value
R1= 5 ohm
R2= 10 ohm
R3= 15 ohm
R= ?
Solution
`R= R_(1 )+ R_2+R_3`
R= 5+ 10+15 = 30 ohm
11. Three
resistances of 5 ohm,10 ohm, and 15 ohm are connected in parallel, find the total
resistance.
Given values
R1= 5 ohm
R2= 10 ohm
R3= 15 ohm
R= ?
Solution
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3`
`1/R= 1/5+1/10+1/15`
`1/R= (6+3+2 )/30=11/30`
`1/R=11/30`
`R=30/11=2.72` ohm
12. Three
resistances of 5 ohm,10 ohm, and 15 ohm are connected in series, and the system is
connected to 90-volt battery. What will the current flow in the circuit?
Given values
R1= 5 ohm
R2= 10 ohm
R3= 15 ohm
V= 90 volt
I =?
Solution
`I=V/R`
We don’t have the value of ‘ R’ so first we will find the value
R= 5+ 10+15=30 ohm
`I=V/R= 90/(30 )`=3 A
13. Three
resistances of 5 ohm,10 ohm, and 15 ohm are connected in parallel combination and
the circuit is connected to a 100-volt battery. Find the electric current flowing
in each of the resistances.
Given values
R2=
10 ohm
R3=
15 ohm
V=
100 volt
I1
= ?
I2=
?
I3=
?
Solution
`I_1=V/R_1`
`I_1=100/5=20 A`
`I_2=V/R_2 `
`I_2=100/10=10 A`
`I_3=V/R_3`
`I_3=100/15=6.66 A`
(Note : Current in all resistors is different in the parallel
combination.)
14. Three
resistors of 5 ohm,10 ohm, and 15 ohm are connected in series combination, and a 10 ampere current is flowing in the system when connected with 110 Volt. Find the
potential difference between the two ends of each resistor.
Given values
R1= 5 ohm
R2= 10 ohm
R3= 15 ohm
V= 110 volt
I =10 A
V1 = ?
V2= ?
V3= ?
Solution
`V_1=IR_1`
`V_1=10×5`=50 volt
`V_2=IR_2`
`V_2=10×10`=100 volt
`V_3=IR_3`
`V_3=10×15`=150 volt
15. Three
resistances of 2 ohm, 3 ohm, and 6 ohm are connected in series and then in parallel.
Find the total resistance in both arrangements.
Given values
R1= 2 ohm
R2= 3 ohm
R3= 6 ohm
R =
Total resistance =?
Solution
i. For series combination
`R= R_(1 )+ R_2+R_3`
R= 2 + 3 +6 =11 ohm
ii.For parallel combination
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3`
`1/R= 1/2+1/3+1/6`
`1/R= (6+4+2 )/12 = 12/12`
R= 1 ohm
16. A
18 Volt battery is connected across a lamp whose resistance is 50 ohm, through
a variable resistor. If the current flowing through the circuit is 0.3 A. Calculate
the value of resistance used from the variable resistor.
Given values
Voltage (V) = 18 volt
Current (I) = 0.3 A
Resistance of bulb (r) = 50 ohm
R1 = resistance form variable resistor =?
Solution
Let R1 be the resistance from a variable resistor
that is used
Both R1 and r are is series combination so
the resultant resistance is
R= R1
+ r
According to Ohm’s law
V=IR
15 = 0.3 × (R1 + r)
`R1 + 50 = frac\{18}{0.3}` = 60
R1 = 60 -50 = 10 ohm
Numerical Problems Based on the Circuit diagrams
To solve the numerical problems based on the circuit
diagrams, we will use the formulas given above.
17.Calculate
the total resistance of the following circuit.
Given values
`R_1`= 5 ohm
`R_2`= 10 ohm
`R_3`= 20 ohm
R =?
Solution
All resistances in the given circuit are connected in the series so total resistance
`R= R_(1 )+ R_2+R_3`
R= 5+ 10+20=35 ohm
18. Calculate the total resistance in the given circuit
Given values
`R_1`= 5 ohm
`R_2`= 10 ohm
`R_3`= 20 ohm
R =?
Solution
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3`
`1/R= 1/5+1/10+1/20`
`1/R= (4+2+1)/20=7/20`
`R= 20/7=2.85 ohm`
19. You have been given the following circuit diagram.
Find the following
i. Electric current through each resistor
ii. Total resistance
iii. Total
current
Given values
`R_1`= 5 ohm
`R_2`= 10 ohm
`R_3`= 30 ohm
V = 6 volt
R =?
I1= ? , I2= ? and I3 =?
I =?
Solution
All the resistors are connected in parallel combination
i.Current through each resistor
`V=I_1 R_1`
`6=I_1×5`
`I_1= 6/5=1.2 A`
`V=I_2 R_2`
`6=I_2×10`
`I_2= 6/10=0.6 A`
`V=I_3 R_3`
` 6=I_3×30`
`I_3= 6/30=0.2 A`
ii. Total resistance (R)
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2 +1/R_3 `
`1/R= 1/5+1/10+1/30`
`1/R= (6 +3 +1)/30= 10/30`
`R= 30/10=3 Ohm`
iii. Total current (I)
`V=IR`
6=I×3
`I= 6/3=2 A`
20. Find the equivalent resistance in the given circuit and the current flowing through the circuit.
Given values
R1
= 3 ohm
R2
= 6 ohm
V=
4.5 volt
R=?
Solution
We
can see that the resistors of 3 ohm and 6 ohm are connected in parallel
combination so the equivalent resistance R
`1/R= 1/R_1 +1/R_2`
`1/R= 1/3+1/6`
`1/R= (2 +1 )/6= 3/6`
`
`R= 6/3=2 ohm`
According to Ohm’s law
`V=IR`
`4.5 = I× 2`
`I= 4.5/2=2.25 A`
22. You have been given the following circuit of resistors connected with a battery.
Calculate
i. total resistance of the circuit
ii. total current
iii.voltage
across 5 ohm resistor
Given values
`R_1` = 10 ohm
`R_2`= 10 ohm
`R_3`= 5 ohm
V= 6 volt
Solution
i. Total resistance
We can see that `R_1` and `R_2` are in parallel so the total resistance `R_A`
`1/R_A = 1/R_1 + 1/R_2`
`1/R_A = 1/10+ 1/10`
`1/R_A = (1+1 )/10= 2/10`
`R_A= 10/2=5 Ohm`
Now `R_A` and `R_3` are in series so the total resistance R
`R = R_A + R_3`
`R = 5 + 5 =10 Ohm`
ii. Total current
`I= V/R= 6/10=0.6 A`
iii. Voltage across 5 ohm resistor
`V_1= IR_1`
`V_1 = 0.6 × 5`
`V_1` = 3 volt
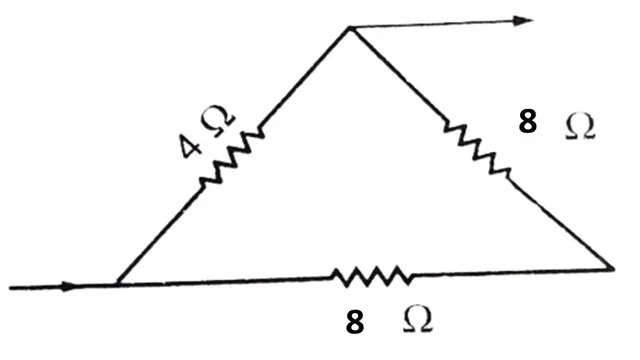
23. Find
the equivalent resistance of the following circuit of resistors.
Given values
R1= 4Ohm
R2 = 8Ohm
R3 =8 Ohm
R =?
Solution
In the given circuit diagram we can see that R2 and R3
are series so
RA = R2
+ R3
RA = 8 + 8 =16 Ohm
Now the `R_A` is parallel to `R_1` so the equivalent resistance R
`1/R=1/R_1 + 1/R_A`
`1/R=1/4+ 1/16`
`1/R=(4+1)/16=5/16`
`R=16/5=3.2` Ohm
(i) Power
P=VI
P = 2.5 ×0.65 = 1.625 W
(ii). Resistance
`R=V/I`
`R=2.5/0.65=3.84` Ohm
✅Related Topics
1. Derive the formula of work done when current flows through a conductor or resistor
2. Numerial Based on Electric Current





.jpg)



No comments:
Post a Comment