In this article, we will discuss the electrolysis of water for class 10 students. This topic comes from Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.
We will perform electrolysis of water using a voltameter.
Voltameter:
- The apparatus used for carrying out electrolysis is called a voltameter.
Working model of voltameter:
- This model can easily be made. We take a plastic mug and drill two holes at
the bottom of it.
Now we take two carbon electrodes and fix them in the holes and close
the holes with adhesives.
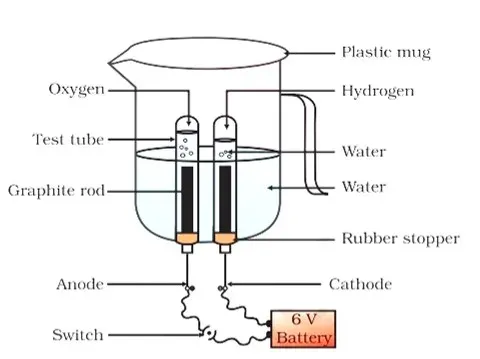 |
| Volatmeter |
Electrolysis of water
We fill the water to its half in the voltameter and connect the electrodes
with a 6-volt battery and a key. Now we add a few drops of dilute sulphuric
acid.
We take two tests tube filled with water and invert them on
electrodes and allow the current to pass through the circuit and voltameter.
Leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
Observation:
- Electrolysis starts and the formation of bubbles takes place at both electrodes.
After some time, stops passing the current and test the collected gases in both
test tubes.
In the electrolysis of water, hydrogen is
formed at the cathode, and oxygen is formed at the anode.
Also, we find the volume of hydrogen is about double of oxygen.
`H_2O → 2H_(2g) +O_(2g)`
Result:- during the electrolysis
of water, hydrogen and oxygen gases are formed in a ratio of 2:1 by volume.
Related Topics
1. What happens during a chemical reaction
FAQs
1. During the electrolysis
of water what is formed at the anode
Ans.- Oxygen gas is
collected at the anode.
2. Which
gas is collected at the cathode in electrolysis of water class 10?
Ans.- Hydrogen is collected at the cathode in the electrolysis of water.
3. What
is the ratio of hydrogen and oxygen gases collected during electrolysis?
Ans.- 2:1




No comments:
Post a Comment