In this post, you will find NCERT Class 10 Science Book Activities Solutions Chapter 9 which is completely based on Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
NCERT Class 10 Science Book Activities Solutions Chapter 9
|
S.N. |
Contents |
|
1 |
|
|
2 |
Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Activity 9.1
Activity - Observe the ears of all the students in the class. Prepare a list of students having free or attached ear lobes and calculate the percentage of students having each
Find out about the ear lobes of the
parents of each student of the class. Correlate the ear lobe type of each
student with that of their parents. Based on this evidence, suggest a possible
rule for the inheritance of ear lobe type.
Discussion – The presence of free and
attached ear lobes in an example of an insignificant variation of human
population.
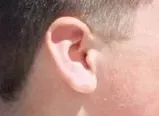
Free ear lobe – The lowest part of
ear (ear lobe) is free from the side of the head.
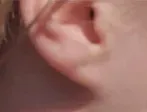
Attached ear lobe
– The lowest part of ear lobe is closely attached to the side of the head.
When you observe the ear lobes of your classmate you
would find that majority of the students
have free ear lobes. Some have attached ear lobes as well.
When the ears of the parents of students having free
ear lobes are observed its is revealed that either both or atleast one of their
parent must have free ear lobe. For students having attached ear lobes their
parents may have free or attached ear lobes.
Like any other trait inheritance of ear lobe
is controlled by a gene. For the trait of ear lobe type, there are two
alternate forms. Free ear lobe gene is dominant over the attached ear lobe
gene. If we give a symbol of ‘D’ to the free lobe gene and ‘d ’ to the attached ear
lobe gene, then the following three genotypes are possible in the human population.
1. Genotype
– DD [for free ear lobe]
2. Genotype
Dd [for free ear lobe and D is dominant over d]
3. Genotype
dd [for attached ear lobe]
Now
on the basis of the above genotypes, there may be the following conditions in its inheritance
(i) If father is Dd and
mother is Dd
|
|
D |
d |
|
D |
DD |
Dd |
|
D |
DD |
Dd |
In the above chart, all the children have free ear lobes
because D is dominant.
(ii). If both
parents are Dd
|
|
D |
d |
|
D |
DD |
Dd |
|
d |
Dd |
dd |
(iii). If both parents are dd then their children will
have attached ear lobe only.
Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Activity 9.2
Activity
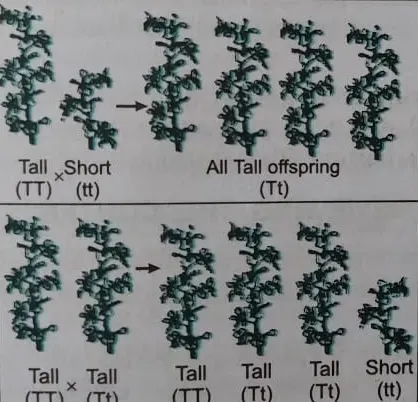
-In the figure shown here, what
experiment would we do to confirm that F2 generation did in fact have 1 : 2 : 1 ratio of TT, Tt and tt trait combination.
Discussion – In a monohybrid cross
the F2 ratio is 3 : 1. It means 3 plants are tell and 1 is dwarf.
This ration is called phenotypic ration or monohybrid ratio.
To know whether a tall plant is true
breeding or not or to know that a plant
is pure or hybrid we do Test cross.
Test cross is a cross in which a
plant of unknown genotype is crossed with a recessive parent.
If the unknown plant is pure (TT) and it is crossed with the recessive plant (tt) , we will get all tall
plants
|
|
t |
t |
|
T |
Tt |
Tt |
|
T |
Tt |
Tt |
If the unknown plant is a hybrid(Tt) and it is crossed with a recessive plant(tt),
we will get 50% tall plants and 50% dwarf plants.
|
|
t |
t |
|
T |
Tt |
Tt |
|
t |
tt |
tt |
So with
the help test cross, we can prove that phenotype 3:1 ratio is genotypic ratio
1:2:1.
so these activities are based on Chater 9 Heredity and Evolution.
Related searches -
2. Extra Questions of Chapter 9
.jpg)


