Here you will find NCERT Solutions for Class10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds contains all the main and important topics which have a complete and detailed description. NCERT Solutions for Class10 Science Chapter 4 solutions will help the students of class 10 to understand concepts.
Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Solutions |
Carbon and its compounds questions and answers cover the complete syllabus and let you secure the best results in CBSE and other board
exams. NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 4 will help you to solve
homework and home assignments in an easy way.
NCERT Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Exercise Solutions
The
students can download NCERT Solutions for Class10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and
its Compounds in PDF format for offline use.
10th Science Part 2 Chapter 4 Exercise with Answers
You must know the
topics and subtopic of 10th Science Part 2 Chapter 4 Exercise with Answers of NCERT Science book before you go through
the Solutions of Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds of NCERT Science for Class 10.
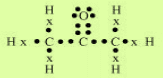
1. Bonding in Carbon- The Covalent Bond
2. Versatile Nature of Carbon
3. Chemical Properties of Carbon Compounds
4. Some Important Carbon Compounds – Ethanol and
Ethanoic Acid
5. Soaps And Detergents
Students of the CBSE
board, RBSE, and other state boards of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat, and all other states
can download Solutions of Chapter 4 Carbon and its
Compounds of NCERT Science for Class 10 in English medium and
Hindi medium in PDF format for free.
You can also watch
videos of Solutions of Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds of NCERT Science for Class 10 online. The solution is based on the latest syllabus of CBSE 2021-22.
Solutions of Chapter 4
Carbon and its Compounds of NCERT Science for Class 10 Intext questions
Carbon and its Compounds intext questions
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS:
Questions (Page 61)
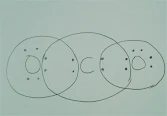
Q.1What would be the electron dot structure of carbon dioxide which has the formula CO2.?
Ans. The electron dot structure of CO2 is
as follows:
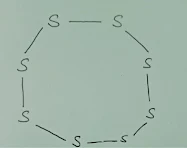
Q.2What would be
the electron dot structure of a molecule of sulphur which is made of eight
atoms of sulphur? [Hint: The eight atoms of sulphur are joined together in the
form of a ring].
Ans.
Questions (Page 68)
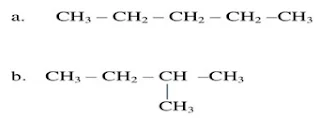
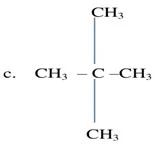
Q.1 How many
structural isomers can you draw for pentane?
Ans. We can draw three structural isomers for
pentane.
Q.2What are two
properties of carbon that lead to the huge number of carbon compounds we see
around us?
Ans (i).Catenation –The ability of a carbon atom to form bonds with other atoms of carbon is called
catenation. So carbon atoms join with one another to form a long chain.
(ii). Tetravalency–Carbon is a
tetravalent element. It has four free electrons in its outermost shell so
carbon atoms share its four-electron with other carbon atoms, oxygen, hydrogen, etc. that’s why carbon is capable
of bonding with four other atoms.
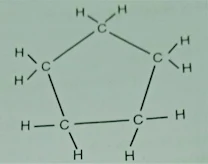
Q.3 What will be the
formula and electron dot structure of cyclopentane?
Ans. Formula C5H10
Q.4 Draw the structures for the following :
(i) Ethanoic acid
(ii)
Brompentane(all possible isomers)
(iii) Butanone
(iv) Hexanal
(ii) Bromopentane
(iii). Butanone
(iv).
Hexanal
Q.5 How would you
name the following compounds?
(i) CH3-CH2-Br
.
Ans. (i) Bromo
ethane
(i) Methanal
(ii) Hexyne
Questions (Page 74)
Q.1Conversion of
ethanoic acid from ethanol is called oxidation reaction. Why?
Ans. Conversion of ethanoic acid from ethanol is
called oxidation reaction because oxygen is added to ethanol. It is an oxidation reaction.
Q.2 A mixture of
oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding. Can you tell why a mixture of ethyne
and air is not used?
Ans. When Ethyne is burnt with oxygen, it gives a clean flame
with high temperature because of
complete combustion. That’s why this oxy-acetylene flame is used for welding.
This is the reason why a mixture of ethyne and air is not used.
But when Ethyne is burnt in
air, it gives a sooty flame due to incomplete
combustion. Its incomplete combustion takes place in air and carbon particles
remain unburnt. That’s why a mixture of Ethyne and air is not used for welding.
Questions (Page 75)
Q.1 How would you
distinguish experimentally between an alcohol and a carboxylic acid?
Ans. We
can distinguish between alcohol and carboxylic acid on the basis of their
chemical reactions
(i)Add some litmus solution to both the
test tubes containing ethanol and ethanoic acid. Colour of the litmus solution in
the test tune containing Ethanoic acid [Carboxylic acid] gets changed to red,
but no change in colour in the test tube containing ethanol.
Ethanoic acid + litmus solution → Red litmus solution
Ethanol +
litmus solution → no colour change
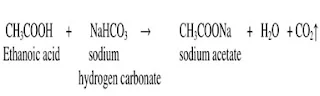
(ii)Add sodium hydrogen carbonate or
sodium carbonate to both the test tubes containing ethanol and carboxylic acid. The formation of carbon dioxide gas with effervescence indicates the presence of
carboxylic acid. But ethanol does not react with carbonates and hydrogen
carbonates
Ethanoic acid + metal
carbonate/ metal hydrogen carbonate → salt + water + carbon di oxide
Q.2 What are
oxidising agents?
Ans. The substances that oxidise the other
substance are called oxidising agents.
Questions (Page 76)
Q.1Would you be
able to check if water is hard by using a detergent?
Ans.Detergents are ammonium or sulphonate salts of long chain
carboxylic acids and they do not react
with calcium and magnesium ions present in hard water to form scum so detergents form lather effectively both in soft and hard water.
That’s why detergents can’t be used in checking whether water is hard or soft.
Q.2 People use a
variety of methods to wash clothes, usually after adding the soap, they ‘beat’
the clothes on a stone, or beat it with a paddle, scrub with a brush or the
mixture is agitated in a washing machine. Why is agitation necessary to get
clean clothes?
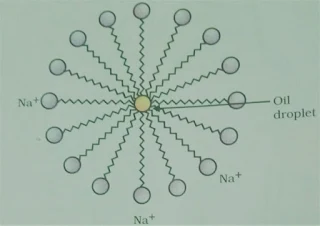
Ans. A soap molecule has two parts namely
hydrophobic and hydrophilic .These two ends of soap molecule attaché with dirt
or grease particles to form micelles. The Micelles entrap oil or grease
molecules and attachment of dirt particles become weak. To remove the dirt
particles agitation is necessary.
.
10th science part 2 chapter 4 exercise with answers
Q.1 Ethane, with the
molecular formula – C2H6 – has
(a) 6 covalent bonds
(b) 7 covalent bonds
(c) 8 covalent bonds
(d) 9 covalent bonds
Ans. (b) 7
covalent bonds
Q.2 Butanone is a
four-carbon compound with the functional group
(a) carboxylic acid
(b) aldehyde
(c) ketone
(d) alcohol
Ans. (c) ketone
Q.3 While cooking,
if the bottom of the vessel is getting blackened on the side, it means that
(a) the
food is not cooked completely
(b) the
fuel is not burning completely
(c) the
fuel is wet
(d) the
fuel is burning completely
Ans. (b) the
fuel is not burning completely
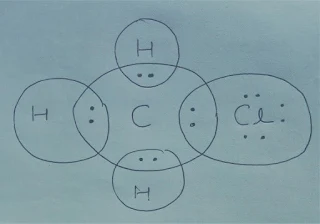
Q.4 Explain the
nature of the covalent bond using the bond formation in CH3Cl.
Ans. The electronic configuration of Cl is 2, 8, 7 and it requires 1 electron to
complete its octet and each hydrogen requires 1 electron to complete its
doublet. So the following electron dot structure is given for CH3Cl.
So C forms 4 single covalent bonds, 3 with 3 H atoms and one with Cl atom.
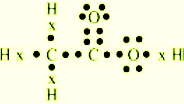
Q.5 Draw the
electron dot structure for
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b) H2S
(c) Propanone
(d) F2
Ans.
(a) Ethanoic acid
(b)
H2S
(c)
Propanone
(d). F2
Q.6 What is
homologous series?
Ans. The series of organic compounds have
similar different numbers of carbon atoms but contain the same functional
group. The two adjacent members have a difference of CH2 unit, is
called homologous series.
The
general formula of this series is CnH2n +2.
Q.7 How can ethanol
and ethanoic acid be differentiated on the basis of their physical and chemical
properties?
Ans. On the basis of physical and chemical properties, ethanol and ethanoic acid can be distinguished as follows;
1. Ethanol is a liquid at room temperature with a pleasant odour while ethanoic acid vinegar-like smell. The melting point of ethanoic acid is 290K.,it freezes during winters.
2. Ethanoic acid changes blue litmus solution to red, while ethanol shows no change in litmus solution.
3 On adding sodium carbonate or sodium hydrogen carbonate, ethanoic acid produces carbon dioxide gas which turns lime water milky, while no reaction takes place with ethanol.
Q.8 Why micelle
formation does take place when soap is added to water? Will a micelle be formed
in other solvents like ethanol also?
Ans. A soap is a sodium or potassium salt of long
chain fatty acids. It has one polar end and one non-polar end.
(i) a long hydrocarbon part
and
(ii) a short ionic part –
COONa+ group.
The long hydrocarbon part is the hydrophobic (water-repelling) part while COONa+ is the hydrophilic
(water-attracting) part. When soap is added to water, soap molecules arrange
themselves in a cluster to keep the non-polar portion out of the water such that
the non-polar ends are in the interior of the cluster and the polar ends are on
the surface of the cluster. This formation is called a micelle. Micelle will not
be formed in other solvents such as ethanol.
Q.9 Why are carbon
and its compounds are used as fuels for most applications?
Ans.Most of the carbon compounds give a lot of
heat and light when burnt in air.that why the carbon compounds are used as
a fuel.
Q.10 Explain the
formation of scum when hard water is treated with soap?
Ans. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium
salts. A soap is a sodium or potassium salt of long-chain fatty acids. When
soap is added to hard water, calcium and magnesium ions present in water
displace sodium or potassium ions from the soap molecules forming an insoluble
substance called scum.
Q.11 What change will
you observe if you test soap with litmus paper (red or blue)?
Ans. Soap is basic in nature. When soap is tested
with litmus paper, it will affect the colour of litmus paper.It will turn red
litmus blue. However, the colour of blue litmus will remain blue.
Q.12 What is
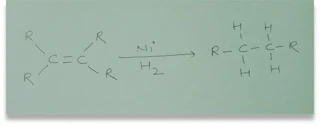
hydrogenation? What is the industrial application?
Ans. Hydrogenation – In this process hydrogen is added to unsaturated
hydrocarbons.
Industrial
use of hydrogenation - Vegetable oil contains an unsaturated hydrocarbon chain. When hydrogen is passed through them in the
presence of palladium and nickel catalysts to give saturated hydrocarbons.
Q.13 Which of the
followings hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions C2H6,
CH8, C3H6, C2H2, and CH4?
Ans. Hydrocarbons C3H6, C2H2,
and CH4 will undergo addition reactions because they are
unsaturated hydrocarbons.
C2H2 +
H2 →C2H6
Q.14 Give a test that
can be used to differentiate chemically between butter and cooking oil.
Ans. Cooking oil contains unsaturated fatty acids. That
is why it can be hydrogenated to saturated fats. On the other hand, butter
contains saturated fats. Therefore, it cannot be hydrogenated.
Q.15 Explain the
mechanism of the cleaning action of soaps.
Ans. A soap molecule is made up of two parts- i).
long hydrocarbon chain and ii). Short ionic part short ionic part – COONa+group.The long hydrocarbon part is the hydrophobic (water-repelling) part while COONa+ is the hydrophilic (water-attracting) part. When soap is added to water, soap
molecules arrange themselves in a cluster to keep the non-polar portion out of the water such that the non-polar ends are in the interior of the cluster and the
polar ends are on the surface of the cluster. This cluster is called a micelle.
The dirt and grease particles get entrapped in micelle and are removed when
treated with water.
.
These NCERT solutions
and study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board and Other state
board exams.
Related sources for you
Remedial Education Point.com provides you complete study material for class 10 absolutely free. Now you can get an accurate 10th science part 2 chapter 4 exercise with answers prepared by our expert teachers.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How
do carbon compounds harm human health and the environment?
Carbon forms numerous compounds. They
are used in our day-to-day life. Out of them, some are poisonous, they can harm
human health and the environment also.
Carbon mono oxide and carbon dioxide cause global warming and CO is poisonous.
2. What
are four types of carbon compounds?
Carbohydrates, lipids, protein, and nucleic
acids are four types of carbon compounds but basically carbon forms numerous compounds.
These carbon compounds can be classified as alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, alkanines, etc.
3. What
are unsaturated carbon compounds?
Unsaturated carbon compounds are hydrocarbons
that have a double or triple bond between two adjacent carbon atoms. These compounds
show an addition reaction. In these compounds, carbon has free electrons to share
with other atoms of elements.
4. List
of carbon compounds in everyday use.
In everyday use, there are so many
carbon compounds that are used like- milk, kerosene, petrol, wax, paper, cotton, etc
and so many.
If you find any difficulty,
please comment.


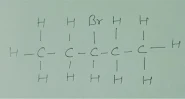
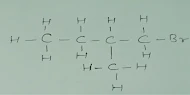

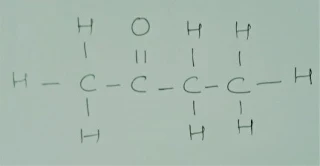
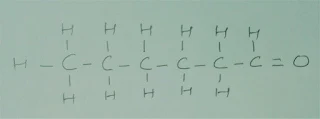


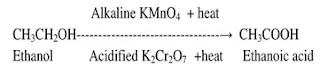


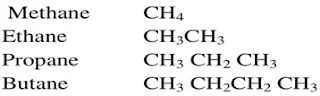
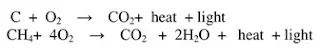




No comments:
Post a Comment