In this post, you can read and study NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13contains all the main and important topics which have a complete and detailed description. NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 is the chapter of physics class 10 science which is the most important in the context of board examinations 2021-22.
 |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 |
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13
NCERT
Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 covers the complete syllabus and lets you secure the best results in CBSE,
RBSE, and other board exams. Class 10 Science chapter 13 solutions
will help you to solve homework and home assignments in an easy way.
Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Solutions
Following are the main topics and subtopics of Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Solutions,
you must be familiar with them.
1. Magnetic Field and
Field Lines
2. Properties of
magnet
3. Properties of
magnetic field lines
4. Right-hand thumb
rule
5. Magnetic field due
to circular loop
6. Direction and magnitude
of the magnetic field of a solenoid
7. Magnetic Field Due
to A Current – Carrying Conductor
8. Permanent magnet
9. Uses of an electromagnet
10. Difference between permanent magnet and electromagnet
11. Fleming’s left-hand rule
12 Fleming’s right-hand rule
13. Uses of magnetism in medical science
14. Principle of DC motor
15. Force On a Current-Carrying Conductor in A Magnetic Field
16. Electric Motor
17. Electromagnetic Induction
18. Electric Generator
19. Faraday’s experiments
20. Alternating current
21. Advantages and disadvantages of AC and Dc
22. Domestic Electric Circuits
23. Safety measurements in using electricity in homes
24. Short-circuiting
25. Overloading
These Class 10 Science Chapter 13 Solutions are very useful for students of the CBSE board, RBSE, and
other state boards of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat, and all other state
boards.
Ch 13 Science Class 10 NCERT Solutions
Intext Question- Answer of Chapter 13- Magnetic
effects of electric current
Questions (Page 5)
Q.1 Why does a compass
needle get deflected when brought near a bar magnet?
Ans. A compass needle is a small bar magnet
and has the North Pole and the South Pole. When it is brought near a magnet same poles
of a bar magnet and needle repel each other and opposite poles attract each other
and a compass needle gets deflection.
Questions (Page 228)
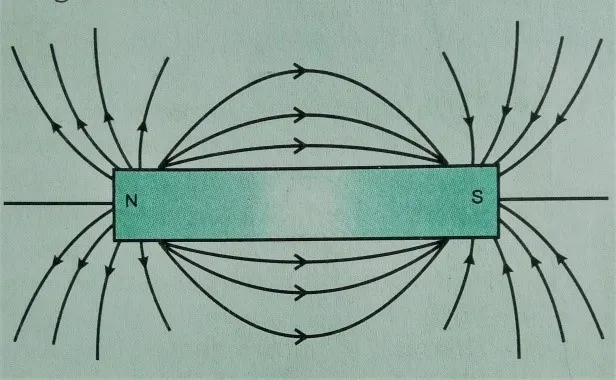
Q.1 Draw magnetic
field lines around a bar magnet.
Ans.
 |
| magnetic field lines around a bar magnet class |
Q.2 List the
properties of magnetic lines of forces.
Ans. (i). Magnetic field lines arise from the
North pole and end in the south pole of
the bar magnet.
(ii). These field lines do not
intersect each other at any point.
(iii). Close magnetic line shows the
stronger magnetic field and separated field lines show the weaker magnetic
field.
Q.3 Why do two
magnetic lines of force not intersect each other?
Ans. Two magnetic lines of force do not intersect
each other because at any point magnetic force acts in one direction.
If they intersect, it means the
magnetic field is in two directions which is not possible.
Questions (Page 229)
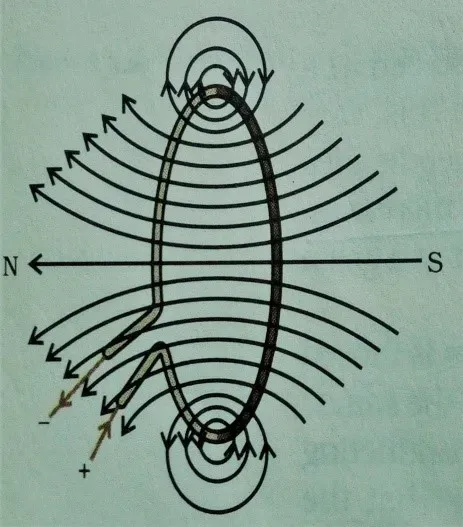
Q.1 Consider a
circular loop of wire lying in the plane of the table. Let the current pass
through the loop clockwise. Apply the right-hand rule to find out the direction
of the magnetic field inside and outside the loop.
Ans. The magnetic field will be downward to upward inside
and upward to downward outside perpendicular to any point on the loop.
 |
| the direction of the magnetic field inside and outside the circularloop. |
Q.2 The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent carrying current :
(a) is zero.
(b) decrease as we move towards the end.
(c) increase
as we move towards the end.
(d) is
the same at all points.
Ans. (d) is
the same at all points.
Questions (Page 231)
Q.1 Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field. [There may be more than one correct answer]
(a) mass
(b) speed
(c) velocity
(d) momentum
Ans. (c) velocity
(d) momentum
Q.2 In activity 3, how
do we think the displacement of rod AB
will be affected if (i) current in rod AB is increased (ii) stronger
horse-shoe magnet is used and (iii) length of the rod AB is increased.
Ans. (i) If the current in rod AB is increases displacement of rod AB will be more.
(ii) If a stronger horse-shoe magnet is used, displacement of rod AB will be increased
(iii) No effect in the displacement, if the length of rod AB is increased.
Q.3 A positivity charged particle (alpha particle projected towards the west is directed towards the north by a magnetic field. The direction of the magnetic field is
(a) towards south
(b) towards east
(c) downward
(d) upward
Ans. (a) towards
south
Questions (Page 233)
Q.1 State Fleming’s
left-hand rule.
Ans. Fleming’s left-hand rule – Stretch the
first finger(index finger), middle finger, and thumb of left hand mutually
perpendicular to each other in such a
way that the first finger represents the direction of the magnetic field, middle
finger represents the direction of
current and thumb will represent the
direction of motion of the conductor.
 |
| Fleming’s left-hand rule-class 10 science |
Q.2 What is the
principle of an electric motor?
Ans. The working of an electric motor is based
on the magnetic effect of the electric current. When a rectangular coil is placed
in a magnetic field and the current is passed through it, the coil feels a force
and starts rotating in the magnetic field. so electric energy supplied to the
motor is converted into mechanical energy.
Q.3 What is the role
of the split ring in an electric motor?
Ans. In an electric motor, split rings act as
commutators and change the direction of the flow of current through the circuit.
Questions (Page 236)
Q.1 Explain different
ways to induce a current in a coil.
Ans. (i). By relative motion between coil and
the magnet.
(ii). By
relative motion between the coil and current-carrying conductor
Questions (Page 237)
Q.1 State the
principle of an electric generator.
Ans. An electric generator is based on the principle
of Electromagnetic Induction. When a coil is rotated in a strong magnetic field, due to a change in the
magnetic force lines, an induced current flows in the coil.
Q.2 Name some sources
of direct current.
Ans. DC Generators, cells, and batteries are the
source of direct current.
Q.3 Which sources
produce alternating current?
Ans.AC generators.
Q.4 Choose the correct
option.
A rectangle coil of copper wires is
rotated in a magnetic field. The direction of the induced current changes
once in each:
(a) two revolutions
(b) one revolution
(c) half revolution
(d) one fourth revolution
Ans. (a) half
revolution
Questions (Page 238)
Q.1 Name two safety
measures commonly used in electric circuits and appliances.
Ans. Fuses and earth wires are used in
electric circuits and appliances.
Q.2 An electric oven
of 2 Kw power is operated in a domestic
electric circuit (220 V) that has a current rating of 5 A. What result do you
expect? Explain.
Ans.
Q.3 What precaution
should be taken to avoid the overloading of domestic electric circuits?
Ans. Electric fuses should be used in domestic
circuits and appliances to prevent damage due to overloading.
NCERT Solutions of Magnetic Effect of Electric Current – Exercise Questions- Answers
Q.1 Which of the
following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
(a) The
field consists of straight lines perpendicular to the wire.
(b) The
field consists of straight lines parallel to the wire.
(c) The
field consists of radial lines originating from the wire.
(d) The
field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
Ans. (d) The
field consists of concentric circles centered on the wire.
Q.2 The phenomenon of
electromagnetic induction is
(a) the
process of charging a body.
(b) the process of generating a magnetic field due to current
passing through a coil.
(c) producing induced current in a coil due to relative motion
between a magnet and the coil.
(d)the process of rotating a coil of an electric motor.
Ans. (c) producing
induced current in a coil due to relative motion between a magnet and the coil.
Q.3 The device used
for producing electric current is called a
(a) generator
(b) galvanometer
(c) ammeter
(d) motor
Ans. (a) generator
Q.4 The essential
difference between an AC generator and a
DC generator is that
(a) AC
generator has an electromagnet while a DC generator has a permanent magnet.
(b) DC
generator will generate a higher voltage.
(c) AC
generator will generate a higher
voltage.
(d) AC
generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Ans. (d) AC
generator has slip rings while the DC generator has a commutator.
Q.5 At the time of the short circuit, the current in the circuit.
(a) reduces substantially
(b) does not change
(c) increase heavily
(d) vary continuously
Ans. (c) increase
heavily
Q.6 State whether the
following statements are true or false.
(a) An
electric motor converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
(b) An
electric generator works on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
(c) The field at the center of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
(d) A wire with green insulation is usually the live wire.
Ans. (a) False
(b) True
(c) True
(d) False
Q.7 List three sources
of the magnetic field.
Ans. The three sources of the magnetic field are:
(i) Magnet
(ii) Current carrying conductor
(iii) electro-magnet
Q.8 How does a
solenoid behave like a magnet? Can you determine the north and south poles of a
current-carrying solenoid with a help of a bar magnet? Explain.
Ans. The magnetic field lines produced in a
solenoid are in the pattern of a bar magnet and it acts as a bar magnet. We can
determine the north and south poles of a current-carrying solenoid with the
help of a bar magnet.
Q.9 When is the force
experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field is
largest?
Ans. According to Fleming’s left l hand
rule, the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a
magnetic field is largest when the direction of current is at a right angle to
the direction of a magnetic field.
Q.10 Think you are
sitting in a chamber with your back to one wall. An electron beam, moving
horizontally from the back wall towards the front wall, is deflected by a strong
magnetic field to your right side. What is the direction of a magnetic field?
Ans. Applying Fleming’s left-hand rule, the Direction of the magnetic field is towards the downside perpendicular to the direction of the current.
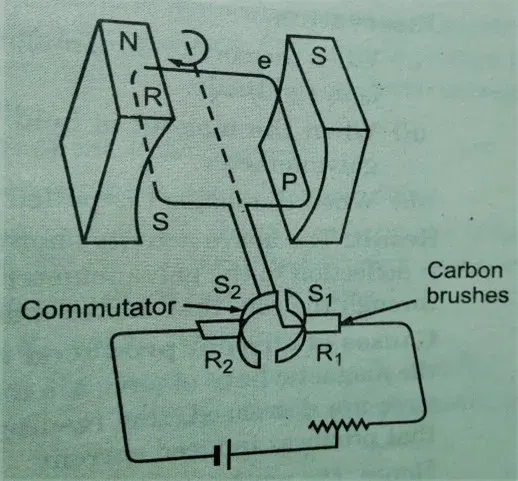
Q.11 Draw a labeled
diagram of an electric motor. Explain its principle and work. What is the
function of a split ring in an electric motor?
Ans.
 |
| Class 10 Science Electric motor |
Principle – The working of an electric motor is based on the magnetic effect of the electric current. When a rectangular coil is placed in a magnetic field and current is passed through it, the coil feels a force and starts rotating in the magnetic field. so electric energy supplied to the motor is converted into mechanical energy
Working - When current is passed through the coil, the current
in the arm AB moves from A to B and in the arm, CD moves from C to D. On
applying Fleming’s left-hand rule, a force acting on arm AB pushes it
downwards and the force acting on arm CD pushes it upwards. In this way, two
equal forces act upon the coil and the coil rotates in the clockwise direction.
At half rotation,
the half-ring S1 makes contact with the brush Q and half ring S2 with brush P. So the current in the coil gets
reversed. Now the direction of force acting on both half rings gets reversed.
The arm AB is pushed upward and arm CD is pushed downward. The reversing of the
current is repeated at each half rotation, giving rise to a continuous rotation
of the coil.
The function of
split rings – Split
rings work as commutators and they change the direction of current through the
circuit so that the current flow in the circuit in one direction that’s why the direction of force
acting on the coil remains the same.
Q.12 Name some devices
in which electric motors are used.
Ans. The devices in which electric motors are used:
Electric fans, mixers, washing machines,
refrigerators, computers. MP3 players etc.
Q.13 A coil of insulated
copper wire is connected to a galvanometer. What will happen if a bar magnet is
(i) Pushed
into the coil.
(ii) Withdrawn from inside the coil.
(iii) Held stationary inside the coil?
Ans. (i). When a bar magnet is pushed into the
coil, the magnetic flux related to the coil also changes, and due to this an induced current flows in
the coil and the galvanometer will show a momentary deflection
(ii). When a bar magnet is
withdrawn from the coil, the magnetic
flux related to the coil changes again and due to this an induced current flows in
the coil but in the opposite direction, and the galvanometer will show a momentary
deflection in opposite direction.
(iii). When the magnet is held
stationary inside the coil, there is no change (stationary) in magnetic flux
related to the coil. So no flow of induced current in the coil and galvanometer
shows no deflection.
Q.14 Two circular coils
A and B are placed closed to each other. If the current in coil A is
changed, will some current be induced in coil B? Give reasons.
Ans. Yes, some current will be inducted in the
coil B, because when current is flowing in coil A, it acts as a magnet and when the current in coil A is changed, there will be a change in magnetic field lines
related to coil A so magnetic flux related to coil B also changes.
Q.15 State the rule to
determine the direction of an (i) magnetic field produced around a straight
conductor carrying current, (ii) force experienced by a current-carrying
straight conductor placed in a magnetic field that is perpendicular to it, and
(iii) current induced in a coil due to its rotation in a magnetic field.
Ans. (a) Maxwell’s
right-hand rule.
(b) Fleming’s
left-hand rule.
(c) Fleming’s
right-hand rule.
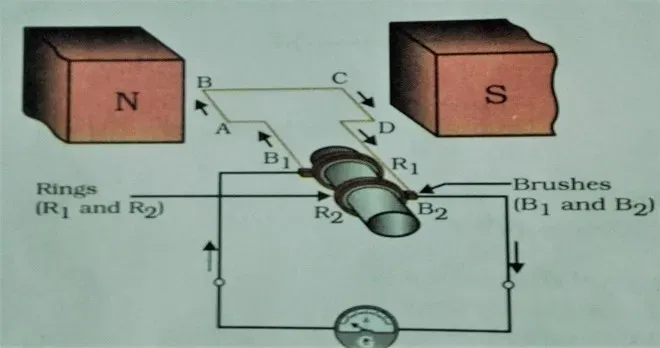
Q.16 Explain the
underlying principle and working of an electric generator by drawing a labeled
diagram. What is the function of brushes?
Ans. Principle - An electric generator is
based on electromagnetic induction. When a coil is rotated in s strong
magnetic field, the number of magnetic force lines through the coil changes, and
due to this, a current is induced in the coil. The direction of current can be
determined by Fleming’s right-hand rule.
 |
| ELECTRIC GENERATOR |
Working - When an armature (coil ABCD)
rotates in a strong magnetic field NS, it cuts the magnetic field lines and
produced a current in the coil and the current begins to flow through the brush B1
to brush B2. The direction of current can be fined by Fleming’s right-hand rule.
In the first half
cycle the current flows in one direction from brush B1 to brush B2
but in the second half cycle the direction of current from brush B2
to B1. This process continues
and the direction of current in the coil changes continuously so it is known as
alternating current.
The function of
brushes- Both the brushes
remain in the contact with the ring and provide current in the external
circuit.
Q.17 When does an
electric short circuit occur?
Ans. A short circuit occurs when the live wire
comes directly in contact with the neutral wire due to damage to the insulation
of wires or overloading.
Q.18 What is the
function of an earth wire? Why is it necessary to earth metallic appliances?
Ans. The earth wire ensures that if there is
any leakage of current to the metallic body of the appliance keeps its
potential to that of the earth and the user may not get a severe electric shock
and so earth wire is used as a safety wire.
Important point of Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
1. A
compass needle is a small magnet. Its one end which points toward the north is
called a north pole and the other end, which points towards the south is called the
south pole.
2. A
magnetic field exists in the region surrounding a magnet, in which the force of
the magnet can be detected.
3. Field
lines are used to represent a magnetic field. A field line is a path along
which a hypothetical free north pole would tend to move. The direction of the
magnetic field at a point is given by the direction that a north pole placed at
that point would take. Field lines are shown closer together where the magnetic
field is greater.
4. A
metallic wire carrying an electric current has associated with it a magnetic
field. The field line about the wire consists of a series of concentric circles
whose direction is given by the right-hand rule.
5. The
pattern of the magnetic field around due to an electric current flowing through
it depends on the shape of the conductor. The magnetic field of a solenoid
carrying a current is similar to that pf a bar magnet.
6. An
electromagnet consists of a core of soft iron wrapped around with a coil of
insulated copper wire.
7. A
current-carrying conductor when placed in a magnetic field experiences a force,
if the direction of the field and that of the current are mutually
perpendicular to each other, then the force acting on the conductor will be
perpendicular to both and will be given by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
This is the basis of an electric motor. An electric motor is a device that
converts electric energy into mechanical energy.
8. The
phenomenon of electromagnet induction is the production of induced current in a
coil placed in a region where the magnetic field changes with time. The magnetic
field may change due to a relative motion between the coil and a magnet
placed near to the coil. If the coil is placed near to a current-carrying conductor,
the magnetic field may change either due to a change in a change in the current
through the conductor or due to the relative motion between the coil and the
conductor. The direction of the induced current is given by Fleming’s
right-hand rule.
9. A
generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. it works on the
basis of electromagnetic induction.
10. In
our houses we receive AC electric power of 220 V . one of the wires in this
supply is with red insulation, called live wire. The other one is of black
insulation which is a neutral wire. The potential difference between the two is
220V. the third is the earth wire that has green insulation and this is
connected to a metallic body deep inside the earth. It is used as a safety measure
to ensure that any leakage of current to a metallic body does not give any
severe shock to a user.
11. Fuse
is the most important safety device, used for protecting the circuits due to short-circuiting or overloading of the circuits.
These NCERT solutions and study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board, RBSE, and Other state board exams.
Related Searches for you
Remedial Education Point.com provides you complete study material for class 10 absolutely free. Now you can get accurate NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 13 prepared by our expert teachers.





No comments:
Post a Comment