NCERT
Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 will help you in the CBSE board exams
for session 2021-22. In this article, you have been provided with intext
questions on page no. 128,133,139 and End exercise question of NCERT solutions
for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in English medium. When you read the following solutions, also read the How Do Organisms Reproduce Class 10 MCQ, which will be very useful for you.
.webp) |
| NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 |
You
will find NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi medium.
Students are free to use all contents without any hesitation. You can download
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in PDF format at no cost.
In this
article, you have also provided important points related to NCERT solutions
for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 which will be very helpful to you to understand
the chapter in a better way.
NCERT
Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 will be very useful to students of the CBSE board of different states using the NCERT Science textbook.
You
will be glad to know that here Extra questions related to chapter 8 How do
organisms Reproduce? These extra questions will certainly lead you ahead.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8
Before you go through
the NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8,
you should know the main topics and subtopics.
1. Do Organisms Create Exact Copies Of Themselves?
i.The
Importance of Variations
2. Modes of Reproduction
used by single Organisms
i.Fission
ii. Fragmentation
iii.Regeneration
iv. Budding
v. Vegetative
Propagation
vi. Spore Formation
3. Sexual Reproduction
i.Why the Sexual Mode of Reproduction?
ii. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
iii. Reproduction in Human Beings
a.Male Reproductive system
b.Female Reproductive system
c.What happens when the Egg is not Fertilised?
d.Reproductive Health
Students of CBSE
board, RBSE, and other state boards of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat
and all other states can download Solutions of Chapter 8
How Do Organisms Reproduce? of NCERT Science for Class 10 in English medium and Hindi medium in PDF
format for free.
You can also watch
videos of NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science
Chapter 8 Class 10 for online. The solution is based on the latest syllabus of CBSE 2021-22.
Chapter 8
How Do Organisms Reproduce?
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Questions Page 128
Q.1What is the
importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Ans. The environment is not stable; it changes continuously so the particular species will not be
able to survive in changing environment. Reproduction is a process in which an
organism produces a young one similar to itself. In this process, characters are
transmitted by DNA copying.
DNA
copying has the following importance in reproduction
i. Maintains
the characteristics of species.
ii. Maintains
the continuous survival of life
iii. The characteristics of organisms are
transmitted to their progeny.
iv. It produces variations in organisms
which is the basis of the evolution of new species.
Q.2Why is
variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Ans. The variations are beneficial to a
species and enable them to survive in a changing environment. A favorable
variation in a species makes them survive in a changing environment. In a
changing environment, individual organisms would die but their offsprings with
variations survive in a changing environment. So we can say that variations are
beneficial to a species but not for the individual.
Questions Page 133
Q.1How does
binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Ans.Binary fission: - In this
method; nucleus divides into two parts and by division of cytoplasm, two
daughter organisms are formed.
Multiple fission:
- In this method; nucleus divides into several parts and each nuclear part
getting some cytoplasm forms a daughter organism.
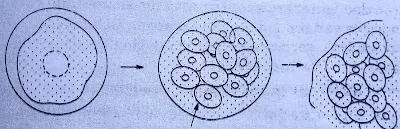 |
| Multiple fission |
Q.2How will an
organism be benefited if it reproduces through spores?
Ans. An organism is benefited if it
reproduces through spores, in the following ways:
i.Spores are formed in large numbers.
ii. Spores have an outer thick wall that
protects them in adverse conditions, when conditions become favorable (Proper
moisture), they can grow.
Q.3Can you
think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals
through regeneration?
Ans.More complex organisms cannot give
rise to new individuals through regeneration because they have specialized
cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems to perform different functions. So
multicellular organisms have high body organization. That’s why they cannot
reproduce through regeneration.
Q.4Why is
vegetative propagation practiced for growing some type of plants?
Ans. Vegetative propagation practiced for
growing some type of plants because of following reasons-
i.Some plants such as banana, orange, and
rose do not produce seeds so the ii. vegetative propagation is practiced to grow
them.
iii. Vegetative propagation is a fast
method for developing new plants earlier.
iv. Plants raised by vegetative propagation
bear flower and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
v.Seedless fruits are produced by the
process of vegetative propagation.
vi. Desired characters can be maintained in
variety of species by this method.
Q.5Why is DNA
copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Ans.DNA copying is an essential part of
the process of reproduction because so that the
characteristics of the parent organisms are transmitted to its offspring and in
this process, some variations are also produced in the offspring. These variations
lead to some changes in offsprings that provide an organism the capability to
survive in changing conditions.
Questions Page 139
Q.1How is the
process of pollination different from fertilization?
Ans. Pollination:
- In this process pollen grains (male gametes) are transferred from the anther
of a flower to the stigma of same or another flower.
Fertilization:- In this method; pollen grains (male gametes)
fuses with female gamete (egg cell) to form a zygote.
Q.2What is the
role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Ans. Seminal vesicle and prostate gland
secrete fluids that form a part of the semen. The fluid secreted from seminal
vesicle forms 60% of semen. It makes the transport of sperms smooth.
This fluid protects the sperms from the
acids present in the urethra and provide nutrition to sperms in the form of
fructose, calcium, and some enzymes.
Q.3What are
the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Ans. The
various changes that occur in girls at puberty are:
i.Breast size increases and mammary gland development.
ii. Hair grows under armpits
and pubic region.
iii. The hips broaden.
iv. Deposition of fat in
various parts of body like hips and thighs.
v.Fallopian tube, uterus, and
vagina enlarge.
vi. Ovaries start to release
eggs.
vii. Menstruation cycle
starts.
Q.4How does
the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s baby?
Ans. In
mother’s body, the embryo gets nutrition from the mother’s blood with the help
of placenta. Placenta is formed by
fetal and maternal tissue. Placenta contains villi. There are empty spaces in
mother’s tissues that cover the villi. Villi provide a large surface area for
the transfer of glucose, oxygen, and other substances from the mother to the
embryo.
Q.5If a woman
is using a copper-T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted
diseases?
Ans. No
, If a woman is using a copper-T, it will not help in protecting her from
sexually transmitted diseases.
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
End Exercise Questions
Q.1Asexual
reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) Amoeba
(b) Yeast
(c) Plasmodium
(d)Leishmania
Ans. (b) yeast
Q.2Which of
the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a)Ovary
(b)Uterus
(c)Vas deferens
(d)fallopian tube
Ans. (c) vas deferens
Q.3The anther
contains
(a)sepals
(b)ovules
(c)carpel
(d)pollen grains
Ans. (d) pollen grains
Q.4What are
the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Ans. (i) In sexual reproduction the offspring are similar to
their parents, but not identical to them or to one another. This is because the
offspring receive genes from two different parents. So these genes mix in
various different combinations. Due to this all of the offspring have genetic
variations.
So in sexual reproduction, due to
different variations offsprings
have adaptations to their
surroundings and they can survive.
(ii).In asexual reproduction, the offspring
are almost identical to their parent because they have the same genes as their
parent. So, much genetic variation is not possible in asexual reproduction. So
in asexual reproduction due to fewer genetic variations, this inhibits
the evolution of the organism.
Q.5What are
the functions performed by the testes in human beings?
Ans. Functions
of testes are as follows?
(i)Sperms are formed in testes.
(ii)They secret the hormone testosterone
which regulates the formation of sperms and brings changes in appearance of
boys at the time of puberty.
Q.6Why does
menstruation occur?
Ans. At
puberty in girls or females, ovaries release eggs(ovum) regularly and at the
same time lining of uterus starts thickening to receive fertilized egg but if the egg(ovum) does not get fertilized due
unavailability of sperm then the thick and soft inner lining of uterus is no
longer needed and hence it breaks.
So, the thick and soft inner lining of uterus
along with the blood vessels and the dead eggs comes out of the vagina in the
form of blood called menstruation. Menstruation occurs after the interval of
every 28 days.
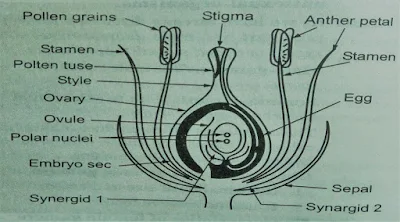
Q.7Draw a
labeled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Ans.
Q.8What are the different methods of contraception?
Ans. Following
are the different methods of contraception-
(i) Chemical method: In this method a
woman uses oral pills which are
hormonal preparations and suppress the release of ovum in fallopian tube. These
are called oral contraceptives.
On the other hand, vaginal pills/ creams are spermicidal. The chemicals in these kill the sperms during their journey in the vaginal tract.
(ii) Barrier method: condom, diaphragm, and cervical caps are used in this
method which prevents the entry of sperms in the female genital tract during
sexual intercourse.
(iii) Intrauterine contraceptive devices: Intrauterine contraceptive
devices such as copper-T are placed safely in the uterus at hospitals. It
prevents the sperms to reach the uterus.
(iv) Surgical method : In this method, a small part of vas deferens of
male and fallopian tube of female is cut or tied by surgery. It is called
vasectomy in males and tubectomy in females.
Q.9How are the
modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Ans. In
unicellular organisms reproduction takes place by binary fusion or multiple
fission (asexual reproduction) while in multicellular organisms reproduction
takes place by budding (hydra), vegetative propagation asexual methods, and fusion of male and female gametes (sexual
reproduction).
Q.10 How does reproduction help in providing stability to
population of species?
Ans. Population
of a particular species decreases due to death or other reasons but
reproduction adds new individuals to the species. Reproduction
also helps to generate copies of individuals who are suited to a particular
environment.
Q.11 What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive
methods?
Ans. Contraceptives
are adopted due to the following reasons:
i.For prevention of unwanted pregnancy.
ii.To control the birth rate
and prevent the increase in population
iii.These methods prevent
sexually transmitted disease.
These NCERT solutions
and study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board and Other states board exams.
Remedial Education
Point.com provides you complete study material for class 10 absolutely free.
Now you can get accurate NCERT Book Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8
How Do Organism Reproduce? prepared by our expert teachers.
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Important Points
Important Points
1. Reproduction, unlike other life processes, is not
essential to maintain the life of an individual organism.
2. Reproduction involves creation of a DNA copy and
additional cellular apparatus by the cell involved in the processes.
3. Various organisms use different modes of reproduction
depending on their body design.
4. In fission, many bacteria and protozoa simply divide
into two or more daughter cells.
5. Organisms such as hydra can regenerate if they are
broken into pieces. They can also give out buds that mature into new
individuals.
6. Roots, stems, and leaves of some plants develop into
new plants through vegetative propagation.
7. These are examples of asexual reproduction where new
generations are created from a single individual.
8. Sexual reproduction involves two
individuals for the creation of a new individual.
9. DNA copying mechanisms create
variations that are useful for ensuring the survival of the species. Modes of
sexual reproduction allow for greater variation to be generated.
10. Reproduction in flowering plants
involves transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma which is
referred to as pollination. This is followed by fertilization.
11. Changes in the body at puberty, such
as increase in breast size in girls and new facial hair growth in boys, are the
signs of sexual maturation.
12. The male reproductive system in human
beings consist of testes which produce sperms, vas deferens, seminal vesicles,
prostate gland, urethra, and penis.
13. The female reproductive system in
human beings consists of ovaries, fallopian tube, uterus and vagina.
14. Sexual reproduction in human beings
involves the introduction of sperm in vagina of females.
15 Pregnancy can be prevented by adopting contraceptive methods. Examples
of this are condoms, birth control pills, copper-T, and other devices.
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Extra questions
Extra Questions
Q1.What is
reproduction?
Ans. The process by which a new generation
is produced is called reproduction.
Q2.What are
the main types or modes of reproduction in living organisms?
Ans. Mainly two types or mode of
reproduction in living organisms –
i).Sexual reproduction
ii).Asexual reproduction
Q3. What is a
sexual reproduction?
Ans. In this type of reproduction, fusion
of male and female gametes occur.
Q4.Define
asexual reproduction?
Ans. In this type of reproduction, there
is no fusion of male and female gametes occur. Only one living organism
produces offspring or a new generation.
Q5.Name any
two organisms that show binary fission.
Ans. Paramaecium and amoeba
Q6.Name the
reproductive part of a plant.
Ans. A flower is a reproductive part of
plant.
Q7. Which
parts of a flower develop into fruit and seed?
Ans. Ovary develops into fruit and ovule
develops into a seed.
Q8.Name any
two organisms in which asexual reproduction takes place by budding.
Ans. Hydra and yeast
Q9. Name the
different modes or types of asexual reproduction.
Ans. Following are the main mode or types
of asexual reproduction-
i).Fission
ii).Fragmentation
iii).Budding
iv).Regeneration
v).Vegetative propagation
Q10. Write the
process of asexual reproduction in flat worm and spirogyra.
Ans. Fragmentation
Q11.Name the
organ where sperms are produced in a man.
Ans. sperms are produced in testes in a
man.
Q12. Name the
organ where ova or eggs are produced in a woman.
Ans. Ova or eggs are produced in ovaries
in a woman.
Q13.Name the
hormone secreted by testes in man.
Ans. Testosterone is secreted by testes.
Q14. Name the
hormones secreted by ovaries in a woman.
Ans. Two hormones are secreted by ovaries
in a woman named –
i).Estrogen
ii). Progesterone
Q15. How the
zygote is formed?
Ans. Zygote is formed when male gametes
(sperms) and female gametes (ova) fuse with each other.
Q16. Name the
modes of reproduction in amoeba and hydra.
Ans. Amoeba- binary fission
Hydra- budding
Q17.Name the
mode of reproduction in planaria.
Ans. Regeneration
Q18.Name the
process that is necessary for growth in living organisms.
Ans. Cell division is the process that
is responsible for growth in a living organism.
Q19. How
variation is useful?
Ans. The environment is continuously
changing, so variations are useful to a particular species because they provide
better chances of survival.
Q20.What is
the duration of human pregnancy?
Ans. The duration of pregnancy in human
beings is 280 days (Approx. 9 months).
Q21. What is
fertilization in plants?
Ans. Fusion of male gametes with egg cells
in ovary is called fertilization.
Q22. What do
you mean by – (i) Oviparous (ii) Viviparous
Ans. (i) Oviparous – Egg lying
animals are called oviparous.
(ii)Viviparous- The animals who
produces young one are called viviparous.
Q23.What is
vasectomy?
Ans. The removal of a part of vas
deference in males in human beings is called vasectomy.
Q24.Name any
two plants in which vegetative propagation takes place by stem or branches.
Ans. Sugar cane and Rose
Q25.What method
will you use for growing jasmine and rose plants?
Ans. Mount layering is used for growing
jasmine and roles plants.
Q26.What is
tubectomy?
Ans. The removal of fallopian tube in
female is called tubectomy.
Q27.Give the
full form of IUCD.
Ans. IUCD- Intrauterine Contraceptive
Device.
Q28. Give full
form of DNA.
Ans. DNA- De oxy ribose nucleic acid
Q29.Name one
Intrauterine Contraceptive Device.
Ans. Copper-T is one of the Intrauterine
Contraceptive Device.
Q30.Give full
form of HIV.
Ans. HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus
Q31. Write
full form of AIDS.
Ans. AIDS- Acquired Immunodeficiency
Syndrome
Q32. Name the
pathogen of AIDS.
Ans. The pathogen of AIDS is HIV.
Q33.Why
variations are produced in progeny in sexually reproduction?
Ans. In sexual reproduction, Two parent
cells fuse to form a new single cell(zygote), so copy of DNA is not identical
to copy of DNA of parent cell, that’s why variations are produced in progeny.
Q34. Name one
sexually transmitted disease caused by Bactria.
Ans. Syphilis
Q35. Write the
full form of STD as term of Biology.
Ans. STD- Sexually Transmitted Disease
Q36. Name one
sexually transmitted disease caused by virus.
Ans. AIDS
Q37. Which
contraceptive is used to prevent AIDS?
Ans. Condom is the commonly used
contraceptive to prevent AIDS.
Q38.Name the
tissue or structure that provides nutrition to embryo.
Ans. Placenta provides nutrition to
embryo.
Q39. Name two
plants that are propagated by stem cutting.
Ans. Rose and sugarcane
Q40.What is
the main function of a flower?
Ans. Sexual reproduction
Q41.Name the
part that connects stigma to ovary?
Ans. Style
Q42.Name a barrier method of contraceptive.
Ans. Condom and Cervical cap
Q43. Difference
between asexual and sexual reproduction.
Ans.
|
Asexual Reproduction |
Sexual Reproduction |
|
1. In this method, no formation and
fusion of gametes take place. |
1. Formation and fusion of gametes take place. |
|
2. Only one parent produces daughter cells or progeny. |
2. Two parents are involved in producing progeny. |
|
3. Daughter cell or progeny is identical to parent cell. |
3. Daughter cell or progeny is not
identical to parent cell. |
|
4. Variations are not found generally. |
4. Variations are found. |
Q44. Where
does fertilization between sperm and egg occur in human beings?
Ans. Fallopian tube
Q45.Name two
glands of male human reproductive system which produce a liquid medium for
sperms.
Ans. Prostate gland and seminal vesicle
Q46.Difference
between self-pollination and cross-pollination.
Ans.
|
Self-Pollination |
Cross Pollination |
|
1. Transfer of pollen grains from anther
to the stigma of the same flower. |
1. .Transfer of pollen grains from
anther of one flower to the stigma of the flower. |
|
2. Pollen grains are produced in small
quantity. |
2. Pollen grains are produced in large
quantity. |
|
3. No vector is involved in transfer of
pollen grains. |
3. Vector-like insects, birds are
involved in transfer of pollen grains. |
Q47.Where does
a fertilized egg develop into a foetus in human beings?
Ans. A fertilized egg develop into foetus
in uterus in a human being.
Q48. Describe
vegetative propagation.
Ans. Vegetative propagation is a type of
asexual reproduction in which new plant is produced from vegetative parts like
stem, roots, leaves, or branches of parent plant.
Q49.What is a
flower bearing both carpel and stamen known as?
Ans. A flower-bearing carpel and
stamen is known as bisexual or hermaphrodite.
Q50. Name the
common biological process which help in the continuation of a species.
Ans. Reproduction
Q51.Name a
hormone that regulates the formation of sperms in human beings.
Ans. Testosterone
Q52. Name a muscular bag like structure that is formed by the union of two fallopian
tubes.
Ans. Uterus
Q53.What is a junction of vagina and uterus known as?
Ans.
Junction of vagina and uterus is known as ‘Cervix’.
Q54. Name
parts of a flower.
Ans. A flower has following parts-
i.Sepals
ii. Petals
iii.Stamens
iv. Carpel
Q55.Name the
main methods for birth control in human beings.
Ans. Birth control methods are divided into
following categories-
i. Barrier method
ii.Chemical method
Q56. Name some
common sexually transmitted diseases in human beings.
Ans. Following are some common sexually
transmitted diseases in human beings-
i.AIDS
ii.Syphilis
iii.Gonorrhoea
iv.Warts disease
Q57. Name some
common methods of vegetative propagation in plants.
Ans. Following methods of vegetative
propagation are used –
i.Grafting
ii.Cutting
iii.Layering
Q58. Name two
parts of a flower that contain germ cells.
Ans. Carpel and stamens are the two parts
that contain germ cells.
Q59.Describe
the process of fertilization and development of embryo in human beings.
Ans. Fertilization and development – By mating, sperm are delivered to the
vaginal tract and from there they reach the fallopian tube and there the sperm
and egg is fertilized and the zygote is formed.
The zygote gets implanted in the uterus in this
process is called pregnancy. In the uterus, the zygote develops into an embryo
by cleavage and division. The foetus receives nutrition from the mother's blood
through a saucer-like structure and the waste material produced by the embryo
is delivered to the mother's blood through this structure which is called
placenta. The growth and development of the baby takes place at about nine
months
Q60.If a woman is using
Copper-T, will it protect her from sexually transmitted diseases?
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi हिंदी
माध्यम में उपलब्ध करवाए गए हैं । छात्र बिना किसी संकोच और परेशानी के सभी
सामग्री का उपयोग कर सकते हैं । आप NCERT solutions for Class 10
Science Chapter 8 in Hindi को PDF प्रारूप
में बिना किसी शुल्क के डाउनलोड कर सकते हैं।
इस लेख में आपको NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi से संबंधित महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु भी प्रदान किए हैं
जो अध्याय को बेहतर तरीके से समझने में आपके लिए बहुत मददगार होंगे। NCERT solutions for
Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi एनसीईआरटी विज्ञान
पाठ्य पुस्तक का उपयोग करने वाले विभिन्न राज्यों के CBSE बोर्ड
के छात्रों के लिए बहुत उपयोगी होंगे।
आपको यह जानकर खुशी होगी कि यहां अध्याय 8 से संबंधित
अतिरिक्त प्रश्न जीव जनन कैसे करते हैं? ये अतिरिक्त
प्रश्न निश्चित रूप से आपका मार्गदर्शन करेंगे।
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 in Hindi पढ़ने से पहले, आपको मुख्य विषयों और उप-विषयों को जानना चाहिए।
1.क्या जीव पूर्णत: अपनी प्रतिकृति का सृजन करते हैं ?
i. विभिन्नता का महत्व
2. एकल जीवों में प्रजनन की विधि
i.विखंडन
ii.खंडन
iii.पुनरुद्भवन(पुनर्जनन)
iv.मुकुलन
v. कायिक प्रवर्धन
vi. बीजाणु समासंघ
3.लैंगिक जनन
i.लैंगिक जनन प्रणाली क्यों?
ii. पुष्पी पौधों में लैंगिक जनन
iii. मानव में लैंगिक जनन
a.नर जनन तंत्र
b. मादा जनन तंत्र
c. क्या होता है जब अंड का निषेचन नहीं होता?
d. जनन स्वास्थ्य
CBSE, RBSE और राजस्थान, उत्तर प्रदेश, एमपी, गुजरात और अन्य सभी राज्यों के अन्य राज्य बोर्डों के छात्र कक्षा 10 के लिए एनसीईआरटी विज्ञान के अध्याय 8 के समाधान अंग्रेजी माध्यम और हिंदी माध्यम में पीडीएफ प्रारूप में नि: शुल्क। डाउनलोड कर सकते हैं। आप कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 8 के NCERT समाधान के वीडियो ऑनलाइन भी देख सकते हैं। समाधान सीबीएसई 2021-22 के नवीनतम पाठ्यक्रम पर आधारित हैं।
पाठ्य पुस्तक पाठगत प्रश्न
पृष्ठ संख्या - 142
Q.1 डीएनए प्रतिकृति का प्रजनन में क्या महत्व है?
उत्तर- पर्यावरण स्थिर नहीं है; यह लगातार बदलता रहता है इसलिए विशेष प्रजाति इस परिवर्तित वातावरण में जीवित नहीं रह पाएगी । प्रजनन एक ऐसी प्रक्रिया है जिसमें एक जीव अपने सामान संतान या संतति उत्पन्न करता है। इस प्रक्रिया में लक्षण या गुण डीएनए प्रतिकृति के द्वारा अगली पीढ़ी में प्रेषित होते हैं।
प्रजनन में डीएनए प्रतिकृति का निम्नलिखित महत्व है
i. प्रजातियों की विशेषताओं या लक्षणों को बनाए रखता है।
ii. जीवन के निरंतर अस्तित्व को बनाए रखता है
iii. जीवों के लक्षण उनकी संतति को संचरित होते हैं।
iv. यह जीवों में भिन्नता उत्पन्न करता है जो नई प्रजातियों के विकास का आधार है।
Q.2 जीवों में विभिन्नता स्पीशीज के लिए आवश्यक है परन्तु व्यष्टि के लिए आवश्यक नहीं है ,क्यों ?
उत्तर- विविधताएं एक प्रजाति के लिए आवश्यक होती हैं और उन्हें बदले हुए वातावरण में जीवित रहने में सक्षम बनाती हैं। एक प्रजाति में एक अनुकूल भिन्नता उन्हें बदले हुए वातावरण में जीवित रखती है। एक बदले हुए वातावरण में अलग-अलग जीव मर जाते हैं लेकिन उनकी संतानें एक बदले हुए वातावरण में जीवित रहती हैं। इसलिए हम कह सकते हैं कि विविधताएं एक प्रजाति के लिए आवश्यक होती हैं लेकिन व्यष्टि के लिए आवश्यक नहीं है |
पृष्ठ संख्या - 146
Q.1 द्विखंडन बहु खंडन से किस प्रकार भिन्न होता है?
उत्तर- द्विखंडन :- इस विधि में; केन्द्रक दो भागों में विभाजित होता है और कोशिकाद्रव्य के विभाजन से दो पुत्री जीव बनते हैं।
बहुखंडन :- इस विधि में; नाभिक कई भागों में विभाजित होता है और प्रत्येक परमाणु भाग को कुछ कोशिका द्रव्य प्राप्त करने से एक पुत्री जीव बनता है।
Q2. बीजाणु द्वारा जनन से जीव किस प्रकार लाभान्वित होता है ?
उत्तर- एक जीव बीजाणुओं के माध्यम से प्रजनन करता है तो उसे को निम्नलिखित तरीकों से लाभ होता है -
(i) बीजाणु बड़ी संख्या में बनते हैं।
(ii) बीजाणुओं की एक बाहरी मोटी परत होती है जो प्रतिकूल परिस्थितियों में उनकी रक्षा करती है, जब परिस्थितियां अनुकूल (उचित नमी) हो जाती हैं, तो वे वृद्धि कर सकते हैं।
Q.3 क्या आप कुछ कारण सोच सकते हैं जिससे पता चलता है कि जटिल संरचना वाले जीव पुनरुद्धभवन द्वारा नयी संतति उत्पन्न नहीं कर सकते हैं ?
उत्तर- अधिक जटिल जीव पुनरुद्धभवन के माध्यम से नए जीवों को जन्म नहीं दे सकते क्योंकि बहुकोशिकीय जीवों के पास उच्च और जटिल शरीर संगठन होता है , विभिन्न कार्य करने के लिए विशेष कोशिकाएं, ऊतक, अंग और अंग प्रणालियां हैं, इसलिए वे पुनरुद्धभवन के माध्यम से प्रजनन नहीं कर सकते।
Q.4 कुछ पौधों को उगाने के लिए कायिक प्रवर्धन का उपयोग क्यों किया जाता है?
उत्तर- निम्नलिखित कारणों से कुछ प्रकार के पौधों को उगाने के लिए कायिक प्रवर्धन का उपयोग किया जाता है-
(i) कुछ पौधे जैसे केला, संतरा और गुलाब बीज पैदा नहीं करते हैं इसलिए उन्हें उगाने के लिए कायिक प्रवर्धन का अभ्यास किया जाता है।
(ii) नए पौधों को पहले विकसित करने के लिए कायिक प्रवर्धन एक तीव्र तरीका है।
(iii) कायिक प्रवर्धन द्वारा उगाए गए पौधों में बीज से उत्पन्न होने वाले पौधों की तुलना में पहले फूल और फल लगते हैं।
(iv) कायिक प्रवर्धन की प्रक्रिया द्वारा बीजरहित फल उत्पन्न होते हैं।
(v) इस विधि द्वारा विभिन्न प्रजातियों में वांछित लक्षणों को बनाए रखा जा सकता है।
Q.5 डीएनए की प्रतिकृति बनाना जनन के लिए आवश्यक है क्यों?
उत्तर- डीएनए की प्रतिकृति जनन की प्रक्रिया के लिए आवश्यक है क्योंकिइससे जीवों की विशेषताओं को उसकी संतानों तक पहुँचाया जा सकता है और इस प्रक्रिया में कुछ संतानों में विभिन्नताएँ भी उत्पन्न होती हैं। इन विविधताओं से संतानों में कुछ परिवर्तन होते हैं जो एक जीव को बदलती परिस्थितियों में जीवित रहने की क्षमता प्रदान करते हैं।
पृष्ठ संख्या - 154
Q.1 परागण क्रिया निषेचन से किस प्रकार भिन्न है?
उत्तर- परागण:- इस प्रक्रिया में परागकण (नर युग्मक) फूल के परागकोष से उसी या अन्य फूल के वर्तिकाग्र में स्थानांतरित हो जाते हैं।
निषेचन :- इस विधि में ; परागकण (नर युग्मक) मादा युग्मक (अंडा कोशिका) के साथ मिलकर युग्मनज बनाते हैं।
Q.2 शुक्राशय और प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि की क्या भूमिका है?
उत्तर- शुक्राशय और प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि एक तरल पदार्थ को स्रावित करता है जो वीर्य का एक हिस्सा बनाता है। शुक्राशय (वीर्य पुटिका) से स्रावित द्रव 60% वीर्य का निर्माण करता है। यह शुक्राणुओं के परिवहन को सुचारू बनाता है। यह द्रव मूत्रमार्ग में मौजूद एसिड से शुक्राणुओं की रक्षा करता है और शुक्राणुओं को फ्रुक्टोज, कैल्शियम और कुछ एंजाइमों के रूप में पोषण प्रदान करता है।
Q.3 यौवनारम्भ के समय लड़कियों में क्या परिवर्तन दिखाई देते हैं?
उत्तर- यौवनारम्भ के समय लड़कियों में होने वाले विभिन्न परिवर्तन निम्न हैं:
1. स्तन और आकार बढ़ता है और स्तन ग्रंथि विकसित होती है।
2. बगल और जांघ क्षेत्र के नीचे बाल उगते हैं।
3. कूल्हे चौड़े होते हैं।
4. शरीर के विभिन्न हिस्सों जैसे कूल्हों और जांघों में वसा का जमाव।
5. फैलोपियन ट्यूब, गर्भाशय और योनि का बढ़ना।
6. अंडाशय से अंडोत्सर्ग शुरू होता हैं।
7. मासिक धर्म चक्र शुरू होता है।
Q.4 मां के शरीर से गर्भस्थ भ्रूण को पोषण किस प्रकार प्राप्त होता है?
उत्तर- मां के शरीर में भ्रूण को मां के रक्त से प्लेसेंटा(अपरा) की मदद से पोषण मिलता है। प्लेसेंटा भ्रूण और मातृ ऊतक द्वारा बनता है। प्लेसेंटा में विली होता है। माँ के ऊतकों में रिक्त स्थान होते हैं जो विली को ढकते हैं। विली मां से भ्रूण तक ग्लूकोज, ऑक्सीजन और अन्य पदार्थों के हस्तांतरण के लिए एक बड़ा सतह क्षेत्र प्रदान करता है।
Q.5 यदि कोई महिला कॉपर-टी का उपयोग कर रही है, तो क्या यह उसे यौन संचारित रोगों सेरक्षा करेगा ?
उत्तर- नहीं, यदि कोई महिला कॉपर-टी का उपयोग कर रही है, तो यह उसे यौन संचारित रोगों से बचाने में मदद नहीं करेगी।
अभ्यास प्रश्न
Q.1अलैंगिक जनन मुकुलन द्वारा होता है?
(a) अमीबा
(b) यीस्ट
(c) प्लास्मोडियम
(d) लेस्मानिया
उत्तर- (b) यीस्ट
Q.2 निम्न में से कौन मानव में मादा जनन तंत्र का भाग नहीं है?
(a) अंडाशय
(b) गर्भाशय
(c) शुक्र वाहिका
(d) डिम्ब वाहिनी
उत्तर- (c) शुक्र वाहिका
Q.3परागकोश में होते है
(a) बाह्यदल
(b) अंडाशय
(c) अंडप
(d) पराग कण
उत्तर- (d) पराग कण
Q.4 अलैंगिक जनन की अपेक्षा लैंगिक जनन के क्या लाभ हैं?
उत्तर- (i) लैंगिक प्रजनन में संतान अपने माता-पिता के समान होती है, लेकिन सम्पूर्ण रूप से उनके समान या एक दूसरे के समान नहीं होती है। ऐसा इसलिए है क्योंकि संतान को दो अलग-अलग माता-पिता से जीन प्राप्त होते हैं। ये जीन विभिन्न संयोजनों में आपस में योजित होते हैं। इसके कारण सभी संतानों में आनुवंशिक भिन्नताएँ होती हैं। इसलिए लैंगिक जनन में, विभिन्न विविधताओं के कारण संतानों के पास अपने परिवेश के अनुकूलन होते हैं और वे जीवित रह सकते हैं।
(ii) अलैंगिक जनन में संतति अपने माता-पिता के लगभग समान हैं क्योंकि उनके पास उनके माता-पिता के समान जीन हैं। अत: अलैंगिक जनन में अधिक आनुवंशिक भिन्नता संभव नहीं है। तो अलैंगिक प्रजनन में कम आनुवंशिक विविधताओं के कारण, यह जैव उद्विकास को रोकता है।
.
Q.5 मानव में वृषण के क्या कार्य हैं?
उत्तर- वृषण के कार्य इस प्रकार हैं
(i) वृषण में शुक्राणु बनते हैं।
(ii) ये टेस्टोस्टेरोन हार्मोन को स्त्रावित करते हैं जो शुक्राणुओं के निर्माण को नियंत्रित करता है औरयौवनारम्भ के समय लड़कों के लक्षणों में परिवर्तन उत्पन्न करता है।
Q.6 ऋतु स्त्राव क्यों होता है?
उत्तर- लड़कियों या महिलाओं में युवावस्था में, अंडाशय नियमित रूप से अंडे (डिंब) उत्सर्जित करते रहते हैं और साथ ही गर्भाशय की परत निषेचित अंडे प्राप्त करने के लिए मोटी होने लगती है लेकिन यदि शुक्राणु उपलब्ध नहीं होते है तो अंडा (डिंब) निषेचित नहीं होता है तो मोटी और मुलायम आंतरिक परत की अब गर्भाशय को जरूरत नहीं होती है और इसलिए वह परत धीरे धीरे टूटने लगती है | रक्त और मृत अंडों के साथ-साथ गर्भाशय की मोटी और मुलायम अंदरूनी परत योनि से रक्त के रूप में बाहर आता है जिसे मासिक धर्म कहा जाता है। मासिक धर्म हर 28 दिनों के अंतराल के बाद होता है।
Q.7 पुष्प की अनुदैर्ध्य काट का नामांकित चित्र बनाइए।
उत्तर – चित्र
Q.8 गर्भनिरोधन की विभिन्न विधियां कौनसी हैं?
उत्तर- गर्भनिरोधक के विभिन्न तरीके निम्नलिखित हैं-
(i) रासायनिक विधि: इस विधि में एक महिला गोलियों का उपयोग करती है जो हार्मोनल संतुलन को प्रभावित करती हैं और फैलोपियन ट्यूब में डिंब(अण्डों)के उत्सर्ग को दबा देती हैं। इन्हें मौखिक गर्भनिरोधक कहा जाता है। इसके साथ दूसरी ओर योनि में रखने के लिए गोलियाँ/क्रीम का उपयोग किया जाता इनमें मौजूद रसायन शुक्राणुनाशक होते हैं जो योनि मार्ग में यात्रा के दौरान शुक्राणुओं को मार देते हैं।
(ii) निरोधक विधि: इस विधि में कंडोम, डायाफ्राम और सरवाइकल कैप का उपयोग किया जाता है जो संभोग के दौरान महिला जननांग पथ में शुक्राणुओं के प्रवेश को रोकता है।
(iii) अंतर्गर्भाशयी गर्भनिरोधक उपकरण: अंतर्गर्भाशयी गर्भनिरोधक उपकरण जैसे कॉपर-टी को अस्पतालों में गर्भाशय में सुरक्षित रूप से रखा जाता है। यह शुक्राणुओं को गर्भाशय तक पहुंचने से रोकता है।
(iv) सर्जिकल विधि : इस विधि में नर के वास डिफेरेन्स(शुक्र वाहिका) का एक छोटा सा भाग तथा स्त्री की फैलोपियन ट्यूब को शल्य चिकित्सा द्वारा काटा या बांधा जाता है। इसे पुरुषों में पुरुष नसबंदी और महिलाओं में ट्यूबेक्टॉमी कहा जाता है।
Q.9 एककोशिक और बहुकोशिक जीवों में जनन के पद्धति में क्या अंतर हैं?
उत्तर- एककोशिकीय जीवों में प्रजनन द्विखंडन या बहुखंडन (अलैंगिक प्रजनन) द्वारा होता है जबकि बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में प्रजनन नवोदित (हाइड्रा), कायिक प्रसार अलैंगिक विधियों और नर और मादा युग्मकों (यौन प्रजनन) के संलयन द्वारा होता है।
Q.10 जनन किसी स्पीशीज की समष्टि के स्थायित्व में किस प्रकार सहायक है?
उत्तर- किसी विशेष प्रजाति की जनसंख्या मृत्यु या अन्य कारणों से घटती है लेकिन प्रजनन नए जीवों को स्पीशीज (प्रजातियों) में जोड़ता है। प्रजनन उन जीवों की प्रतियां बनाने में भी मदद करता है जो एक विशेष वातावरण के अनुकूल होते हैं।
Q. 11 गर्भनिरोधक युक्तियाँ अपनाने के क्या कारण हो सकते हैं?
उत्तर- गर्भ निरोधकों युक्तियों को अपनाने के निम्नलिखित कारण:
(i) अनचाहे गर्भ की रोकथाम के लिए।
(ii) जन्म दर को नियंत्रित करने और जनसंख्या में वृद्धि को रोकने के लिए
(iii) ये विधियां यौन संचारित रोग को रोकती हैं।
ये NCERTसमाधान और अध्ययन सामग्री आपके CBSEबोर्ड और अन्य राज्य बोर्ड परीक्षाओं के लिए अच्छे अंक लाने में आपकी मदद करेगी। Remedialeducaitonpoint.com आपको कक्षा 10 के लिए पूरी तरह से मुफ्त अध्ययन सामग्री प्रदान करता है। अब आप कक्षा 10 एनसीईआरटी पुस्तक समाधान विज्ञान अध्याय 8 जीव जनन कैसे करते हैं ?,प्राप्त कर सकते हैं?
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 important points in Hindi
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
1. अन्य जैव प्रक्रमों के विपरीत, किसी जीव के अपने अस्तित्व के लिए जनन आवश्यक नहीं है।
2. जनन मेंके कोशिका द्वारा डी.एन.ए. प्रतिकृति का निर्माण तथा अतिरिक्त कोशिकीय संगठन का सृजन होता है |
3. विभिन्न जीवों द्वारा अपनाए जाने वाले जनन की प्रणाली उनके शारीरिक अभिकल्प पर निर्भर करती हैं।
4. खंडन विधि में जीवाणु और प्रोटोजोआ की कोशिका विभाजित होकर दो या बस दो या अधिक संतति कोशिका का निर्माण करती है।
5. यदि हाइड्रा जैसे जीवों का शरीर कई टुकड़ों में विलग हो जाए तो प्रत्येक भाग से पुन्रुद्भवन द्वारा नए जीव विकसित हो जाते हैं |इनमे कुछ मुकुल उभर कर नए जीव में विकसित हो जाते हैं |
6. कुछ पौधों में कायिक प्रवर्धन द्वारा जड़,तना अथवा पत्ती से नए पौधे विकसित होते है।
7. उपरोक्त अलैंगिक जनन के उदाहरण हैं जिसमे संतति की उत्पति एक एकल जीव (व्यष्टि) द्वारा होती हैं।
8. लैंगिक जनन में संतति उत्पान हेतु दो जीव भाग लेते हैं |
9. डीएनए की प्रतिकृति की तकनीक से विभिन्नता उत्पन्न होती है जो स्पीशीज के अस्तित्व के लिए लाभप्रद है | लैंगिक जनन द्वारा अधिक विभिन्नताएं उत्पन्न होती हैं |
10. पुष्पी पौधों में जनन प्रक्रम में परागकण परागकोश से स्त्रीकेसर के वर्तिकाग्र तक स्थानांनतरित होते हैं जिसे परागण कहते हैं। इसका अनुगमन निषेचन द्वारा होता है।
11. यौवनारम्भ में शरीर में अनेक परिवर्तनआते हैं उदाहरण के लिए लड़कियों में स्तन का विकास और लड़कों में चेहरे पर नए बालों का आना ,लैंगिक परिपक्वता के चिह्न हैं।
12. मानव में नर जनन तंत्र में वृषण, शुक्राणुवाहिनी, शुक्राशय , प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि, मूत्रमार्ग और शिश्न होते हैं ।वृषण शुक्राणु उत्पन्न करते हैं |
13. मानव में मादा जनन तंत्र में अंडाशय, डिम्ब वाहिनी , गर्भाशय और योनि पाए जाते है।
14. मानव में लैंगिक जनन प्रक्रिया में शुक्राणुओ को स्त्री की योनि में स्थानान्तरण होता है तथा निषेचन डिम्ब वाहिनी में होता है |
15.गर्भ निरोधी युक्तियाँ अपनाकर गर्भ धारण रोका जा सकता है|कन्डोम ,गर्भ निरोधी गोलियाँ,कॉपर टी तथा अन्य युक्तियाँ इसके उदाहरण हैं |
NCERT solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Extra questions in Hindi
अतिरिक्त प्रश्न
Q1. प्रजनन क्या है?
उत्तर- वह प्रक्रिया जिसके द्वारा एक नई पीढ़ी का निर्माण होता है, प्रजनन कहलाती है।
Q2.जीवित जीवों में प्रजनन के मुख्य प्रकार या तरीके क्या हैं?
उत्तर- सजीवों में जनन के मुख्य रूप से दो प्रकार या तरीके हैं
i).लैंगिक जनन ii) अलैंगिक जनन
Q3. लैंगिक जनन क्या है?
उत्तर- इस प्रकार के जनन में नर और मादा युग्मकों का संलयन होता है।
Q4.अलैंगिक जनन को परिभाषित करें?
उत्तर- इस प्रकार के जनन में नर और मादा युग्मकों का संलयन नहीं होता है। केवल एक जीवित जीव ही संतान या नई पीढ़ी उत्पन्न करता है।
Q5. किन्हीं दो जीवों के नाम लिखिए जो द्विविखंडन प्रदर्शित करते हैं।
उत्तर- पैरामीशियम और अमीबा
Q6.पौधे के जनन अंग का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- पुष्प पौधे का जनन अंग है।
Q7. पुष्प के कौन से भाग फल और बीज में विकसित होते हैं?
उत्तर- अंडाशय,, फल में विकसित होता है और बीजांड, बीज में विकसित होता है।
Q8. किन्हीं दो जीवों के नाम लिखिए जिनमें अलैंगिक जनन मुकुलन द्वारा होता है।
उत्तर- हाइड्रा और यीस्ट
Q 9. अलैंगिक जनन के विभिन्न तरीके या प्रकार के नाम लिखिये।
उत्तर- अलैंगिक जनन के तरीके या प्रकार निम्नलिखित हैं-
i) विखंडन
ii) खंडन
iii) मुकुलन
iv) पुनरुद्भवन (पुनर्जनन)
v) कायिक प्रवर्धन
Q10. फीता कृमि तथा स्पाइरोगाइरा में अलैंगिक जनन की विधि के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- विखंडन
Q11.उस अंग का नाम बताइए जहां पुरुष में शुक्राणु पैदा होते हैं।
उत्तर- पुरुष में वृषण में शुक्राणु पैदा होते हैं।
Q12. उस अंग का नाम बताइए जहाँ एक महिला में अंडाणु या अंडाणु उत्पन्न होते हैं। उत्तर- एक महिला में अंडाशय में ओवा या अंडे का उत्पादन होता है।
Q13.मनुष्य में वृषण द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- टेस्टोस्टेरोन वृषण द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन होता है।
Q14. एक महिला में अंडाशय द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- एक महिला में अंडाशय द्वारा दो हार्मोन स्रावित होते हैं जिसका नाम है - i).एस्ट्रोजन ii) प्रोजेस्टेरोन
Q15. युग्मनज कैसे बनता है?
उत्तर- जब नर युग्मक (शुक्राणु) और मादा युग्मक (ओवा) परस्पर संलायित होते है तो युग्मनज (जाइगोट) तब बनता है
Q16. अमीबा और हाइड्रा में जनन की विधियों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- अमीबा- द्वि विखंडन (बाइनरी)
हाइड्रा- मुकुलन
Q17. प्लेनेरिया में जनन विधि का नाम बताओ |
उत्तर- पुनरुद्भवन (पुनर्जनन)
Q18.उस प्रक्रिया का नाम बताइए जो जीवों में वृद्धि के लिए आवश्यक है।
उत्तर- 'कोशिका विभाजन' वह प्रक्रिया है जो एक जीवित जीव में वृद्धि के लिए जिम्मेदार है।
Q19. विविधता कैसे उपयोगी है?
उत्तर- पर्यावरण लगातार बदल रहा है, इसलिए विविधताएं एक विशेष प्रजाति के लिए उपयोगी हैं क्योंकि विविधता जीवित रहने की बेहतर संभावनाएं प्रदान करती हैं।
Q20.मनुष्य में गर्भावस्था की अवधि क्या है?
उत्तर- मनुष्य में गर्भावस्था की अवधि 280 दिन (लगभग 9 महीने) होती है।
Q 21. पौधों में निषेचन क्या है?
उत्तर- अंडाशय में नर युग्मकों का अंडाणु के साथ संलयन निषेचन कहलाता है।
Q 22. निम्न से आपका क्या तात्पर्य है –
(i) ओवीपेरस (अंडज)
(ii) विविपेरस (जरायुज)
उत्तर- (i) ओविपेरस (Oviparous) - अंडे देने वाले जंतु अंडप्रजक कहलाते हैं।
(ii) विविपेरस (Viviparous)- वे जीव जो बच्चे पैदा करते हैं उन्हें विविपेरस कहते हैं।
Q 23. पुरुष नसबंदी क्या है?
उत्तर- मनुष्य में पुरुष में शुक्र वाहिका (वास डिफरेंस) के एक भाग को शल्य क्रिया द्वारा हटा दिया जाता है जिसे पुरुष नसबंदी कहा जाता है।
Q 24. ऐसे किन्हीं दो पौधों के नाम लिखिए जिनमेंतने या शाखाएँ द्वारा कायिक प्रवर्धन होता है|
उत्तर- गन्ना और गुलाब
Q25.चमेली और गुलाब के पौधे उगाने के लिए आप किस विधि का उपयोग करेंगे?
उत्तर- टीला विधि (माउंट लेयरिंग)विधि का उपयोग चमेली और गुलाब के पौधे उगाने के लिए किया जाता है।
Q26.ट्यूबक्टॉमी क्या है?
उत्तर- महिलाओं में फैलोपियन ट्यूब को हटाना ट्यूबेक्टोमी कहलाता है।
Q27.IUCD का पूर्ण रूप बताएं।
उत्तर- IUCD- Intrauterine Contraceptive Device (अंतर्गर्भाशयी गर्भनिरोधक उपकरण)
Q 28. DNA का पूरा नाम लिखो ।
उत्तर- DNA-- De oxy ribose nucleic acid(डी ऑक्सी राइबोज न्यूक्लिक एसिड)
Q29.एक अंतर्गर्भाशयी गर्भनिरोधक उपकरण का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- कॉपर-टी अंतर्गर्भाशयी गर्भनिरोधक उपकरण में से एक है।
Q30.HIV एचआईवी का पूरा नाम लिखो।
उत्तर- HIV- Human Immunodeficiency Virus(ह्यूमन इम्यूनो डेफिसिएंसी वायरस)
Q. 31. AIDS(एड्स) का पूर्ण रूप लिखिए।
उत्तर- AIDS- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (एक्वायर्ड इम्यूनोडिफीसिअन्सी सिंड्रोम)
Q.32. एड्स के रोगज़नक़ का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- एड्स का रोगज़नक़ HIV (एचआईवी) है।
Q.33.संतानों में लैंगिक जनन में विभिन्नताएँ क्यों उत्पन्न होती हैं?
उत्तर- लैंगिक जनन में, दो जनक कोशिकाएं एक नई एकल कोशिका युग्मनज (जाइगोट) बनाने के लिए परस्पर संलायित होती हैं, इसलिए डीएनए की प्रतिलिपि जनक कोशिका के डीएनए की प्रतिलिपि के समान नहीं होती है, इसलिए संतान में विविधताएं उत्पन्न होती हैं।
Q.34. नाम जीवाणु के कारण होने वाला एक यौन संचारित रोग का नाम लिखो ।
उत्तर- सिफलिस(उपदंश)
Q. 35. STD का पूरा नाम बायोलॉजी टर्म के रूप में लिखिए।
उत्तर- STD - Sexually Transmitted Disease(यौन संचारित रोग)
प्रश्न 36. वायरस से होने वाले एक यौन संचारित रोग का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर - एड्स
प्रश्न 37. एड्स से बचाव के लिए किस गर्भनिरोधक का प्रयोग किया जाता है?
उत्तर- एड्स से बचाव के लिए कंडोम आमतौर पर इस्तेमाल किया जाने वाला गर्भनिरोधक है।
Q.38. उस ऊतक या संरचना का नाम बताइए जो भ्रूण को पोषण प्रदान करता है।
उत्तर- प्लेसेंटा(अपरा), भ्रूण को पोषण प्रदान करता है।
Q.39. ऐसे दो पौधों के नाम लिखिए जिनका प्रवर्धन तने द्वारा होता हैं।
उत्तर- गुलाब और गन्ना
Q40.पुष्प का मुख्य कार्य क्या है?
उत्तर- लैंगिक जनन
Q41. उस भाग का नाम बताइए जो वर्तिकाग्र को अंडाशय से जोड़ता है?
उत्तर- वर्तिका
Q42.गर्भनिरोधन अवरोधक तरीकों के नाम बताएं।
उत्तर- कंडोम और सरवाइकल कैप
Q.43. अलैंगिक और लैंगिक जनन के बीच अंतर लिखो |
उत्तर- अलैंगिक प्रजनन और लैंगिक जनन के बीच अंतर
अलैंगिक जनन | लैंगिक जनन |
1. इस विधि में युग्मकों का निर्माण और संलयन नहीं होता है। | 1. युग्मकों का निर्माण एवं संलयन होता है। |
2. केवल एक जनक संतति कोशिका से संतति उत्पन्न होती है। | 2. दो माता-पिता संतान उत्पन्न करने में सम्मिलित होते हैं। |
3. पुत्री कोशिका या संतति जनक कोशिका के समान होती है। | 3.पुत्री कोशिका या संतति मूल कोशिका के समान नहीं होती है। |
4.संतति में विविधता सामान्यतः नहीं पाई जाती है। | 4. संतति में विविधताएं पायी जाती हैं | |
Q44. मनुष्य में शुक्राणु और अंडाणु के बीच निषेचन कहाँ होता है?
उत्तर- मनुष्य में शुक्राणु और अंडाणु के बीच निषेचन फलोपियन ट्यूब में होता है |
Q45.मनुष्य में नर जनन तंत्र की दो ग्रंथियों के नाम बताइए जो शुक्राणुओं के लिए तरल माध्यम का निर्माण करती हैं।
उत्तर- प्रोस्टेट ग्रंथि और शुक्राशय (वीर्य पुटिका)
Q46.स्व-परागण और पर-परागण के बीच अंतर।
उत्तर-
स्व परागण | पर परागण |
1. परागकणों का परागकोश से उसी पुष्प के वर्तिकाग्र पर पहुँचाना स्व परागण कहलाता है | | 1. एक पुष्प के परागकोष से दूसरे पुष्प के वर्तिकाग्र तक परागकणों का स्थानांतरण होना पर परागण कहलाता है | |
2. परागकणों का उत्पादन कम मात्रा में होता है। | 2. परागकणों का उत्पादन बड़ी मात्रा में होता है। |
3. परागकणों के स्थानांतरण में कोई माध्यम सम्मिलित नहीं है। | 3. परागकणों के स्थानांतरण में माध्यम जैसे कीट, पक्षी आदि सम्मिलित होते हैं। |
Q47.मनुष्यों में एक निषेचित अंडा भ्रूण के रूप में कहाँ विकसित होता है?
उत्तर-एक निषेचित अंडा मनुष्य के गर्भाशय में भ्रूण के रूप में विकसित होता है।
Q48. कायिक प्रवर्धन का वर्णन कीजिए।
उत्तर- कायिक प्रवर्धन एक प्रकार का अलैंगिक प्रजनन है जिसमें नए पौधे का उत्पादन वानस्पतिक भागों जैसे तना, जड़, पत्ते , मूल, पौधे की शाखाओं से होता है ।
Q49. उस पुष्प या पादप को क्या कहते है जिसमे स्त्रीकेसर और पुंकेसर दोनों पाए जाते हैं ?
उत्तर- जिस पुष्प या पादप में स्त्रीकेसर और पुंकेसर दोनों पाए जाते हैं उसे उभयलिंगी कहते हैं।
Q50. उस सामान्य जैविक प्रक्रिया का नाम बताइए जो किसी प्रजाति के अस्तित्व को बनाए रखने में मदद करती है।
उत्तर- प्रजनन
Q51. एक हार्मोन का नाम बताइए जो मानव में शुक्राणुओं के निर्माण को नियंत्रित करता है।
उत्तर- टेस्टोस्टेरोन हार्मोन
Q52. उस पेशीय थैली जैसी संरचना का नाम बताइए जो दो फैलोपियन ट्यूबों के मिलने से बनती है।
उत्तर -गर्भाशय
Q53.योनि और गर्भाशय के जंक्शन या संधि स्थल को क्या कहते हैं?
उत्तर- योनि और गर्भाशय के जंक्शनया संधि स्थल को 'सर्विक्स' के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Q54. एक पुष्प के भागों के नाम बताइए।
उत्तर-एक पुष्प के निम्नलिखित भाग होते हैं-
i.बाह्य दल
ii. दल
iii.पुंकेसर
iv.कार्पेल
Q55.मनुष्य में जन्म नियंत्रण की मुख्य विधियों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- जन्म नियंत्रण विधियों को निम्नलिखित श्रेणियों में बांटा गया है-
i). निरोधक विधि
ii).रासायनिक विधि
Q56. मनुष्य में होने वाले कुछ सामान्य यौन संचारित रोगों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- मनुष्य में कुछ सामान्य यौन संचारित रोग निम्नलिखित हैं-
i. एड्स
ii.सिफलिस
iii.सूजाक(गोनोरिया)
iv.मौसा रोग (Warts disease)
Q57. पौधों मेंकायिक प्रवर्धन की कुछ सामान्य विधियों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- कायिक प्रवर्धन की निम्नलिखित विधियों का उपयोग किया जाता है –
i.ग्राफ्टिंग
ii.कटिंग
iii.लेयरिंग
Q58. एक पुष्प के दो भागों के नाम लिखिए जिनमें जनन कोशिकाएँ होती हैं।
उत्तर- स्त्रीकेसर और पुंकेसर दो भाग हैं जिनमें जनन कोशिकाएं होती हैं।
Q59. मानव में भ्रूण के निषेचन और विकास की प्रक्रिया का वर्णन करें।
उत्तर -निषेचन और परिवर्धन – मैथून द्वारा शुक्राणु योनि मार्ग में पंहुचा दिए जाते है और वहाँ से ये अंड वाहिनी में पंहुच जाते है और वहाँ शुक्राणु और अंडाणु का निषेचन हो जाता है और युग्मनज का निर्माण होता है |युग्मनज गर्भाशय में स्थापित हो जाता है इस प्रक्रिया को गर्भधारण कहते है |
गर्भाशय में युग्मनज विदलन और विभजन द्वारा भ्रूण में परिवर्धित होता है |
भ्रूण को माँ के रुधिर से एक तश्तरी नुमा संरचना द्वारा पोषण प्राप्त होता है और भ्रूण द्वारा उत्पन्न अपशिष्ट पदार्थ इस संरचना के द्वारा माँ के रुधिर में पंहुचा दिए जाते है , इस संरचना को प्लेसेंटा(अपरा) कहते हैं| लगभग नौ माह में शिशु का परिवर्धन और विकास होता है|
Q60. यदि कोई महिला कॉपर – टी का प्रयोग कर रही है तो क्या यह उसकी यौन संचारित रोगों से रक्षा करेगा ?
उत्तर - यदि कोई महिला कॉपर – टी का प्रयोग कर रही है तो यह उसकी यौन संचारित रोगों से रक्षा नही करेगा | यह केवल गर्भधारण रोकने का साधन है|

.png)

No comments:
Post a Comment