In this
article, we have provided you with NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter
7 prepared by expert and experienced teachers. You can find an explanation of the Activity of chapter 7 which is also useful for you.
If you are a class 10 student and searching for the best educational content for NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 7 and ways to download, then you are in a good and right place. The students of class 9 will find out Diversity In Living Organisms Class 9 NCERT Solutions
NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 7
NCERT
solutions for class 10 science chapter 7 helps the students to understand and
practice important concepts in an easy way.
NCERT
solutions for class 10 science chapter 7 also clear your doubt related to “Control
and Coordination” so that you will be able to do your homework and assignments
in an easy manner.
NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 7
If you are
eager to secure high marks in CBSE class 10 board exams, then NCERT solutions
for class 10 science chapter 7 will provide the easiest ways to get good
results.
Control and
Coordination is related to Biology segment of your NCERT Science book and
various topics have been discussed in this chapter such as central nervous
system, reflex action, and structure of the human brain, animal, and plant hormones.
1.
Animals - Nervous System
i. What happens in Reflex actions?
ii. Human brain
iii. How are these Tissues
protected?
iv. How does the Nervous
Tissue cause action?
2.
Coordination In Plants
i. Immediate
Response to stimulus
ii. Movement Due to Growth
Free download
NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 7 is useful to both Hindi and English medium
students of CBSE board, RBSE, and other state boards of
Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat, and all other states can download
Solutions of Chapter 7 Control and Coordination of NCERT Science for Class 10 in English medium and Hindi medium in PDF
format for free.
You can also watch
videos of Solutions of Chapter 7 Control and Coordination of NCERT Science for Class 10 for online. The solution is based on the latest
syllabus of CBSE 2021-22.
NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 7
Chapter 7-Control and Coordination
TEXTBOOK
QUESTIONS
Intext questions
Page No- 119
Q.1What is the
difference between a reflex action and walking?
Ans.Difference
between Reflex action and walking
|
Reflex Action |
Walking |
|
A reflex
action is an automatic and rapid response to a stimulus. |
Walking is a
voluntary action. |
|
Spinal cord
is involved in it. |
It is a
conscious and deliberate action i.e. it is done afterthought is processed
by the brain. |
|
No thinking or feeling involved in
controlling the action. |
we have
acquired through learning |
|
Spinal cord is
involved in this. |
It is
directly controlled by hind-brain |
|
Our eyes close when bright light falls on it,
a knee-jerk is an example of reflex action. |
Walking in a straight line, riding a bicycle,
picking up a pencil |
Q.2What happens at
the synapse between the neurons?
Ans. Synapse is a very small gap between the last
portion of axon of one neuron and the dendron of the other neuron. At the
synapse, the two neurons join together. It acts as
A one-way valve to transmit impulses.
Synapse performs the following tasks:
1. It allows the information to pass from one neuron to another.
2. It ensures the passage of nerve impulse in one direction only.
Q.3 Which part of the
brain maintains posture equilibrium of the body?
Ans.
Cerebellum (a part of hindbrain)
maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body.
Q.4 How do we detect
the smell of an agarbatti (incense sticks)?
Ans. Olfactoreceptors (in nose) send the
information about the smell of incense stick to fore-brain where olfactory
lobes of forebrain analyze and produce the sensation of smell. The for-brain
interprets it along with information received from other receptors as well as
with information that is already stored in the brain.
Q.5 What is the role
of the brain in reflex action?
Ans.
Reflex action is completed by spinal
cord. There is no role of brain in reflex action. These involuntary actions are controlled by
the spinal cord which takes place immediately without thinking. However, impulse
or input also goes to the brain.
Page No. 122
Q.1What are plant
hormones?
Ans. Plant hormones are also called phytohormones. They are the chemical substances that help in controlling growth, flowering, height, development of plants, and their response to the environment.
Following are the main phytohormones –
i).auxins,
ii).Gibberellins
iii)Cytokinins
iv).abscisic acid
v).ethylene.
Q.2How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plants different from the
movement of a
shoot towards light?
Ans.
|
Movement
of leaves in sensitive plant |
Movement
of shoot |
|
1
Movement of leaves of sensitive plant
is independent of growth |
1
movement of a shoot towards light depends on
growth |
|
2
Touch is the stimulus. |
2Light
is the stimulus. |
|
3
This movement is caused by a sudden loss of water. |
3
This movement is caused by unequal growth. |
Q.3Give an example
of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Ans.
Plant hormone auxin and gibberellins
promote growth of plant.
Q.4How do auxin
promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Ans.
Auxin plant hormone is found at the tip
tendril When the tip of a tendril touches support, then the auxins present in
its tip move to that side of the tip which is away from the support and So, due to more auxins in it, the side of
tendril away from the support grows faster than the side which is in contact with the
support that’s why the tendril bend)
around the support.
Q.5Design an
experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Ans. The movement of plant parts towards the availability of water is called hydrotropism. Roots always move toward water.
we plant tiny seedlings in two different trough A and B. Near them we place a clay pot filled with water. We water the soil in trough A daily but Do not water the soil in trough B. Leave both the troughs for a few days.
After a few days, we dig up the
seedlings carefully from both the troughs without damaging their roots. We find
that the root of seedling in trough A is straight. On the other hand, the root
of seedling in trough B got bent towards the clay pot containing water.
This experiment shows that the
root of a plant grows towards water.
Page No.-125
Q.1 How does chemical
coordination take place in animals?
Ans. Chemical coordination takes place in
animals by secreting hormones from endocrine glands.
Q.2Why is the use of
iodised salt advisable?
Ans.Iodine
is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. Deficiency of iodine in the body
causes swollen neck or through which called goiter.
Q.3 How does our body
respond when adrenalin is secreted into the blood?
Ans.
Adrenalin hormone is secreted by
endocrine gland ‘Adrenal’, located on each kidney. When adrenalin hormone is
secreted into blood, heartbeat becomes faster to supply more oxygen to muscles,
but at the same time blood supply is reduced to digestive system and skin, so
breathing rate increases. This leads the animal (human) body to deal with adverse conditions.
Q.4Why are some patients
with diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Ans.
Diabetes is caused by a deficiency of insulin hormone. Insulin regulated sugar
metabolism. When the amount of insulin decreases in blood, it leads to high sugar
level in blood that’s why patients with diabetes are treated by giving injections
of insulin.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters below
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
EXERCISES
Q.1 Which of the
following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) thyroxin
(c)Oestrogen
(d)cytokinin
Ans. (d) cytokinin
Q.2The gap between
two neurons is called a
(a)Dendrite
(b)synapse
(c) Axon
(d) impulse
Ans. (b) synapse
Q.3The brain is
responsible for
(a) Thinking
(b) regulating the heartbeat
(c)Balancing the body
(d) all of the above
Ans. (d) all
of the above
Q.4What is the
function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors don’t
work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Ans.
Receptors – These are the
nerve cells which receive information from surrounding environment, are called
receptors.
|
Stimulus/information |
Receptors
|
|
Smell
|
Olfactoreceptors
|
|
Taste
|
Tangoreceptors
|
|
Light
|
Photo
receptors |
|
Pain
|
Algesireceptors
|
|
Sound
|
Phono
receptors |
When any receptor does not work properly, we will not be able to respond any stimulus or changes in our surroundings.
For example – In cold, our nose does not work properly, we are not able to detect any smell and taste of food properly because our olfactory receptors do not work properly at this time.
Q.5 Draw the
structure of a neuron and explain its function?
Ans. Structure of Neuron
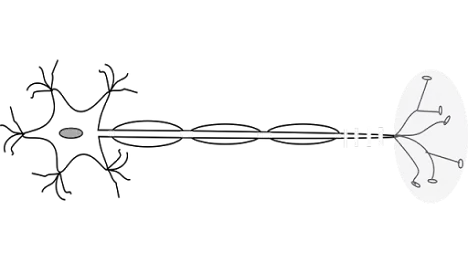 |
| Nerve cell (Neuron) |
Function of a neuron :-
The information passing through neurons is
in the form of chemical and electrical signals are called nerve impulse.
Dentrite receive information of change (stimuli)
in surrounding and sensory neuron transmit this information to the central
nervous system. This information travels
in form of an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from dentrite to the
cell body and then along the axon to its end. At the end the electrical impulse
changes into chemicals which reach the dentrites of other nerve cell where they
create electrical impulse. The gap between two nerve cells is called synapse. In this way impulse travel in body.
Q.6How does
phototropism occur in plants?
Ans.
We take a conical flask filled half with
water and cover the neck of the flask a wire mesh. Now we keep two-three germinated been seeds
on the wire mesh in such a way that water is in contact with germinated seeds.
Now we keep the flask in a cardboard in such a manner that the open side of the
box faces light from window.
After
two or three days we see that shoot turns towards the light and roots moves
away from the light.
Now
we turn the flask away from the sun and roots towards the sun and keep it for
four to five days. After that, we see the flask the shoot turns again towards
the light and roots move again away from light. This shows phototropism.
Q.7Which signals
will get disrupted in case of spinal cord injury?
Ans.
Spinal cord carries messages to brain and
from brain to effector organs. In case of spinal cord injury the signals for
reflex action and motor nerves connected to the receptor and this part will get
disrupted.
Q.8How does chemical
coordination occur in plants?
Ans. Plants do not have any nervous system so all
the coordination is conducted by chemicals. These chemicals are called plant
hormones.
Plants respond to light, water,
gravity, and other chemicals. Auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins and abscisic acid , etc
Q9What is the need
for a system of control and co-ordination in an organism?
Ans. Our body performs different kinds of
activities and during these activities different organs work in coordination. For
example, when we take food, our eyes locate the food, our nose detects the
smell, our hand brings the food to our mouth, the teeth and jaw muscles chew
the food and saliva starts the digestive process.
Q.10 How are involuntary
actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans.
Involuntary actions: - The
actions that are performed without the will of organism but controlled by the brain
are called involuntary actions such as salivation, heart function, blood
pressure breathing etc.
Reflex action: - The action which
is spontaneous and automatic without the response of brain and the will of
organism such removing of hand when a pin is pierced into it.
Q.11 Compare and
contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in
animals.
Ans.
Comparison and contrast between nervous
and hormonal mechanism
|
Nervous mechanism
|
Hormonal mechanism |
|
1.This is performed by nervous system.
|
This
is performed by chemical substances called hormones. |
|
2.Information (impulses) is received by
receptors and acts through effectors. |
These
hormones are secreted by endocrine glands. |
|
3.Chemical change occurs in the cellular
composition of muscular cells.
|
Hormones
produced in on part of the organism, move to other parts of body. |
|
4.It is related to control and coordinate the
functions. |
It
is also related to control and coordination. |
Q.12 What is the
difference between the manner in which movement in the sensitive plant and
movement in our legs takes place?
Ans.
When a part sensitive plant is touched.
The information that the plant has been touched is communicated from cell to
cell using electrical and chemical means, but plants have no specialized tissue
for the conduction of information. Finally the cells should change their shape.
It is performed by change in amount of water.
In
animals, movement of legs is controlled by nervous system. Movement in legs is
a voluntary action. When we think to move our legs, the brain takes action
based on thinking. Forebrain is associated where the sensory information is
interpreted by putting it together with information from other receptors as
well as the information already stored in the brain. On this basis, decision is
taken and information already stored in the brain. On this basis decision is
taken and information is passed to motor area which controls the movement of
voluntary muscles.
|
Movement in a
sensitive plant |
Movement in legs
of a human |
|
1. The leaves of a sensitive plant-like are sensitive to touch. Eg. mimosa |
1. Our leg is in control of nerve muscles. |
|
2. This is not controlled by any part of the plant. |
2. This is controlled by brain and spinal cord. |
|
3. In this, cells change their shape by changing the amount of water in them. |
3. Amount of water has no
effect on the movement of muscles. |
These NCERT solutions
and study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board and Other state
board exams.
Remedial Education
Point.com provides you complete study material for class 10 absolutely free. Now
you can get accurate NCERT Book Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7
Control and Coordination prepared by our expert teachers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters below
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter 6 Life Processes
Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction
Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful Worl
Chapter 12 Electricity
Chapter 13 Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
Chapter 15 Our Environment
Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
Important points
1. Control and coordination are the
functions of the nervous system and hormones in our bodies.
2. The responses of the nervous system can
be classified as reflex action, voluntary action, or involuntary actions.
3. The nervous system uses electrical
impulses to transmit messages.
4. The nervous system gets information
from our sense organs and acts through our muscles.
5. Chemical coordination is seen in both
plants and animals.
6. Hormones produced in one part of an
organism move to another part to achieve the desired effect.
7. A feedback mechanism regulates the action of the hormones.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions
Extra questions
Q1.Name the
receptors for light and sound in animals.
Ans. Sens organs are called receptors
which collect information or sensations from surroundings. The receptor of
light is called photoreceptor and receptor of sound is called a phono receptor.
Q2.Define
chemotropism.
Ans. The tropic movement of plant part in
response to the stimulus of chemicals is called chemotropism.
Q3.Why are
roots of plants called positively geotropic?
Ans. The roots of plants always grow
towards the gravity of the earth so they are called positively called
geotropic.
Q4.Name the
parts of the brain included in hind brain.
Ans. The main parts of hindbrain are
cerebellum, pons and medulla oblongata.
Q5.What are
endocrine glands?
Ans. These are ductless glands that
secrete hormones directly in blood. These endocrine glands are also called
ductless glands.
Q6.One
suddenly withdraw one’s hand when pin pricks, name the type of response
involved in this action.
Ans. Reflex action
Q7.What term
is used for the movement of plant shoot towards the light?
Ans. Phototropism
Q8.Name the
hormone responsible for development of secondary sexual characters in females in
human beings.
Ans. Estrogen from ovaries
Q9.Name the
structural and functional unit of nervous system in human beings.
Ans. Neuron or nerve cell
Q10. What is
the main function of thyroxin hormone in our body?
Ans. Thyroxin hormone regulates metabolism
of fat, carbohydrate and protein our body.
Q11.Name the
tissues that provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms.
Ans. Nervous tissues and muscular tissues
provide control and coordination in multicellular organisms.
Q12.Name the
hormone which lower the glucose level in blood in human beings.
Ans. Insulin hormone secreted by pancreas
lowers the level of glucose in blood.
Q13.Define
synapse.
Ans. The fine gap between axon of one
neuron and dendrites of the other adjacent neuron is called synapse.
Q14.Define
nerve impulse.
Ans. Nerve impulse is the information
passing through neuron in the form of chemical and electrical signals.
Q15.What is a
neuron?
Ans. The structural and functional unit of
the nervous system in organisms is called a neuron or nerve cell.
Q16.What are
hormones?
Ans. Hormones are organic substance
secreted by endocrine glands.
Q17.Name the
hormones secreted by the following endocrine glands-
a. Adrenal gland
b. Thyroid gland
Ans. a. Adrenal gland- Adrenaline hormone
b. Thyroid gland- Thyroxine hormone
Q18.Which part
of the nervous system controls reflex action?
Ans. Spinal cord
Q19. Define
tropism.
Ans- The movement of plant parts towards
or in the direction of stimulus is called tropism.
Q20.What are
tango receptors?
Ans. The sense organs that detects the
taste are called tango receptors.
Q21.Name the
effectors.
Ans. Muscles and glands are effectors.
Q22.Name sex
hormones in human beings.
Ans. In female – Estrogen and in male-
Testosterone.
Q23.Name the
part of the brain which control the involuntary actions.
Ans. Medulla oblongata
Q24.Name the
largest cell in the human body.
Ans. Neuron or nerve cell
Q25.Name the
plant which shows the nastic movement.
Ans. ‘Touch me not’
Q26.What is
reflex action?
Ans. Reflex action is an unconscious,
sudden and involuntary response of effectors to a stimulus.
Q27.Name the
part of hind brain which regulates respiration.
Ans. Pones
Q28.Name one
growth regulator in plants.
Ans. Auxins and gibberellins
Q29.Name any
two types of tropism.
Ans. Geotropism and phototropism.
Q30.What do
you know about olfactory receptors?
Ans. The sense organs that receive smell
are called olfactory receptors.
Q31.Why do
organisms show movement?
Ans. Movement shown by organisms is an
attempt to use the change in the surroundings to their advantages.
Q32.What are
the main functions of sensory neuron and motor neuron?
Ans. Sensory neuron pass information from
receptors to brain and motor neuron pass information form the brain to effectors
(organs).
Q33. Name the
systems that perform control and coordination in organisms.
Ans. Endocrine system and nervous system
perform control and coordination in organisms.
Q34.What are
plant hormones?
Ans. The chemical substances that perform
control and coordination in plants are called plant hormones.
Q35.Write the
numbers of spinal nerves arises from spinal cord.
Ans. Thirty-one spinal nerves arises from
spinal cord.
Q36.Name the
hormone secreted by parathyroid gland.
Ans. Calcitonin hormone
Q37.Name the
gland which secrete hormones estrogen and progesterone in female.
Ans. Estrogen and progesterone hormone are
secreted by ovaries in female.
Q38.When a
person suffers from diabetes?
Ans. Insulin hormones is responsible for
regulation of glucose (sugar) level in blood. When this particular hormone is
secreted in less amount, the level of sugar is increased in the blood. This
condition is called ‘diabetes’.
Q39.A potted
plant is kept in horizontal position, which part of plant will show-
a).Positive geotropism?
b). Negative geotropism?
Ans.a). Positive geotropism- Roots
b). Negative geotropism- Stem
Q40.Write
examples of reflex action.
Ans. Sneezing, yawing, and blinking of eyes
are examples of reflex action.
Q41.Name the
membrane that covers the brain.
Ans. Three membranes cover the brain and
they are called ‘meninges’
Q42.How is
spinal cord protected in the body?
Ans. Spinal cord is situated inside the
vertebral column or backbone so it is protected.
Q43.How the
brain is protected in the body?
Ans. The brain is very delicate part, it is situated in the bone box which is called ‘Cranium’ commonly known as skull
Q44.Name the
hormone secreted by testes.
Ans. Testosterone hormone is secreted by
testes in male.
Q45.Define
geotropism.
Ans. The movement of roots toward the
gravity of the earth is called geotropism.
Q46.Write the
function of cerebellum.
Ans. Cerebellum is the part of hind brain
and it control the balance of body and muscular activity.
Q47.What is
phototropism?
Ans. The movement of plant part towards
light is called phototropism. Shoot of plant shows the phototropism.
Q48. Name the
two components of central nervous system.
Ans. Brain and spinal cord.
Q49.Name the
gland which produces growth hormone.
Ans. Pituitary gland
Q50.Which
mineral is required for synthesis of thyroxine hormone?
Ans. Iodine is essential for synthesis of
thyroxine hormone.
Q51.Name three
plant hormones and state their functions also.
Ans. Following are the plant hormones-
(i). Auxin- For shoot growth, cell
elongation
(ii).Gibberellins –For growth
(iii) Cytokinine – Promotes cell division
Q52.State the
functions of testosterone and estrogen hormones in human beings.
Ans. Function of testosterone- This
is male sex hormone and it promotes development of secondary sex
characteristics like growth of mustache and beard and harshness of voice
during puberty.
Function of estrogen
- This is female sex hormone and it promotes development of secondary sex
characteristics like mammary glands, soft skin, and soft voice during puberty.
Q53.How is
brain protected?
Ans. The brain is very soft and delicate
part of our body.it is protected in following manner-
(i). It is situated in a boney box called
cranium or skull. This is very hard.
(ii).It is covered by three protective
layers called meninges.
(iii). There is a cerebrospinal fluid
between the layers and it acts like shock absorber.
Q54.What is
spinal cord? What is its function?
Ans. Spinal cord is a thread like
structure and part of central nervous system.it is situated in the cavity of
vertebral column.it emerges from hind brain (medulla oblongata).
Function-Its
main function is to control reflex actions. It a part of central nervous system
so it transmit information between brain and sensory organs.
Q55.Which plant hormone is responsible for
the wilting and falling of leaves?
Ans. Abscisic acid
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science All Chapters below
NCERT solutions for class 10 chapter 7 in Hindi
यदि आप कक्षा 10 के छात्र हैं और NCERT solutions for class 10 chapter 7 डाउनलोड करने के तरीकों और सर्वोत्तम शैक्षिक सामग्री खोज रहे हैं, तो आपका
स्वागत और आप सही जगह पर हैं।
NCERT solutions for class 10 chapter 7 छात्रों को महत्वपूर्ण अवधारणाओं
को आसान तरीके से समझने और अभ्यास करने में मदद करता है। NCERT solutions for
class 10 chapter 7 "नियंत्रण और समन्वय" से संबंधित आपके संदेह को भी
दूर करते हैं ताकि आप अपना होमवर्क और असाइनमेंट आसान तरीके से कर सकें।
यदि आप CBSE कक्षा 10 की बोर्ड
परीक्षाओं में उच्च अंक प्राप्त करने के लिए उत्सुक हैं, तो NCERT
solutions for class 10 chapter 7 अच्छे परिणाम प्राप्त करने के सबसे आसान तरीके
प्रदान करेंगे।
नियंत्रण और समन्वय आपकी NCERT विज्ञान पुस्तक के जीव विज्ञान खंड से संबंधित
है और इस अध्याय में विभिन्न विषयों पर चर्चा की गई है जैसे केंद्रीय तंत्रिका
तंत्र, प्रतिवर्ती
क्रिया, और मानव
मस्तिष्क की संरचना, जंतु और पादप हार्मोन आदि |
1. जंतु -
तंत्रिका तंत्र
i.प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में क्या होता है?
ii. मानव मस्तिष्क
iii.ये उत्तक रक्षित कैसे होते है?
iv. तंत्रिका ऊतक कैसे क्रिया करता है?
2.पादपों में
समन्वय
i.उद्दीपन के
लिए तत्काल अनुक्रिया
ii. वृद्धि के कारण गति
3. जंतुओं में हार्मोन
NCERT solutions for class 10 chapter 7 CBSE बोर्ड, राजस्थान, उत्तर
प्रदेश, एमपी, गुजरात
और अन्य सभी राज्यों के हिंदी और अंग्रेजी माध्यम के छात्रों के लिए उपयोगी है, NCERT solutions
for class 10 chapter 7 डाउनलोड कर सकते
हैं।
NCERT solutions for class 10 chapter 7 अंग्रेजी माध्यम और हिंदी माध्यम में पीडीएफ
प्रारूप में मुफ्त मेंउपलब्ध है । आप कक्षा 10 के लिए
NCERT विज्ञान के अध्याय 7 नियंत्रण
और समन्वय के समाधान के वीडियो ऑनलाइन भी देख सकते हैं। समाधान CBSE 2021-22 के नवीनतम पाठ्यक्रम पर आधारित हैं।
अध्याय 7 नियंत्रण और समन्वय
पाठ्य पुस्तक
पृष्ठ संख्या - 132
Q.1 प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया और टहलने में
क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर-
|
प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया |
टहलना |
|
प्रतिवर्त क्रिया किसी उद्दीपन के लिए एक स्वचालित और तीव्र प्रतिक्रिया है। |
टहलना एक स्वैच्छिक क्रिया है। |
|
इस क्रिया में मेरुरज्जु शामिल होती
है। |
यह सीधे पश्च-मस्तिष्क द्वारा नियंत्रित होता है| |
|
इस क्रिया को नियंत्रित करने में कोई सोच या विचार शामिल नहीं है। |
यह एक सचेत और सुविचारित क्रिया है अर्थात इस क्रिया में मस्तिष्क द्वारा संपादित की जाती है | |
|
तेज रोशनी पडने पर हमारी आंखें बंद
हो जाती हैं, घुटने का झटका प्रतिवर्त क्रिया के उदाहरण हैं। |
एक सीधी रेखा में चलना, साइकिल चलाना, पेंसिल उठाना |
Q.2 दो तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं (न्यूरॉन्स) के मध्य अंतर्ग्रंथन
(सिनेप्स) में क्या होता है?
उत्तर-सिनैप्स एक न्यूरॉन
के अक्षतंतु के अंतिम भाग और दूसरे न्यूरॉन के दृमाश्य (डेंड्रोन) के बीच एक बहुत
छोटा अंतर है। सिनैप्स पर दो न्यूरॉन्स एक साथ जुड़ते हैं। यह आवेगों को संचारित
करने के लिए एकतरफा वाल्व के रूप में कार्य करता है।
सिनैप्स निम्नलिखित कार्य करता है:
1. यह एक न्यूरॉन से दूसरे न्यूरॉन में सूचनाओं को जाने की
अनुमति देता है ।
2. यह केवल एक दिशा में तंत्रिका आवेग के प्रवाहित होने
को सुनिश्चित करता है।
Q.3 मस्तिष्क का कौन सा भाग शरीर की
स्थिति तथा संतुलन का अनुरक्षण करता है?
उत्तर- सेरिबैलम (पिछला
मस्तिष्क का एक हिस्सा) शरीर की स्थिति तथा संतुलन का अनुरक्षण करता है।
Q.4 हम एक अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता कैसे लगाते हैं?
उत्तर-
ओल्फैक्टोरिसेप्टर्स (नाक में) अगरबत्ती की गंध के बारे में जानकारी अग्र-मस्तिष्क
को भेजते हैं, जहां अग्र मस्तिष्क के घ्राण लोब विश्लेषण करते हैं और गंध की
अनुभूति उत्पन्न करते हैं। मस्तिष्क अन्य
रिसेप्टर्स से प्राप्त जानकारी के साथ-साथ मस्तिष्क में पहले से संग्रहीत जानकारी
के साथ इसकी व्याख्या करता है। इस प्रकार हमें अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता चलता है |
Q.5 प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क
की क्या भूमिका है?
उत्तर- प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया रीढ़ की हड्डीमें स्थित मेरुरज्जु
द्वारा पूरी होती है। प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की कोई भूमिका नहीं होती
है। ये अनैच्छिक क्रियाएं मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होती हैं जो बिना सोचे समझे तुरंत हो
जाती हैं। हालांकि आवेग या सूचनाएँ मस्तिष्क
में भी जाती है।
पृष्ठ संख्या - 136
उत्तर- पादप हार्मोन को
फाइटोहोर्मोन भी कहा जाता है। वे रासायनिक पदार्थ हैं जो वृद्धि, फूल, ऊंचाई, पौधों के विकास और पर्यावरण के प्रति उनकी प्रतिक्रिया
को नियंत्रित करने में मदद करते हैं।
मुख्य पादप हार्मोन (फाइटोहोर्मोन) निम्नलिखित हैं –
i.ऑक्सिन
ii. गिब्बरलिन्स
iii.साइटोकिनिन
iv. एब्सिसिक एसिड
v. एथिलीन
Q.2 छुई –मुई पादप की पत्तियों की
गति, प्रकाश की ओर प्ररोह की गति से
किस प्रकार भिन्न होती है?
उत्तर-
|
छुई –मुई पादप में पत्तियों की गति |
प्ररोह की गति |
|
1 छुई –मुई पादप की
पत्तियों की गति वृद्धि से स्वतंत्र होती है |
1 प्ररोह का प्रकाश की ओर गति वृद्धि पर निर्भर करता है |
|
2 स्पर्श उद्दीपन है। |
2प्रकाश उद्दीपन है। |
|
3 यह गति पानी की
अचानक कमी के कारण होती है। |
3 यह गति असमान
वृद्धि के कारण होता है। |
Q.3 एक पादप हॉर्मोन का उदाहरण दीजिए जो वृद्धि को बढाता है ।
उत्तर- पादप हार्मोन ऑक्सिन और जिबरेलिन पौधे के
विकास एंव वृद्धि को बढ़ावा देते हैं।
Q.4 किसी सहारे के चारों ओर एक प्रतान की वृद्धि में ऑक्सिन किस प्रकार सहायक है?
उत्तर- ऑक्सिन
एक पादप हारमोन है जो कि प्रतान के शीर्ष पर पाया जाता है जब प्रतान की नोक किसी सहारे को छूती है, तो उसके सिरे में मौजूद ऑक्सिन शीर्ष के उस तरफ चले जाते हैं जो सहारे से दूर होता है और इसलिए, इसमें अधिक ऑक्सिन होने के कारण, सहाए से दूर प्रतान उस भाग की तुलना में तेजी से बढ़ता है जो सहारे के संपर्क में है इसलिए प्रतान सहारे के चारों ओर झुकता है |
Q.5 जलानुवर्तन (हाइड्रोट्रोपिज्म)
को दर्शाने के लिए एक प्रयोग की अभिकल्पना कीजिये ।
उत्तर- जल की
उपलब्धता की ओर पौधों के अंगों की गति को जलानुवरन हाइड्रोट्रोपिज्म कहा जाता है।
जड़ें हमेशा जल की ओर गति करती हैं। हम दो
अलग-अलग कुंड A और B लेते है और उनमे मे
छोटे पादप अंकुर लगाते हैं। उनके पास हम पानी से भरा मिट्टी का बर्तन रखते हैं। हम
मिट्टी के कुंड/ गर्त A में प्रतिदिन पानी देते हैं लेकिन गर्त B में मिट्टी को पानी नहीं देते हैं। दोनों कुंडों को
कुछ दिनों के लिए छोड़ दें। कुछ दिनों के बाद हम दोनों कुंडों से पौधों की जड़ों
को नुकसान पहुंचाए बिना सावधानीपूर्वक खुदाई करते हैं। हम पाते हैं कि कुंड /गर्त A में अंकुर की जड़ सीधी है। दूसरी ओर, कुंड B में अंकुर की जड़ मुड़ी हुई है पानी से भरे
मिट्टी के बर्तन की ओर। इस प्रयोग से पता चलता है कि पौधे की जड़ पानी की ओर बढ़ती
है।
पृष्ठ संख्या – 138
Q.1 जंतुओं में रासायनिक समन्वय कैसे
होता है?
उत्तर- जंतुओं में अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों
से हार्मोन स्रावित करके रासायनिक समन्वय होता है।
Q.2 आयोडीन युक्त नमक के उपयोग की सलाह
क्यो दी जाती है?
उत्तर-आयोडीन थायरोक्सिन
हारमोन के संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक है।
शरीर में आयोडीन की कमी से गर्दन में सूजन हो जाती है या जिससे गोइटर(गलगंड) कहते
हैं।
Q.3 जब एड्रेनलिन रुधिर में स्रावित होता है तो हमारा शरीर क्या अनुक्रिया होती है?
उत्तर- एड्रेनलिन हार्मोन प्रत्येक गुर्दे पर स्थित अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथि 'एड्रेनल' द्वारा स्रावित होता है। जब एड्रेनलिन हार्मोन रक्त में स्रावित होता है, तो मांसपेशियों को अधिक ऑक्सीजन की आपूर्ति करने के
लिए दिल की धड़कन तेज हो जाती है, लेकिन साथ ही पाचन तंत्र और त्वचा को रक्त की आपूर्ति कम हो जाती है, इसलिए सांस लेने की दर बढ़ जाती है। यह मनुष्य शरीर
को प्रतिकूल स्थिति से निपटने के लिए प्रेरित करता है।
Q.4 मधुमेह के कुछ रोगियों की चिकित्सा
इंसुलिन का इंजेक्शन देकर क्यों की
जाती है? उत्तर- मधुमेह इंसुलिन हार्मोन की कमी के कारण होता
है। इंसुलिन शर्करा के चयापचय को नियंत्रित
करता है । जब रक्त में इंसुलिन कम हो जाता
है, इससे रक्त में शर्करा का स्तर बढ़ जाता है इसलिए
मधुमेह के रोगी को इंसुलिन के इंजेक्शन देकर इलाज किया जाता है।
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters below
Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
अभ्यास प्रश्न
Q.1 निम्नलिखित में से कौन –सा एक पादप हार्मोन है?
(a) इंसुलिन
(b) थायरोक्सिन
(d) साइटोकिनिन
उत्तर। (d) साइटोकिनिन
Q.2 दो तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं के मध्य खाली
स्थान को कहते हैं
(a) दृमिका
(b) सिनेप्स
(c) एक्सॉन
(d) आवेग
उत्तर-(b) सिनेप्स
Q.3 मस्तिष्क उत्तरदायी है?
(a) सोचने के लिए
(b) हृदय स्पंदन के लिए
(c) शरीर का संतुलन बनाने के लिए
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर-(d). उपरोक्त सभी
Q.4 हमारे शरीर में ग्राही का क्या
कार्य है? ऎसी स्थिति पर विचार कीजिये
जहां ग्राही उचित प्रकार से कार्य नहीं कर रह हों | क्या समस्याएं उत्पन्न हो सकती है?
उत्तर- ग्राही (Receptors)-
ये तंत्रिका कोशिकाएँ होती हैं जो आसपास के वातावरण
से सूचना प्राप्त करती हैं, ग्राही कहलाती हैं।
जब कोई रिसेप्टर ठीक से
काम नहीं करता है, हम अपने आस-पास किसी भी उत्तेजना या परिवर्तन का जवाब
नहीं दे पाएंगे। उदाहरण के लिए - ठंड में हमारी नाक ठीक से काम नहीं करती है, हम भोजन की किसी भी गंध और स्वाद का ठीक से पता नहीं
लगा पाते हैं क्योंकि हमारे घ्राण ग्राही इस समय ठीक से काम नहीं करते हैं।
|
उद्दीपन /सूचना |
ग्राही |
|
गंध |
ओल्फैक्टोरिसेप्टर्स (घ्राण ग्राही) |
|
स्वाद |
टैंगोरिसेप्टर (स्वाद ग्राही) |
|
प्रकाश |
फोटो रिसेप्टर्स (प्रकाश ग्राही) |
|
दर्द |
अल्जेसिसेप्टर |
|
ध्वनि |
फोनो रिसेप्टर्स |
Q.5 एक तंत्रिका कोशिका (न्यूरॉन) की संरचना बनाइए और इसके कार्यों की वर्णन कीजिए?
उत्तर- न्यूरॉन डेंड्राइट्स की संरचना
 |
| Nerve cell (Neuron) |
न्यूरॉन के कार्य :- न्यूरॉन्स से गुजरने
वाली सूचना रासायनिक और विद्युत संकेतों के रूप में होती है जिसे तंत्रिका आवेग
कहा जाता है।
दृमश्य ( डेंट्राइट)
आसपास के परिवर्तन (उत्तेजना) की जानकारी प्राप्त करते हैं और संवेदी न्यूरॉन इस
जानकारी को केंद्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र तक पहुंचाते हैं। यह जानकारी विद्युत आवेग के
रूप में प्रवाहित होती है। यह आवेग डेंट्राइट से कोशिका शरीर तक और फिर अक्षतंतु
के साथ अपने अंत तक जाता है। अंत में विद्युत आवेग रसायनों में बदल जाता है जो
अन्य तंत्रिका कोशिका के डेंट्राइट्स तक पहुँचते हैं जहाँ वे विद्युत आवेग बनाते
हैं |दो तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं के बीच के खाली स्थानान को सिनैप्स कहा जाता है। इस तरह शरीर में आवेग संचरण
करता है।
Q.6 पादप में प्रकाशानुवर्तन किस प्रकार होता है?
उत्तर- हम आधा पानी से
भरा एक शंक्वाकार फ्लास्क लेते हैं और फ्लास्क की गर्दन को तार की जाली से ढक देते
हैं। अब हम दो-तीन अंकुरित बीजों को तार की जाली पर इस प्रकार रखते हैं कि पानी
अंकुरित बीजों के संपर्क में रहे।
अब हम फ्लास्क को गत्ते में इस प्रकार रखते हैं
कि डिब्बे का खुला भाग खिड़की से प्रकाश की ओर हो। दो या तीन दिनों के बाद हम
देखते हैं कि अंकुर प्रकाश की ओर मुड़ जाता है और जड़ें प्रकाश से दूर चली जाती
हैं। अब हम फ्लास्क को सूरज से दूर कर
देते हैं और जड़ों को सूरज की तरफ घुमाते हैं और चार से पांच दिनों के लिए रख देते
हैं। उसके बाद हम फ्लास्क को देखते हैं कि अंकुर फिर से प्रकाश की ओर मुड़ जाता है
और जड़ें फिर से प्रकाश से दूर चली जाती हैं। इस प्रकार पादप में प्रकाशानुवर्तन
होता है।
Q.7 मेरुरज्जु आघात में किन संकेतों
के आने में व्यवधान होगा ?
उत्तर- मेरुरज्जु , मस्तिष्क और मस्तिष्क से प्रभावकारी
अंगों तक संदेश पहुंचाती है। मेरुरज्जु
में चोट के मामले में प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया के लिए संकेत और रिसेप्टर से जुड़ी मोटर
तंत्रिकाएं का हिस्सा बाधित हो जाएगा।
Q.8 पादप में रासायनिक समन्वय कैसे होता है?
उत्तर- पौधों में कोई
तंत्रिका तंत्र नहीं होता है इसलिए सभी समन्वय रसायनों द्वारा संचालित होते हैं।
इन रसायनों को पादप हार्मोन कहा जाता है। पौधे प्रकाश, पानी, गुरुत्वाकर्षण और अन्य रसायनों पर प्रतिक्रिया करते हैं। ऑक्सिन, गेबरेलिन, साइटोकिनिन और एब्सिसिक एसिड आदि प्रमुख हार्मोन पाए जाते हैं|
Q.9 एक जीव में नियंत्रण और समन्वय
प्रणाली की क्या आवश्यकता है?
उत्तर- हमारा शरीर विभिन्न प्रकार की गतिविधियां करता है और इन गतिविधियों के
दौरान विभिन्न अंग समन्वय में काम करते हैं। उदाहरण के लिए, जब हम भोजन करते हैं, तो हमारी आंखें भोजन का पता लगाती हैं, हमारी नाक गंध का पता लगाती है, हमारा हाथ भोजन को हमारे मुंह में लाता है, दांत और जबड़े की मांसपेशियां भोजन को चबाती हैं और लार पाचन प्रक्रिया शुरू
करती है।
Q.10 अनैच्छिक क्रियाएं तथा प्रतिवर्ती
क्रियाएं एक दूसरे से कैसे भिन्न हैं?
उत्तर- अनैच्छिक क्रियाएं :- वे क्रियाएं जो जीव की इच्छा के बिना की
जाती हैं परंतु मस्तिष्क द्वारा नियंत्रित होती हैं , अनैच्छिक क्रियाएँ कहलाती हैं जैसे लार, हृदय क्रिया, रक्तचाप श्वास आदि।
प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया: - वह क्रिया जो मस्तिष्क की प्रतिक्रिया और जीव की
इच्छा के बिना सहज और स्वचालित होती है जैसे कि पिन चुभने पर हाथ हटाना इसके लिए।
Q.11 जंतुओं में नियंत्रण और समन्वय
के लिए तंत्रिका और हार्मोनक्रियाविधि की तुलना तथा व्यतिरेक (contrast) कीजिये ।
उत्तर- तंत्रिका और हार्मोन क्रियाविधि के बीच तुलना
|
तंत्रिका तंत्र |
हार्मोन क्रियाविधि |
|
(i) यह तंत्रिका तंत्र द्वारा किया जाता है। |
यह हार्मोन नामक रासायनिक पदार्थों द्वारा किया जाता है। |
|
(ii) सूचना (आवेग) रिसेप्टर्स(ग्राही ) द्वारा प्राप्त की जाती है और प्रभावकों(अंगों
) के माध्यम से कार्य करती है। |
ये हार्मोन अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों द्वारा स्रावित होते हैं। |
|
(iii) पेशीय कोशिकाओं की कोशिकीय संरचना में रासायनिक परिवर्तन होता है। |
जीव के अंग में उत्पादित हार्मोन, शरीर के दूसरे भाग में चले
जाते हैं। |
|
(iv) यह कार्यों के नियंत्रण और समन्वय से संबंधित है। |
यह नियंत्रण और समन्वय से भी संबंधित है | |
Q.12 छुई –मुई पादपं में गति और हमारी टांग में होने वाली गति के तरीके में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर- जब किसी संवेदनशील
पौधे को छुआ जाता है, तो इस सूचना को विद्युत और रासायनिक साधनों का उपयोग करके कोशिका
से कोशिका तक संचार किया जाता है, लेकिन पौधों में सूचना के संचालन के लिए कोई विशेष
ऊतक नहीं होता है।
अंत में कोशिकाओं को अपना
आकार बदलना चाहिए। यह पानी की मात्रा में परिवर्तन द्वारा किया जाता है। जानवरों
में, पैरों की गति को तंत्रिका तंत्र द्वारा नियंत्रित
किया जाता है। पैरों में हलचल एक स्वैच्छिक क्रिया है। जब हम अपने पैरों को हिलाने
की सोचते हैं तो दिमाग सोच के आधार पर कार्रवाई करता है। अग्रमस्तिष्क जहां संवेदी जानकारी को अन्य रिसेप्टर्स(ग्राही
) प्राप्त जानकारी के साथ-साथ मस्तिष्क
में पहले से संग्रहीत जानकारी के साथ जोड़कर व्याख्या की जाती है। इस आधार पर
निर्णय लिया जाता है और जानकारी पहले से ही मस्तिष्क में संग्रहीत होती है। इस
आधार पर निर्णय लिया जाता है और मोटर क्षेत्र को सूचना दी जाती है जो कि स्वैच्छिक
मांसपेशियों की गति को नियंत्रित करता है ।
इस प्रकार हमारे पैर में गति होती है |
|
छुई –मुई पादप में गति |
मनुष्य की टांग में गति |
|
1.संवेदनशील पौधे की पत्तियाँ स्पर्श के प्रति संवेदनशील होती हैं। उदा.
मिमोसा |
1.हमारा पैर तंत्रिका मांसपेशियों के नियंत्रण में होता है। |
|
2.यह पौधे के किसी भी भाग द्वारा नियंत्रित नहीं होता है। |
2.यह मस्तिष्क और मेरुरज्जु द्वारा
नियंत्रित होता है। |
|
3.इसमें कोशिकाएँ पानी की मात्रा बदलने पर अपना आकार बदल लेती हैं। |
3.पानी की मात्रा का मांसपेशियों की गति पर कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता है। |
ये एनसीईआरटी समाधान और
अध्ययन सामग्री आपके सीबीएसई बोर्ड और अन्य राज्य बोर्ड परीक्षाओं के लिए अच्छे
अंक लाने में आपकी मदद करेगी।
Remedial Education Point.com आपको कक्षा 10 के लिए पूरी अध्ययन सामग्री बिल्कुल मुफ्त प्रदान करता है। अब
आप हमारे विशेषज्ञ शिक्षकों द्वारा तैयार सटीक एनसीईआरटी कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 7 नियंत्रण और समन्वय प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
कक्षा 10 विज्ञान के लिए एनसीईआरटी समाधान नीचे दिए गए सभी
अध्याय
अध्याय 1 रासायनिक अभिक्रियाएँ और समीकरण
अध्याय 2 अम्ल, क्षारक और लवण
अध्याय 3 धातु और अधातु
अध्याय 4 कार्बन और उसके यौगिक
अध्याय 5 तत्वों का आवर्त वर्गीकरण
अध्याय 6 जैव प्रक्रम
अध्याय 7 नियंत्रण और समन्वय
अध्याय 8 जीव कैसे प्रजनन करते हैं?
अध्याय 9 आनुवंशिकता और जैव विकास
अध्याय 10 प्रकाश परावर्तन और अपवर्तन
अध्याय 11 मानव नेत्र तथा रंग बिरंगा संसार
अध्याय 12 विद्युत
अध्याय 13 विद्युत धारा के चुंबकीय प्रभाव
अध्याय 14 ऊर्जा के स्रोत
अध्याय 15 हमारा पर्यावरण
अध्याय 16 प्राकृतिक संसाधनों का प्रबंधन
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
1. हमारे शरीर में नियंत्रण और समन्वय का कार्य तंत्रिका
तंत्र और हार्मोन का हैं।
2. तंत्रिका तंत्र की अनुक्रियाओं को प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया, स्वैच्छिक क्रिया या अनैच्छिक क्रियाओं के रूप में
वर्गीकृत किया जा सकता है।
3. तंत्रिका तंत्र संदेशों को प्रसारित करने के लिए
विद्युत आवेगों का उपयोग करता है।
4. तंत्रिका तंत्र हमारी इंद्रियों से जानकारी प्राप्त
करता है और हमारी मांसपेशियों के माध्यम से कार्य करता है।
5. रासायनिक समन्वय पौधों और जंतु दोनों में देखा जाता
है।
6. जीव के एक भाग में उत्पन्न हार्मोन वांछित प्रभाव को
प्राप्त करने के लिए दूसरे भाग में चले जाते हैं।
7. हार्मोन की एक क्रिया को पुनर्भरण क्रियाविधि नियंत्रितकरती है।
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Extra Questions
अतिरिक्त प्रश्न
Q1.जंतुओं में प्रकाश और ध्वनि के रिसेप्टर्स (ग्राही) के नाम बताएं।
उत्तर- संवेदी अंगों को रिसेप्टर्स(ग्राही ) कहा
जाता है जो आसपास के वातावरण से जानकारी या संवेदना को एकत्र करते हैं। इन सवेंदानाओं को उद्दीपन कहते हैं |
प्रकाश के रिसेप्टर(ग्राही
) को फोटोरिसेप्टर(प्रकाश ग्राही ) और ध्वनि के रिसेप्टर को फोनो रिसेप्टर कहा
जाता है।
Q2. रसायानानुवर्तन (कीमोट्रोपिज्म)
को परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर- रसायनों के
उद्दीपन की प्रतिक्रिया में पादप भाग की अनुवर्तन गति को रसायनानुवर्तन कहते हैं ।
Q3.पौधों की जड़ों को सकारात्मक गुरुत्वानुवर्तनी क्यों कहा जाता है?
उत्तर- पौधों की जड़ें
हमेशा पृथ्वी के गुरुत्वाकर्षण की ओर बढ़ती हैं इसलिए उन्हें सकारात्मक रूप से गुरुत्वानुवर्तनी
(जियोट्रोपिक) कहा जाता है।
Q4. पश्च मस्तिष्क में शामिल
मस्तिष्क के भागों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर-पश्च मस्तिष्क के मुख्य भाग सेरिबैलम, पोन्स और मेडुला ऑबोंगटा हैं।
Q5.अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियां क्या हैं?
उत्तर- ये नलिकाविहीन ग्रंथियां हैं जो रक्त में सीधे हार्मोन स्रावित करती
हैं। इन अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों को नलिकाविहीन ग्रंथियां भी कहा जाता है।
Q6. पिन चुभने पर कोई अपना हाथ अचानक हटा लेता है, इस क्रिया में शामिल प्रतिक्रिया के प्रकार का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया
Q7. पादप प्ररोह की प्रकाश की ओर
गति के लिए किस शब्द का प्रयोग किया जाता है? उत्तर- फोटोट्रोपिज्म (प्रकाशानुवर्तन )
Q8.मानव में मादा में द्वितीयक यौन
लक्षणों के विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार हार्मोन का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- अंडाशय से
एस्ट्रोजन
Q9.मनुष्य में तंत्रिका तंत्र की
संरचनात्मक और कार्यात्मक इकाई का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- न्यूरॉन या
तंत्रिका कोशिका
प्रश्न10. हमारे शरीर में थायरोक्सिन
हार्मोन का मुख्य कार्य क्या है?
उत्तर- थायरोक्सिन
हार्मोन हमारे शरीर में वसा, कार्बोहाइड्रेट और प्रोटीन के चयापचय(मेटाबोलिस्म) को नियंत्रित करता है।
Q11.उन ऊतकों का नाम बताइए जो बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में नियंत्रण और समन्वय प्रदान
करते हैं।
उत्तर- तंत्रिका ऊतक और पेशीय ऊतक बहुकोशिकीय
जीवों में नियंत्रण और समन्वय प्रदान करते हैं।
Q12.उस हार्मोन का नाम बताइए जो
मानव में रक्त में ग्लूकोज के स्तर को कम करता है। उत्तर- अग्न्याशय द्वारा स्रावित इंसुलिन हार्मोन रक्त में ग्लूकोज के स्तर को
कम करता है।
Q13.सिनेप्स को परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर-एक न्यूरॉन के
अक्षतंतु और दूसरे नजदीकी न्यूरॉन के
डेंड्राइट्स(दृमाश्य) के बीच के महीन अंतराल(खाली स्थान) को सिनैप्स कहा जाता है।
Q14. तंत्रिका आवेग को परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर- तंत्रिका आवेग रासायनिक और विद्युत
संकेतों के रूप में न्यूरॉन से गुजरने वाली सूचना है।
Q15.न्यूरॉन क्या (तंत्रिका कोशिका)
है?
उत्तर- जीवों में तंत्रिका तंत्र की संरचनात्मक और कार्यात्मक इकाई को न्यूरॉन
या तंत्रिका कोशिका कहा जाता है।
Q16.हार्मोन क्या हैं?
उत्तर- हार्मोन
अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों द्वारा स्रावित कार्बनिक पदार्थ हैं।
Q17.निम्नलिखित अंतःस्रावी
ग्रंथियों द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन का नाम बताइए-
(a) एड्रिनल ग्रंथि(अधिवृक्क
ग्रंथि)
(b)थाइरॉयड ग्रंथि
उत्तर। (a) अधिवृक्क
ग्रंथि- एड्रेनलीन हार्मोन
(b) थायराइड ग्रंथि-
थायरोक्सिन हार्मोन
Q18.तंत्रिका तंत्र का कौन सा भाग प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया को नियंत्रित करता है?
उत्तर- मेरुरज्जु
प्रश्न19. (अनुवर्तन गति) ट्रोपिज्म को परिभाषित कीजिए।
उत्तर- पौधे के अंगों का
उद्दीपन की ओर या दिशा में गति करना अनुवर्तन गति (ट्रोपिज्म) कहलाता है।
Q20. स्वाद ग्राही (टैंगो रिसेप्टर्स) क्या हैं?
उत्तर- स्वाद का पता
लगाने वाली इंद्रियों को टैंगो रिसेप्टर्सया स्वाद ग्राही कहा जाता है।
Q21.प्रभावकों(effectors) के नाम
बताइए।
उत्तर- मांसपेशियां और
ग्रंथियां प्रभावकारी हैं।
Q22.मनुष्य में लिंग हार्मोन के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- महिला में -
एस्ट्रोजन और पुरुष में - टेस्टोस्टेरोन।
Q23.मस्तिष्क के उस भाग का नाम
बताइए जो अनैच्छिक क्रियाओं को नियंत्रित करता है। उत्तर- मेडुला ऑबोंगटा
Q24.मानव शरीर की सबसे बड़ी कोशिका
का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- न्यूरॉन या
तंत्रिका कोशिका
Q25. उस पौधे का नाम बताइए जो अनुवर्तन
गति (नैस्टिक मूवमेंट) को दर्शाता है।
उत्तर- 'छुई मुई'
Q26.प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया क्या है?
उत्तर- प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया एक उत्तेजना(उद्दीपन ) के लिए प्रभावकों की एक अचेतन, अचानक और अनैच्छिक प्रतिक्रिया है।
Q27. पश्च मस्तिष्क के उस भाग का नाम
लिखिए जो श्वसन को नियंत्रित करता है।
उत्तर-पोन्स
Q28 पौधों में वृद्धि नियामक का नाम बताओ |
उत्तर-ऑक्सिन और
जिबरेलिन्स
Q29. किन्हीं दो प्रकार के अनुवर्तन गति
(ट्रोपिज्म) के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- गुरुत्वानुवर्तन (जियोट्रोपिज्म)
और प्रकाशानुवर्तन ( फोटोट्रोपिज्म)
Q30. घ्राण रिसेप्टर्स(ग्राही) के
बारे में आप क्या जानते हैं?
उत्तर- गंध प्राप्त करने
वाली इंद्रियों को घ्राण रिसेप्टर्स कहा जाता है।
Q31.जीव गति क्यों दिखाते हैं?
उत्तर- जीवों द्वारा आस पास
होने वाले परिवर्तन को अपने लाभ के लिए
उपयोग करने का प्रयास करता है , इसलिए जीव गति दर्शाते हैं|
Q32.संवेदी न्यूरॉन और मोटर न्यूरॉन
के मुख्य कार्य क्या हैं?
उत्तर-संवेदी न्यूरॉन,(ग्राही ) रिसेप्टर्स से मस्तिष्क तक सूचनाओं को पहुंचाते हैं और मोटर न्यूरॉन सूचनाओं (आवेग) मस्तिष्क को प्रभावकों (अंगों)
तक पहुंचाते हैं।
प्रश्न 33. जीवों में नियंत्रण और समन्वय
करने वाली प्रणालियों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- अंतःस्रावी तंत्र और तंत्रिका तंत्र
जीवों में नियंत्रण और समन्वय करते हैं।
Q34.पादप हार्मोन क्या हैं?
उत्तर- पौधों में नियंत्रण और समन्वय करने वाले रासायनिक पदार्थ पादप हार्मोन
कहलाते हैं।
Q35.मेरुरज्जु से निकलने वाली मेरु तंत्रिकाओं
की संख्या लिखिए।
उत्तर- मेरुरज्जु से इकतीस मेरु तंत्रिकाएँ निकलती हैं ।
Q36.पैराथायराइड ग्रंथि द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- कैल्सीटोनिन हार्मोन
Q37. उस ग्रंथि का नाम बताइए जो महिलाओं में एस्ट्रोजन और प्रोजेस्टेरोन हार्मोन का
स्राव करती है।
उत्तर- महिलाओं में अंडाशय द्वारा एस्ट्रोजन और
प्रोजेस्टेरोन हार्मोन स्रावित होते हैं।
Q38 कोई व्यक्ति मधुमेह से पीड़ित
कब होता है?
उत्तर- इंसुलिन हार्मोन रक्त में ग्लूकोज (शर्करा) के स्तर के नियमन के लिए
जिम्मेदार होते हैं। जब यह विशेष हार्मोन कम मात्रा में स्रावित होता है, तो रक्त में शर्करा का स्तर बढ़ जाता है। इस स्थिति
को 'मधुमेह' कहा जाता है।
Q39.एक गमले वाले पौधे को क्षैतिज स्थिति में रखा जाता है, पौधे का कौन सा भाग दिखाएगा-
(a) सकारात्मक गुरुत्वानुवर्तन ?
(b) नकारात्मक गुरुत्वानुवर्तन ?
उत्तर .(a) सकारात्मक गुरुत्वानुवर्तन - जड़ें
(b) नकारात्मक गुरुत्वानुवर्तन
- तना
Q40.प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया के उदाहरण
लिखिए।
उत्तर- छींकना, जम्हाई लेना और पलक झपकना प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया के उदाहरण हैं।
Q41. मस्तिष्क को आवरित करने वाली झिल्ली का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- तीन झिल्लियां
मस्तिष्क को ढकती हैं और उन्हें 'मेनिन्जेस' कहा जाता है।
Q42.शरीर में मेरुरज्जु (spinal
cord) की रक्षा कैसे होती है?
उत्तर- मेरुरज्जु कशेरुक स्तंभ या रीढ़ की हड्डी के
अंदर स्थित होती है इसलिए यह सुरक्षित है।
Q43.शरीर में मस्तिष्क की रक्षा
कैसे होती है?
उत्तर- मस्तिष्क बहुत मुलायम
और नाजुक हिस्सा होता है, यह अस्थियों के बक्से में स्थित होता है जिसे 'क्रेनियम' कहा जाता है जिसे आमतौर पर खोपड़ी के रूप में जाना जाता है।
Q44.वृषण द्वारा स्रावित हार्मोन का
नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- टेस्टोस्टेरोन
हार्मोन पुरुषों में वृषण द्वारा स्रावित होता है।
Q45.जियोट्रोपिज्म (गुरुत्वानुवर्तन)
को परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर- पृथ्वी के
गुरुत्वाकर्षण की ओर जड़ों की गति को जियोट्रोपिज्म कहा जाता है।
Q46. अनुमस्तिष्क का कार्य लिखिए।
उत्तर- अनुमस्तिष्क (
सेरिबैलम) पश्च मस्तिष्क का हिस्सा है और
यह शरीर और मांसपेशियों की गतिविधि के संतुलन को नियंत्रित करता है।
Q47.प्रकाशानुवर्तन क्या है?
उत्तर- पादप भाग का प्रकाश
की ओर की गति करने को प्रकाशानुवर्तन कहते हैं। पौधे का प्ररोह प्रकाशानुवर्तन
दर्शाता है।
Q48. केन्द्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र के दो
घटकों के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- मस्तिष्क और मेरुरज्जु
।
Q49. वृद्धि हार्मोन का उत्पादन करने
वाली ग्रंथियों का नाम बताइए।
उत्तर- पीयूष ग्रंथि (पिट्यूटरी ग्रंथि )
Q50.थायरोक्सिन हार्मोन के संश्लेषण
के लिए कौन सा खनिज आवश्यक है?
उत्तर-आयोडीन थायरोक्सिन
हार्मोन के संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक है।
Q51. तीन पादप हॉर्मोनों के नाम
लिखिए और उनके कार्य भी बताइए।
उत्तर- पादप हॉर्मोन निम्नलिखित हैं-
(i) ऑक्सिन- प्ररोह
वृद्धि, कोशिका विस्तार के लिए
(ii) गिबरेलिन्स-विकास के लिए
(iii) साइटोकिनिन - कोशिका विभाजन को बढ़ावा देता है
Q52.मनुष्य में टेस्टोस्टेरोन और
एस्ट्रोजन हार्मोन के कार्यों का वर्णन करें।
उत्तर- टेस्टोस्टेरोन का कार्य- यह पुरुष
लिंग हार्मोन है और यह यौवन के दौरान
मूंछों और दाढ़ी की वृद्धि और आवाज की कठोरता जैसी द्वितीयक गौण लैंगिक लक्षणों के विकास को बढ़ावा देता है।
एस्ट्रोजन का कार्य - यह महिला लिंग हार्मोन है और यह यौवन के दौरान स्तन ग्रंथियों, कोमल त्वचा और कोमल आवाज जैसी द्वितीयक गौण लैंगिक लक्षणों के विकास को बढ़ावा देता है।
Q53.मस्तिष्क की रक्षा कैसे की जाती
है?
उत्तर- मस्तिष्क हमारे शरीर का बहुत कोमल और और नाजुक अंग होता
है । यह निम्नलिखित तरीके से सुरक्षित है-
(i) यह कपाल या खोपड़ी
नामक अस्थियों (बोनी) बॉक्स में स्थित होता है। यह बहुत कठोर होता है।
(ii) यह तीन सुरक्षात्मक परतों से ढका होता है जिन्हें
मेनिन्जेस कहा जाता है।
(iii) परतों के बीच एक मस्तिष्कमेरु द्रव होता है और यह बाहरी
आघातों के अवशोषक की तरह कार्य करता है।
Q54.मेरुरज्जु क्या है? इसका कार्य क्या है?
उत्तर- मेरुरज्जु एक धागे की तरह संरचना और केंद्रीय तंत्रिका
तंत्र का हिस्सा है। यह कशेरुक स्तंभ(मेरुदंड/रीढ़ की हड्डी ) की गुहा में स्थित
है। यह पश्च मस्तिष्क (मेडुला ऑबोंगटा) से निकलता है।
मेरुरज्जु के कार्य- इसका मुख्य कार्य प्रतिवर्ती क्रियाओं को नियंत्रित
करना है। यह केंद्रीय तंत्रिका तंत्र का एक हिस्सा है इसलिए यह मस्तिष्क और संवेदी
अंगों के बीच सूचना प्रसारित करता है।
Q55. कौन सा पादप हार्मोन पत्तियों
के मुरझाने और गिरने के लिए उत्तरदायी है?
उत्तर- अब्स्सिसिक एसिड
- Extra Questions Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science PDf free download
- MCQs Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 1
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 2
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 3
- MCQ Questions for Class 10Science Chemistry Chapter 4
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 5
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter6
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 11
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 8
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 10
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 12
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 13
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 15
If you find any difficulty, please do comment.




No comments:
Post a Comment