NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Chapter 3 provides you with a complete solution of intext and End exercise questions. Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules explains important topics like –atoms, molecules, and laws of chemical combination. NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Chapter 3let you understand concepts about writing chemical formulae, mole concepts. After studying Atoms and Molecules, you should also read NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 4 the structure of the atom.
After
reading NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Chapter 3, you will be able to secure good marks in examinations and get help in
doing homework and assignments.
NCERT
Solutions of Class 9 Science Chapter 3 –Atoms and Molecules is a part
of the Chemistry of NCERT book of Class 9.
The
students can download NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter3 Atoms and Molecules in PDF format for offline use.
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Chapter 3
You must know the
topics and subtopic of Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules of NCERT Science for Class 9 before you go through
the Solutions of Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules of NCERT Science for Class 9.
i.Law of Conservation of Mass
ii. Law of Constant Proportions
2. What is an Atom?
i. What are the Modern day
symbols of Atoms of different Elements?
ii. Atomic Mass
iii. How do Atoms Exist?
3. What is a Molecule?
i.Molecules of Elements
ii. Molecules of Compounds
iii. What is an Ion?
4. Writing Chemical Formulae
i. Formulae of Simple Compounds
5. Molecular Mass and Mole Concept
i.Molecular Mass
ii. Formula Unit Mass
iii. Mole Concept
Students of CBSE affiliated schools and, RBSE, and
other state boards of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat, and all other
states can download Solutions of Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecule of NCERT Science
for Class 9 in English medium and Hindi medium in PDF format for free.
You can also watch videos of Solutions of Chapter 3
Atoms and Molecules of NCERT Science for Class 9 for online. The solution is based
on the latest syllabus of CBSE 2021-22.
Solutions of Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules of NCERT Science for Class 9 Intext questions
Chapter
3
Atoms
and Molecules
NCERTTEXTBOOKQUESTIONS
Intext Questions
from page -32
Q.1 In a reaction 5.3 of sodium carbonate reacted with 6 g of ethanoic acid. The products were 2.2 g of carbon dioxide, 0.9 g water and 8.2 g of sodium ethanoate. Show that these observations are in agreement with the law of conservation of mass.
Ans.
Sodium + Ethanoic acid→Sodium Ethanoate+carbondioxide+water
5.3g+6g→8.2g +2.2g +0.9g
Mass of LHS=5.3g+6g=11.3g
Mass of RHS=8.2g+2.2g+0.9g=11.3g
Mass of reactants=mass of products
Thus, the law of conservation of mass is proved
Q.2Hydrogen and oxygen combine in the ratio of 1: 8 by mass to form water. What mass of oxygen gas would be required to react completely with 3 g of hydrogen gas?
Ans. (Hydrogen: Oxygen) form water(H2O)
1:8
As 1g of Hydrogen combines with 8g of Oxygen
3g of hydrogen will react with oxygen=8×3g=24g
Q.3Which postulate Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of the law of conservation of mass?
Ans. In every chemical reaction, the total masses of all the reactants is equal to the masses of all of the products. Atoms cannot be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Q.4Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory can explain the law of definite proportions?
Ans. In a given chemical compound, the proportions by mass of the elements that compose it are constant.
From Page No. 35
Q.1Define the atomic mass unit.
Ans. One atomic mass unit is equal to exactly one-twelfth (1/12)th the mass of one atom of C-12.
Q.2Why is it not possible to see an atom with naked eyes?
Ans. Atoms are very small to be seen with naked eyes. Their size is measured in nanometers.
(1 nm = 10-9 m).
From Page No. 39
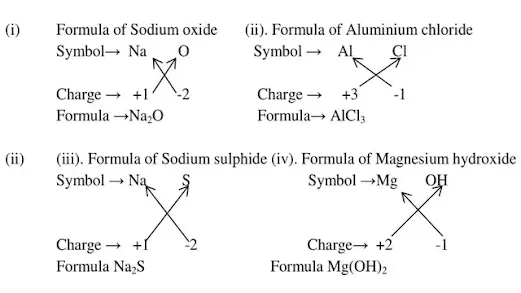
Q.1Write down the formulae of:
(i)Sodium oxide (ii)Aluminium chloride
(iii)Sodium sulphide (iv) Magnesium hydroxide
Ans.
Q.2Write down the names of compounds represented by the following formulae:
(i) Al2(SO4)3 (ii) CaCl2(iii) K2SO4(iv) KNO3 (v)CaCO3
Ans.
(i) Aluminium Sulphate (ii) Calcium Chloride
(iii) Potassium Sulphate (iv) Potassium Nitrate
(v)Calcium Carbonate
Q.3What is meant by the term chemical formula?
Ans. The chemical formula of the compound is a symbolic representation of its composition. Eg- the Chemical formula of Sodium oxide is Na2O
Q.4How many atoms are present in a
(i)H2S molecule and (ii) PO4-3 ion?
Ans.(i) H2S → 3atoms are present (ii) PO4-3 → 5 atoms are present
From Page No. 40
Q.1Calculate the molecular masses of H2, O2, Cl2, CO2, CH4, C2H6, C2H4, NH3, CH3OH
Ans.
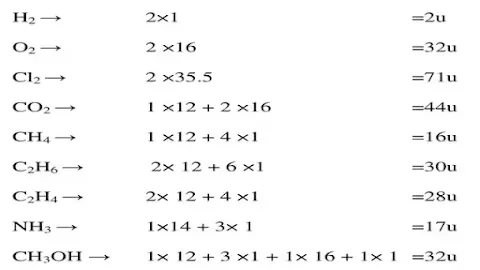
Q.2 Calculate the formula unit masses of ZnO, Na2O, and K2CO3 (Given atomic mass: Zn = 65u, Na = 23u, K= 39u, C= 12u and O = 16u)
Ans.Formula unit mass of Zn= atomic mass of Zn+ atomic mass
of O = 65u + 16 u = 81u
Formula unit mass of Na2O= atomic mass of Na+ atomic mass of O
=2×23u+16u=62u
Formula unit mass of K2CO3=atomic mass of K+ atomic mass of C+atomic mass of O
=2×39g +12u+16u=138u
From Page No. 42
Q.1If one mole of carbon atoms weighs 12 grams, what is the mass (in grams) of 1 atom of carbon?
Ans.1mole of carbon atoms=6.023 × 1023atoms of C =12g
Mass of 1 atom of Carbon = `\frac{12}{6.023\times10^23}`
= 1.99 ×10 23 g
Q.2 Which has more atoms, 100 gram of sodium or 100 gram of iron (given, atomic mass of Na = 23 u, Fe = 56 u.)
Ans. (i) 23g of Na has atoms=6.023×1023
Number of atoms(N)= `\frac{given mass}{Molar mass}\times Avogadro Number`
= `\frac mM\times N_o`
=`\frac{100}{23}\times6.023\times10^{23}`
= `\frac{6023}{23}\times10^{23}`
100g sodium has atom=2.62×1024atoms
(ii). 56g of Fe has atom=6.023×1023
Number of atoms(N)= `\frac{given mass}{Molar mass}\times Avogadro Number`
= `\frac mM\times N_o`
=`\frac{100}{56}\times6.023\times10^{23}`
= `\frac{6023}{56}\times10^{23}`
100g of Fe has atoms=1.075 ×1024atoms
So Na has more atoms
EXERCISE
Q.1 A 0.24 g sample of a compound of oxygen and boron was found by analysis to contain 0.096 g of boron and 0.144 g of oxygen. Calculate the percentage composition of the compound by mass.
Ans.
Percentage of Boron= `\frac{mass of B}{mass of compounds}\times 100`
=`\frac{0.096}{.24}\times100`
=40%
=`\frac{0.144}{0.24}\times100` =60%
Hence, the mass percentage of boron and oxygen in the given compound is 40% and 60% respectively.
Q.2When 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.0 g of oxygen, 11.0 g of carbon dioxide is produced. What mass of carbon dioxide will be formed when 3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 50.0 g of oxygen? Which law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
Ans. C + O2 → CO2
1 mole carbon 1-mole oxygen 1 mole carbon dioxide
12g 32g 44g
For the first case:
3.0 g of carbon is burnt in 8.0 g of oxygen to form 11.0 g of CO2.
For the second case:
3.0 g of carbon must also combine with 8.0 g of oxygen only. This means that (50-8) = 42 g of oxygen will remain un-reacted.
The mass of CO2, in this case, must also be 11 g. So, the law of constant proportion is also valid here.
Q.3 What are polyatomic ions? Give examples.
Ans. The ions which contain more than one atoms and behave as a single unit are called polyatomic ion e.g., PO42-, CO35-, SO42-, OH- etc.
Q.4 Write the chemical formulae of the following:
(a)Magnesium chloride(b)Calcium oxide
(c) Copper nitrate (d)Aluminium chloride
(e) Calcium Carbonate
Ans.
Q.5 Give the names of the elements present in the following compounds:
(a)Quick lime
(b)Hydrogen bromide
(c)Baking powder
(d) Potassium sulphate
Ans. (a)Quick lime is calcium oxide
Elements – Calcium and Oxygen
(b).Hydrogen bromide
Elements – Hydrogen and bromine
( c)Baking powder is Sodium hydrogen carbonate
Elements – Sodium, hydrogen, carbon and oxygen
(d).Potassium sulphate
Elements – Potassium, sulphur, oxygen
Q.6Calculate the molar mass of the following substances:
(a)Ethyene, C2H2
(b)Sulphur molecule, S8
(c)Phosphorous molecule, P4 (Atomic mass of phosphorous = 31)
(d) Hydrochloric acid, HCl
(e)Nitric acid, HNO3.
Ans. The molar
mass of the following:[unit is ‘g’]
(a). Ethyne,C2H2 =2×12+2×1=24+2=26g
(b).Sulphur molecules,S8=8×32=256g
(c) Phosphorus molecule, P4 =4×31=124g
(d) Hydrochloric acid HCl=1 ×1+ 135.5 =1 +35.5 =36.5g
(e) Nitric acid HNO3 = 1× 1+ 1 ×14 + 3×16 =
1 +14 +48=63g
Q.7What is the mass of?
(a)1 mole of nitrogen atoms?
(b)4 moles of aluminium atoms (Atomic mass of aluminium = 27)?
(c)10 moles of sodium sulphite (Na2SO3)?
Ans. (a) Mass
of 1 mole of Nitrogen atom=14g
(b) 4 moles of aluminium atoms
Mass of 1 mole of aluminium atoms =27g
Mass of 4 moles of aluminium atoms= 27 × 4 =108g
(c) 10 moles of sodium sulphate
Mass of 1 mole of sodium sulphite = 2 ×23+32 +3×16=46+32+48=126g
Mass of 10 moles of sodium sulphite = 126 ×10=1260g
.
Q.8Convert into mole:
(a)12 g of oxygen gas
(b) 20 g of water
(c) 22 g of carbon dioxide
Ans. Given mass of Oxygen gas=12g
Molar mass of oxygen gas (O2)= 2 ×16 =32g
Number of moles of oxygen gas =`\frac{mass of O_2}{Molar mass of O_2 gas}`
=`\frac{12g}{32g}` =0.375 mol
So 12g of Oxygen gas is equal to 0.375 mol of Oxygen gas
(b) Given mass of water=20g
Molar mass of water(H2O) =( 2× 1) + 16=18g
Number of moles of water= `\frac{mass of water}{Molar mass of water}`
= `\frac{20g}{18g}`
=1.11 mol
( c) Given mass of Carbon di oxide = 22g
Molar mass of carbon di oxide (CO2) = (1×2)+(2×16)=
44g
Number of moles of Carbon di oxide = `\frac{mass of CO_2}{Molar mass of CO_2}`
= `\frac{22g}{44g}`
= 0.5 mol
Hence, 22 g of carbon dioxide is equal to 0.5 moles of carbon dioxide.
Q.9 What is the mass of :
(a)0.2 mole of oxygen atoms?
(b) 0.5 mole of water molecules?
Ans.
(a) Mole of Oxygen atoms=0.2 mole
Molar mass of Oxygen atoms=16g
Mass of Oxygen atoms= 16 ×0.2 =3.2g
(b). mole of water molecule =05 mole
Molar mass of water molecules=2 ×1 +
16 =18g
Mass of H2O =18×0.5 =9g
Q.10 Calculate the number of molecules of sulphur (S8) present in 16 g of solid sulphur.
AnsNumber of moles of S8 in 16g of Sulphur= `\frac{mass of S_8}{Molar mass of S_8}`
= `\frac{16g}{32\times8g}`mol-1
= `\frac{16}{256}`mol
Number of S8molecules = Number of moles×Avogadro number
= `\frac{16}{256 mol}\times 6.022`× 1023
= 3.76 ×1023 molecules
Q.11 Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.051g of aluminium oxide.
Ans.
Molar mass of aluminium oxide(Al2O3)=(2×27)+3×16)g mol-1
=102g /mol
Number of mole of aluminium oxide= `\frac{mass of Al_2O_3}{Molar mass of Al_2O_3}`
= `\frac{0.051g}{102g mol^1}`
=5.00 ×10-4 mol
1 mol of Al2O3 contains 2 ×6.022
×1023 ions of aluminium
5.00× 10-4 mol of Al2O3 contains 2 × 6.022 1023 × 5.00× 10-4 ions of aluminium =6.0 ×1020ions
So 0.015g of Al2O3 contains 6.0 ×
1020ions of aluminium
These NCERT solutions and study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board and Other state board exams.
Remedial Education Point.com provide you with complete study material for class 10 absolutely free. Now you can get accurate NCERT Book Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Atoms and Molecules prepared by our expert teachers.
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 Extra Questions and Answers
1. 1What is atomic mass unit?
Ans. The sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule of the substance is termed as atomic mass unit.
2. 2.What
is an atom?
Ans. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that takes part in a chemical reaction and
maintains its chemical identity throughout physical and chemical changes.
3. 3.State
law of constant proportion.
Ans. In a chemical substance
(compound) the elements are always present in definite proportions by mass.
4. 4.What
are molecules?
Ans. Molecules represent a group of two or
more atoms chemically bonded to each other and held by a strong attraction force.
5. 5.What
is molecular mass?
Ans. The average
relative mass of a molecule as compared to mass of carbon.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science All Chapters below
Class 9 Science Chapter 3 question answer in Hindi 2021
पृष्ठ संख्या -36 से
Q.1 एक अभिक्रिया में 5.3 ग्राम सोडियम कार्बोनेट ने 6 ग्राम एथेनोइक एसिड के साथ क्रिया की। उत्पाद 2.2 ग्राम कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, 0.9 ग्राम पानी और 8.2 ग्राम सोडियम इथेनोट थे। दिखाएँ कि ये अवलोकन द्रव्यमान के संरक्षण के नियम के अनुरूप हैं।
उत्तर-
सोडियम कार्बोनेट + एथानोइक अम्ल →सोडियम इथनोएट+ कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड
5.3g +6g →8.2g +2.2g +0.9g
बायीं तरफ का द्रव्यमान = 5.3g+6g =11.3g
दायीं तरफ का द्रव्यमान = 8.2g +2.2g +0.9g =11.3g
क्रिया कारकों का द्रव्यमान = क्रिया फल का द्रव्यमान
अत: द्रव्यमान संरक्षण का नियम सिद्ध होता है |
Q.2 हाइड्रोजन और ऑक्सीजन द्रव्यमान के अनुपात में 1:8 के अनुपात में मिलकर पानी बनाते हैं। 3 ग्राम हाइड्रोजन गैस के साथ पूरी तरह से प्रतिक्रिया करने के लिए ऑक्सीजन गैस के कितने द्रव्यमान की आवश्यकता होगी?
उत्तर – हाइड्रोजन : ऑक्सीजन जल बनाते हैं
1 :8
1 g हाइड्रोजन 8g ऑक्सीजन संयोग करता हैं
3g हाइड्रोजन ,ऑक्सीजन से क्रिया करती हैं =8 ×3
=24g
Q.3 कौन सा अभिधारणा डाल्टन का परमाणु सिद्धांत द्रव्यमान के संरक्षण के नियम का परिणाम है?
उत्तर- प्रत्येक रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में सभी अभिकारकों का कुल द्रव्यमान सभी उत्पादों के द्रव्यमान के बराबर होता है। रासायनिक अभिक्रिया में परमाणु न तो बनते हैं और न ही नष्ट होते हैं।
Q.4 डाल्टन के परमाणु सिद्धांत की कौन सी अभिधारणा निश्चित अनुपात के नियम की व्याख्या कर सकती है?
उत्तर-किसी दिए गए रासायनिक यौगिक में, इसे बनाने वाले तत्वों के द्रव्यमान के अनुपात स्थिर होते हैं।
पृष्ठ संख्या 40 . से
Q.1 परमाणु द्रव्यमान इकाई को परिभाषित करें।
उत्तर-एक परमाणु द्रव्यमान इकाई C-12 के एक परमाणु के द्रव्यमान के ठीक एक बारहवें (1/12)वें के बराबर है।
Q.2 परमाणु को नग्न आंखों से देखना संभव क्यों नहीं है?
उत्तर- परमाणु बहुत छोटे होते हैं जिन्हें नग्न आंखों नहीं देखा जा सकता है। इनका आकार नैनोमीटर में मापा जाता है। (1 nm = 10-9 मीटर)।
पृष्ठ संख्या 44 . से
Q.1 निम्न के सूत्र लिखिए:
(i) सोडियम ऑक्साइड
(ii) एल्युमिनियम क्लोराइड
(iii) सोडियम सल्फाइड
(iv) मैग्नीशियम हाइड्रॉक्साइड
उत्तर- (i). Na2O
(ii) Al2Cl3
(iii)Na2S
(iv) Mg(OH)2
Q.2 निम्नलिखित सूत्रों द्वारा निरूपित यौगिकों के नाम लिखिए:
(i) Al2(SO4)3
(ii) CaCl2
(iii) K2SO4
(iv) KNO3
(v) CaCO3
उत्तर- (i) एल्युमिनियम सल्फेट
(ii) कैल्शियम क्लोराइड
(iii) पोटेशियम सल्फेट
(iv) पोटेशियम नाइट्रेट
(v) कैल्शियम कार्बोनेट
Q.3 रासायनिक सूत्र शब्द का क्या अर्थ है?
उत्तर- यौगिक का रासायनिक सूत्र इसकी संरचना का प्रतीकात्मक प्रतिनिधित्व करता है। जैसे- सोडियम ऑक्साइड का रासायनिक सूत्र Na2O है |
Q.4 a (i) H2S अणु और (ii) PO4-3 आयन में कितने परमाणु मौजूद हैं?
उत्तर- (i) H2S → 3 परमाणु मौजूद हैं |
(ii) PO4-3 → 5 परमाणु मौजूद हैं |
पृष्ठ संख्या 46. से
Q.1 H2, O2, Cl2 ,CO2, CH4 ,C2H6 , C2H4 , NH3 ,CH3OH के आणविक द्रव्यमान की गणना करें|
उत्तर –
Q.2 ZnO, Na2O, and K2CO3 के सूत्र इकाई द्रव्यमान की गणना करें (दिया गया परमाणु द्रव्यमान : Zn = 65u, Na = 23u, K= 39u, C= 12u and O = 16u)
उत्तर-
ZnOका सूत्र इकाई द्रव्यमान = Znका परमाणु द्रव्यमान + Oका परमाणु द्रव्यमान
= 65u +16u = 81u
Na2Oका सूत्र इकाई द्रव्यमान = Naका परमाणु द्रव्यमान + Oका परमाणु द्रव्यमान
= 2 ×23u +16u
= 46u +16u= 62u
K2CO3 का सूत्र इकाई द्रव्यमान = Kका परमाणु द्रव्यमान + Cका परमाणु द्रव्यमान + O का परमाणु द्रव्यमान
= 2 ×39u+ 12u +3 ×16u
= 78u+ 12u+ 48u= 138u
पृष्ठ संख्या 48 . से
Q.1 यदि कार्बन परमाणुओं के एक मोल का वजन 12 ग्राम है, तो कार्बन के 1 परमाणु का द्रव्यमान (ग्राम में) क्या होगा?
उत्तर-
एक मोल कार्बन परमाणु = 6.023 ×1023 C = 12g
एक कार्बन परमाणु का द्रव्यमान =`\frac{12}{6.023}\times 10^23`
= 1.99×1023g
Q.2 किसमें अधिक परमाणु हैं, 100 ग्राम सोडियम या 100 ग्राम लोहा (दिया गया है, Na का परमाणु द्रव्यमान = 23 u, Fe = 56 u)
उत्तर-
(i).23 ग्राम सोडियम में परमाणुओं की संख्या =6.023 × 1023
परमाणुओं की संख्या (N)=`\frac{m}{M}\times{N_o}`
= `\frac{100}{23}\times 6.022\times 10^23`
= `\frac{6022}{23}\times 10^23`
100g सोडियम में परमाणुओं की संख्या=`\2.62\times 10^24`
(ii).56 ग्राम आयरन (लोहा) परमाणुओं की संख्या = 6.023 × 1023
परमाणुओं की संख्या (N) =`\frac{m}{M}\times N_o`
m=दिया गया द्रव्यमान
M= मोलर द्रव्यामन
No =आवोगाद्रो संख्या
=`\frac{100}{56}\times 10^23`
=`\frac{6022}{56}\times 10^23`
100ग्राम आयरन में परमाणुओं की संख्या =1.075×1024
अत: सोडियम में परमाणु की संख्या अधिक है |
अभ्यास प्रश्न
Q.1 0.24 g ऑक्सीजन एंव बोरोन युक्त योगिक के नमूने में विश्लेषण द्वारा यह पाया गया की उसमें 0.096 g बोरोन एंव 0.144g ऑक्सीजन है |उस यौगिक के प्रतिशत संघटन का भारात्मक रूप में परिकलन कीजिये |
उत्तर –
बोरोन का प्रतिशत = [बोरोन का द्रव्यमान /यौगिक का द्रव्मान] ×100
=`\frac{0.096}{0.24}\times100`
=40.0
ऑक्सीजन का प्रतिशत = [ऑक्सीजन का द्रव्मान /यौगिक का द्रव्यमान] ×100
=`\frac{0.144}{0.24}\times 100`
=60.0
अत: दिए गए यौगिक में बोरॉन और ऑक्सीजन का द्रव्यमान प्रतिशत क्रमशः 40% और 60% है।
Q.2 3.0g कार्बन 8.00gऑक्सीजन में जलकर कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड निर्मित करता है | जब कार्बन को ऑक्सीजन में जलायेंगे ओत कितने ग्राम कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का निर्माण होगा? आपका उत्तर रासायनिक संयोजन के किस नियम पर आधारित होगा?
उत्तर-
C+O2 →CO2
3.0g+ 8.0g→ 11.0g
पहले मामले के लिए: 3.0 ग्राम कार्बन को 8.0 ग्राम ऑक्सीजन में 11.0 ग्राम CO2 बनाने के लिए जलाया जाता है।
दूसरे मामले के लिए: 3.0 ग्राम कार्बन को भी केवल 8.0 ग्राम ऑक्सीजन के साथ जोड़ना चाहिए। इसका मतलब है कि (50-8) = 42 ग्राम ऑक्सीजन प्रतिक्रियाहीन रहेगी। इस मामले में CO2 का द्रव्यमान भी 11 ग्राम होना चाहिए। अतः यहाँ नियत अनुपात का नियम भी मान्य है।
Q.3 बहुपरमाणुक आयन क्या होते हैं? उदाहरण दीजिए ।
उत्तर। वे आयन जिनमें एक से अधिक परमाणु होते हैं और एक इकाई के रूप में व्यवहार करते हैं, बहुपरमाणुक आयन कहलाते हैं
जैसे, PO42-, CO35-, SO42- , OH- आदि।
Q.4 निम्नलिखित के रासायनिक सूत्र लिखिए:
(a) मैग्नीशियम क्लोराइड
(b) कैल्शियम ऑक्साइड
(c) कॉपर नाइट्रेट
(d) एल्युमिनियम क्लोराइड
(e) केल्सियम कार्बोनेट
उत्तर-
Q.5 निम्नलिखित यौगिकों में विद्यमान तत्वों के नाम दें:
(a) बुझा हुआ चूना
(बb) हाइड्रोजन ब्रोमाइड
(c) बेकिंग पाउडर (खाने वाला सोडा)
(d) पोटेशियम सल्फेट
(a) बुझा हुआ चूना में तत्व है - कैल्शियम और ऑक्सीजन
(b) हाइड्रोजन ब्रोमाइड में तत्व - हाइड्रोजन और ब्रोमीन
(c) बेकिंग पाउडर (खाने वाला सोडा)में तत्व है - सोडियम, हाइड्रोजन, कार्बन और ऑक्सीजन
(d)पोटेशियम सल्फेट में तत्व - पोटेशियम, सफ़र, ऑक्सीजनQ6 निम्नलिखित पदार्थों के मोलर द्रव्यमान का परिकलन कीजिए:
(a) एथाइन, C2H2
(b) सल्फर अणु, S8
(c) फॉस्फोरस अणु, P4 (फॉस्फोरस का परमाणु द्रव्यमान = 31)
(d) हाइड्रोक्लोरिक एसिड, HCl
(e) नाइट्रिक एसिड, HNO3
उत्तर- मोलर द्रव्यमान निम्न है –[मात्रक - g]
(a) एथाइन, C2H2 – 2 ×12+2 ×1= 26g
(b) सल्फर अणु, S8- 8 ×32 =256g
(c) फॉस्फोरस अणु,P4(फॉस्फोरस का परमाणु द्रव्यमान = 31)
4 ×31= 124g
(d) हाइड्रोक्लोरिक एसिड, HCl – 1 ×1+ 1 ×35.5 = 36.5g
(e) नाइट्रिक एसिड, HNO3 – 1 ×1 +1× 14 + 3 ×16 =63g
(a) नाइट्रोजन परमाणुओं का 1 मोल?
(b) एल्यूमीनियम परमाणुओं के 4 मोल (एल्यूमीनियम का परमाणु द्रव्यमान = 27)?
(c) सोडियम सल्फाइट के 10 मोल (Na2SO3)?
उत्तर-(a) नाइट्रोजन परमाणुओं का 1 मोल= 14g
(b) एल्यूमीनियम परमाणुओं के 4 मोल (एल्यूमीनियम का परमाणु द्रव्यमान = 27)
4 मोल एल्युमिनियम का द्रव्यमान = 27× 4 = 108g
(c) सोडियम सल्फाइट के 10 मोल (Na2SO3)
1 मोल सोडियम सल्फाइट का द्रव्यमान =2 ×23 + 3 ×32 + 3 ×16= 126g
10 मोल सोडियम सल्फाइट का द्रव्यमान =126 ×10=1260g
Q.8 मोल में परिवर्तित कीजिए :
(a) 12 ग्राम ऑक्सीजन गैस
(b) 20 ग्राम पानी
(c) 22 ग्राम कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड
उत्तर-
(a) ऑक्सीजन का दिया गया द्रव्यमान = 1
ऑक्सीजन का मोलर द्रव्यमान = 2 ×16 =32g
ऑक्सीजन गैस में मोल की संख्या = ऑक्सीजन का द्रव्यमान /ऑक्सीजन का मोलर द्रव्यमान
=`\frac{12 g}{32 g}`
= 0.375मोल
अत: 12 ग्राम ऑक्सीजन गैस 0.375 मोल ऑक्सीजन के बराबर है|
(b) जल का दिया गया द्रव्यमान = 20g
जल का मोलर द्रव्यमान = 18g
जल में मोल की संख्या =जल का द्रव्यमान /जला का मोलर द्रव्यमान
=`\frac{20 g]{18 g}`
= 1.11मोल
अत: 20 gजल 1.11मोल के बराबर है |
(c) कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का दिया गया द्रव्य्मान =22g
कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का मोलर द्रव्यमान =1 ×12+ 2×16=44g
कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड के मोल की संख्या =कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का द्रव्यमान /कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का मोलर द्रव्यमान
=`\frac{22 g}{44 g}`
= 0.5 मोल
अत: 22 gकार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड 0.5मोल के बराबर है |
(a) 0.2 मोल ऑक्सीजन परमाणुओं का द्रव्यमान क्या है?
(b) 0.5 मोल पानी के अणु?
उत्तर-
(a). ऑक्सीजन परमाणु के मोल =0.2
ऑक्सीजन परमाणु का मोलर द्रव्यमान =16 g
0.2 मोल आक्सीजन परमाणु का द्रव्यमान = 16 ×0.2 =3.2g
(b) जल के अणु के मोल = 0.5 मोल
जल के अणुओं का मोलर द्रव्यामान = 2 ×1 + 16 = 18g
0.5 मोलजल के अणुओं का द्रव्यमान =18 ×0.5 = 9 g
Q.10 16 ग्राम ठोस सल्फर में मौजूद सल्फर (S8) के अणुओं की संख्या का परिकलन कीजिए ।
उत्तर-
16 ग्राम सल्फर में S8 मोल की संख्या =सल्फर का द्रव्यमान/ S8का मोलर द्रव्यमान =`\frac{16 g}{32 g\times S_8}`
S8 के अणुओं की संख्या = मोल कीसंख्या ×आवोगाद्रो संख्या
=`\frac{16}{256}\times 6.022\times 10^23`
=3.76 ×1022अणु
Q.11 0.051g एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड में मौजूद एल्यूमीनियम आयनों की संख्या की गणना करें।
उत्तर-
एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड का मोलर द्रव्यमान =2 ×27 +3 ×16 = 102 g/mol
एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड के मोल की संख्या = एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइडका द्रव्यमान / एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड का मोलर द्रव्यमान
=`\frac{0.05 g}{102 g/mol}`=5.00 ×10-4मोल
एक मोल एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड में एल्युमिनियम आयनों की संख्या
= 2× 6.022× 1023
5.00 ×10-4मोल एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड में एल्युमिनियम आयनों की संख्या
= 2× 6.022× 1023 × 5.00 ×10-4मोल
=6.0 ×1020
0.051g एल्यूमीनियम ऑक्साइड में एल्यूमीनियम आयनों की संख्या=6.0 ×1020
अतिरिक्त प्रश्न
1. परमाणु द्रव्यमान इकाई क्या है?
उत्तर- पदार्थ के एक अणु में सभी परमाणुओं के परमाणु द्रव्यमान के योग को
परमाणु द्रव्यमान इकाई कहा जाता है।
2. परमाणु क्या है?
उत्तर-परमाणु एक तत्व का सबसे छोटा कण है जो रासायनिक प्रतिक्रिया में भाग
लेता है और भौतिक और रासायनिक परिवर्तनों के दौरान अपनी रासायनिक पहचान बनाए रखता
है।
3. स्थिर अनुपात का नियम क्या हैं ?
उत्तर- एक रासायनिक पदार्थ (यौगिक) में तत्व हमेशा द्रव्यमान के निश्चित
अनुपात में मौजूद होते हैं।
4. अणु क्या होते हैं?
उत्तर- अणु दो के समूह का प्रतिनिधित्व करते हैं या अधिक परमाणु रासायनिक रूप
से एक दूसरे से बंधे होते हैं और मजबूत आकर्षण बल द्वारा धारण किए जाते हैं।
5. आणविक द्रव्यमान क्या है?
उत्तर- कार्बन के द्रव्यमान की तुलना में अणु का औसत सापेक्ष द्रव्यमान।
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science All Chapters below





No comments:
Post a Comment