NCERT Solutions of Class10 Science Chapter 6 has been prepared by experienced teachers and the language used in this article named NCERT Solutions of Class10 Science Chapter 6 is so easy to understand. You can also read Activity 6.1 of class 10 NCERT science.
NCERT Solutions of Class10
Science Chapter 6 lets you secure maximum marks in board exams 2022. You will
find important points which help you understand chapter 6 Life Processes better.
You can download NCERT
Solutions of Class10 Science Chapter 6 in pdf format for offline use. NCERT
Solutions of Class10 Science Chapter 6 provide covers the complete syllabus of CBSE
board Exams2021-22.
NCERT Solutions of Class10 Science Chapter 6
Table of
contents
|
Intext questions |
NCERT Solutions of Class10
Science Chapter 6 covers topics and subtopic of Chapter 6 Life Processes of
NCERT Science for Class 10 before you go through the Solutions of Chapter 6 Life
Processes of NCERT Science for Class 10.
1.
What Are Life Processes?
2.
Nutrition
i.How do living things get their
food?
a.Autotrophic Nutrition
b.Hetrotrophic Nutrition
c.How do Organisms obtain their
Nutrition?
d.Nutrition in Human Beings
3.
Respiration
4.
Transportation
i.Transportation in Human Beings
ii.Transportatio in Plants
5.
Excretion
i.Excretion in Human Beings
ii. Excretion in Plants
Students of CBSE board,
RBSE and other state boards of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, M.P., Gujrat, and all
other states can download Solutions of Chapter 6 Life Processes of NCERT
Science for Class 10 in English medium and Hindi medium in PDF format for free.
You can also watch videos
of Solutions of Chapter 6 Life Processes of NCERT Science for Class 10 online. The solution is based on the latest syllabus of CBSE 2021-22.
Solutions of Chapter 6 Life
Processes of NCERT Science for Class 10 Intext questions
Chapter 6
Life Processes
TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS
Questions (Page 95)
Q.1Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of
multi-cellular organisms like us?
Ans.Multicellular
organisms such as humans possess complex body designs. All the body cells are not in direct contact
with the surrounding environment. They have specialized cells and tissues for performing various necessary
functions of the body Therefore, every cell of the body will not get oxygen as
per need by the process of diffusion from the environment. Therefore diffusion
is insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms.
Q.2What criteria do we use to decide whether something is alive?
Ans. The criteria of molecular
movement is used to decide whether something is alive. Living beings also
show growth and movement
Q.3What are outside raw materials used by an organism?
Ans. An organism uses
outside raw materials mostly in the form of food and oxygen. Life on earth
depends on carbon-based molecules. So carbon-based raw materials are used by an
organism. The raw materials
required by an organism can be quite varied depending on the complexity of the
organism and its environment.
Q.4 What processes would you consider essential for
maintaining life.
Ans.Life processes such as
nutrition, respiration, transportation, excretion, etc. are essential for maintaining life.
Questions (Page 101)
Q.1What are the differences between autotrophic nutrition and
heterotrophic nutrition?
Ans.
|
Autotrophic nutrition |
Heterotrophic
nutrition |
|
(i). They can synthesise food from simple
inorganic raw materials such as carbon dioxide and water. |
(i). They get food directly or indirectly from autotrophs. This food is broken down with the help of enzymes. |
|
(ii). Presence of green pigment (chlorophyll) is necessary. |
(ii). No pigment is required in this type of
nutrition. |
|
(iii). Food is generally prepared during day time |
(iii) Food can be prepared at all times |
Q.2Where do the plants get each of the raw materials and photosynthesis?
Ans. Photosynthesis in
plants require following raw materials
-The raw material carbon dioxide enters from the atmosphere through
stomata. Water is absorbed from the soil by the plant roots. Sunlight, is
essential component to manufacture food, is absorbed by the chlorophyll and
other green parts of the plants.
Q.3What is the role of the acid in our stomach?
Ans.Gastric glands present
in the wall of stomach release hydrochloric acid. It performs the following two
functions. Hydrochloric acid is released in stomach and provides an acidic medium.
Enzyme pepsin digests protein and this enzyme acts in an acidic medium only. The
harmful germs (pathogens) coming with food, are also killed by hydrochloric
acid.
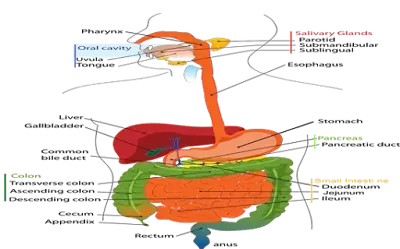
Q.4What is the function of digestive enzymes?
Ans.Digestive enzymes
break complex food materials into simpler molecules. Enzymes such as amylase,
lipase, pepsin, trypsin, etc. help in the breaking down of complex food particles into simple ones Proteins are
converted to amino acids, fats into fatty acids, and complex carbohydrates into
glucose.
Q.5How is the small intestine designed to absorb the digested food?
Ans. The small intestine
has millions of tiny finger-like projections called villi. So the surface area for absorption is
increased many times. Many blood vessels
are present in villi that absorb the digested food and carry it to the bloodstream. From the bloodstream, the absorbed food is delivered to each and every
cell of the body.
Questions (Page 105)
Q.1What advantage over an aquatic organism does a terrestrial organism
have with regards to obtaining oxygen for respiration?
Ans. Terrestrial organisms
take up oxygen from the air whereas aquatic animals need to utilize oxygen present in the water. . Since the content of
oxygen in the air is high, the terrestrial animals do not have to breathe faster to
get more oxygen. On the other hand, aquatic organisms take oxygen dissolved in
water, and amount of oxygen in water is very low. Aquatic animals spend more energy than
terrestrial animals.
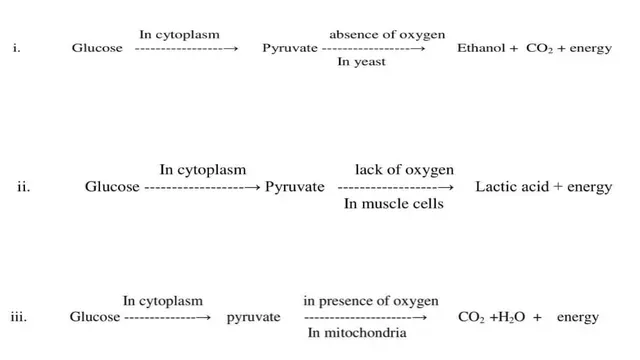
Q.2What are the different ways in which glucose is oxidized to provide
energy in various organisms?
Ans. At first, Glucose is
broken down in the cell cytoplasm into a three-carbon molecule called pyruvate. Pyruvate is further broken
down into different ways to provide energy.
The breakdown of glucose by different pathways can be illustrated as
follows.
Q.3How oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in human beings?
Ans. In human beings,
oxygen and carbon dioxide are transported in the following ways-
Haemoglobin transports
oxygen molecules to all the body cells for cellular respiration. The haemoglobin pigment present in
the blood gets attached to oxygen molecules and form oxyhaemoglobin. This oxygenated blood is
then distributed to all the body cells by the heart. Carbon dioxide is soluble
in water so most of the carbon dioxide produced during respiration is
transported in dissolved form in blood through the lungs.
Q.4How are lungs designed in human beings to maximize the area for
exchange of gases?
Ans. In human beings, to maximize the area for exchange of gases, inner surface of lungs has smaller and smaller tubes that finally terminate into balloon-like structures which are called alveoli. Thus, alveoli are the site for exchange of gases. The walls of alveoli have an extensive network of blood vessels (capillaries). Each lung contains millions of alveoli. These numerous alveoli increase the surface area for gaseous exchange making the process of respiration more efficient. The lungs get filled up with air during the process of inhalation as ribs are lifted up and diaphragm is flattened. The air that is rushed inside the lungs fills the numerous alveoli present in the lungs.
Questions (Page 110)
Q.1What are the components of the transport system in human beings? What
are the functions of these components?
Ans.The main components of
the transport system in human beings are as follows:
(i)Blood
(ii)Blood vessels
(iii)Heart
Functions
(i)Blood:- It is a fluid
connective tissue and blood helps in the transport of oxygen, nutrients, CO2,
and nitrogenous wastes.
(ii)Blood Vessels:- The
blood vessels are two types: arteries and veins. Arteries carry blood from
heart to different organs of the body and veins bring blood back to the heart.
(iii)Heart. It is a
muscular organ that pumps oxygenated blood into arteries and receives
deoxygenated blood from the different body organs through veins.
Q.2Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in
mammals and birds?
Ans. Warm-blooded animals
such as birds and mammals maintain a constant body temperature. So these
animals require more oxygen (O2) for more cellular respiration so that they can
produce more energy to maintain their body temperature. It is necessary to
separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds because they
need high energy quantities and a large amount of oxygen. Separation of oxygenated
and deoxygenated blood provides high oxygen supply to the organs.
Q.3What are the components for the transport system in a highly organised
plants?
Ans. The components of the
transport system in highly organized plants are as follows:
(i)Xylem (ii).
Phloem
(i)Xylem. Conducts water
and minerals absorbed by roots to different parts of the plant.
(ii)Phloem. Conducts
prepared food from leaves to the different parts of the plant.
Q.4How are water and minerals transported in plants?
Ans.Horizontal transpiration plays an important role in the transportation of water and minerals in plants. The components of xylem tissue (tracheids and vessels) of roots, stems, and leaves are interconnected to form a continuous system of water-conducting channels that reaches all parts of the plant.
Transpiration
creates a suction pressure, as a result of which water is forced into the xylem
cells of the roots. The root hairs are unicellular and in contact with soil and
water. These root hairs absorb water and
mineral. Transpiration from the leaves maintain a steady column of water from
roots to leaves. Then there is a steady movement of water from the root xylem
to all the plant parts through the interconnected water-conducting channels.
Q.5How is food transported in plants?
Ans. Food is prepared in green leaves of plants. Food is supplied to all parts of plants and this transportation is conducted by Phloem. Phloem transports food materials from the leaves to different parts of the plant body. The transportation of food in phloem is achieved by utilizing energy from ATP. As a result of this, the osmotic pressure in the tissue increases causing water to move into it. Food molecules enter the phloem cells and transported upward and downward. This movement of food is known as translocation.
Questions (Page 112)
Q.1Describe the structure and functioning of nephrons.
Ans. Each kidney consists
of numerous tubes like structures called nephrons. Nephron is a structural and
functional unit of kidney. Each nephron has a bowl-like structure which is
called Bowman’s capsule. Inside the Bowman’s capsule, there is network of
capillaries which is called Glomeruli. Each nephron opens into a tube which is
called a collecting duct. There is a network of blood vessels around the
collecting duct. The tube becomes U shaped which is called Henle’s loop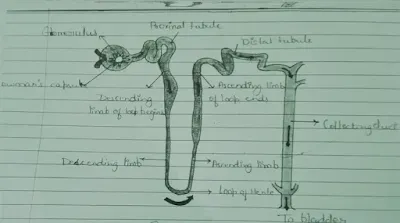
Structure of Nephron
Function – The
circulatory system has nutrients as well as waste materials. The arteriole entering into Bowman’s capsule has larger
diameter while arteriole coming out has a small diameter. The pressure is
inside the glomerulus is increased and wastes, as well as useful substances, are
filtered off. This is called initial filtration. Glucose, amino acids, salts, and water are selectively re-absorbed as the urine flows along the tube. Now
the urine is sent to urinary bladder through ureter.
Q.2What are the methods used by plants to get rid of excreting products?
Ans. Plants have no
excretory organs. They use following methods-
Resins, Latex, and other
materials are excluded from lenticels.
Exchange of gases takes
place by stomata in leaves.
Dead tissues are stored in
cork, bark, etc.
Excess water is transpired
by leaves.
Q.3How the amount of urine is produced regulated?
Ans. The amount of urine produced depends on the amount of excess water and dissolved wastes present in the body. About 180 litres of fluid is collected in nephrons daily but most of the water is reabsorbed by the tubule. The urine enters a long tube, called ureter which moves upto urinary bladder. Urine is stored in it and it is passed out when needed.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science All Chapters below
End Exercise Questions
Q.1The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for
(a)nutrition
(b)respiration
(c)excretion
(d)transportation
Ans. (c)excretion
Q.2Xylem in plants are responsible for
(a)transport of water
(b)transport of food
(c)transport of amino acids
(d)transport
of oxygen
Ans. (a)transport of water
Q.3The autotrophic mode of nutrition requires
(a)carbon dioxide and water
(b)chlorophyll
(c)Sunlight
(d)all of the above
Ans. (c)all of the above
Q.4The breakdown of pyruvate to give carbon dioxide, water, and energy
takes place in
(a)Cytoplasm
(b)mitochondria
(c)Chloroplast
(d)nucleus
Ans. (c)mitochondria
Q.5How are fats digested in our body? Where this process does take
place?
Ans. Digestion of fats
takes place in small intestine. Fats are present in the form of large globules
in the small intestine. The small intestine gets the secretions in the form of bile juice and pancreatic
juice respectively from the liver and the pancreas. The digestion of fats
completes in the following steps:
Bile salts break larger
globules into smaller globules. Pancreatic juice secreted by pancreas has
enzyme lipase which breaks down emulsified fats. Enzymes secreted from the
walls of small intestine finally convert fats into fatty acids.
Q.6What is role of saliva in the digestion of food?
Ans. Saliva is a watery
fluid that contains salivary amylase enzymes and mucous. Saliva plays the
following role in the digestion of food. Saliva moistens and softens the food
for a smooth passage. Saliva contains enzyme amylase which is also called
ptyalin which breaks down starch (a complex molecule) to maltose (a simple
molecule of sugar).
Salivary amylase
Starch-------------------→ Maltose
Q.7What are the necessary conditions for autotrophic nutrition and what
are its byproducts?
Ans. The necessary
conditions for autotrophic nutrition are as follow:
(i). Chlorophyll
(ii)Water
(iii) Carbon dioxide
(iv)Sunlight
oxygen is its
byproduct.
Q.8What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
Name some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration.
Ans.
|
Aerobic respiration |
Anaerobic respiration |
|
It occurs in the presence of O2. |
It occurs in the absence of O2. |
|
Exchange of gases takes place. |
The exchange of gases is absent. |
|
It occurs in cytoplasm and mitochondria. |
It occurs only in cytoplasm. |
|
Glucose is completely oxidized into carbon di
oxide, water, and energy. |
Glucose is oxidized into lactic acid and ethyl
alcohol. |
|
It yields 36 ATPs. |
It yields only 2 ATPs. |
Q.9How are the alveoli designed to maximize the exchange of gases?
Ans. The alveoli are the
small balloon-like structures present in the lungs which maximize the area for
exchange of gases. The walls of alveoli have an extensive network of blood vessels.
Each lung contains 300−350
million alveoli. This large surface area makes the gaseous exchange more
efficient.
Q.10What would be the consequences of a deficiency of
hemoglobin in our body?
Ans. Haemoglobin is the
respiratory pigment that transports oxygen to the body cells for cellular respiration. The deficiency of
hemoglobin in our body will affect the supply of oxygen to tissues and cells. It
can also lead to a disease called anaemia. It will result in a short breath,
tiredness in doing hard work, etc.
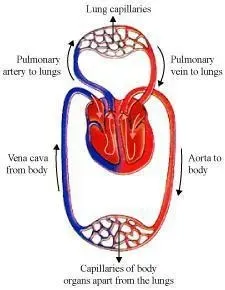
Q.11Describe double circulation in human beings. Why is it
necessary?
Ans. The blood flows twice through the heart in each
cardiac cycle. From body parts deoxygenated blood is taken to right atrium and
right ventricle. When right ventricle contracts, the blood is taken to lungs by
Pulmonary artery. Now oxygenated blood is taken by Pulmonary vein to left
atrium and left ventricle. When left ventricle contracts, the blood is
distributed to all body parts. so the blood flows two times in one cardiac
cycle, this known as ‘Double circulation’.
Importance of
double circulation:
Double circulation keeps the oxygenated and
deoxygenated blood separated so that the blood does not get mixed. This allows
highly efficient supply of oxygen to all body parts and cells. Warm-blooded
animals like human and birds have to maintain constant body temperature so they
need more oxygen to maintain body temperature, double circulation allows more
supply of oxygen to body parts.

12What are the differences between the transport of materials in xylem and phloem?
Ans. Difference between
transport of materials in xylem and phloem
|
Xylem |
Phloem |
|
(i).Xylem
tissue helps in the minerals. |
(i)Food
prepared by leaves is transported by phloem. |
|
(ii).Transportation
is in upward direction. |
(ii)Transportation
is from leaves to other parts such as roots, fruits, and seeds. |
|
(iii). It
largely takes place using simple physical forces like transpiration. |
(iii)It
is achieved using energy in the form of ATP |
Q.13 Compare the
functioning of alveoli in the lungs and nephrons in the kidneys with respect to
their structure and functioning.
Ans.
|
Alveoli |
Nephron |
|
(i).Alveoli
are balloon-like structures at the end of the fine tubes of lungs. |
(i).Nephrons
are the tubular structures present in the kidneys |
|
(ii).Alveoli
are the unit of respiratory system. |
(ii).Nephron
is the unit of the excretory system. |
|
(iii).The
walls of the alveoli are one cell thick and it contains an extensive network
of blood Capillaries. |
(iii).Nephrons
are made of glomerulus, bowman’s capsule, and a long renal tube. It also contains a cluster of thin-walled Capillaries. |
|
(iv).In
alveoli exchange of gases takes place. |
(iv).In
nephrons, waste products are filtered and selective reabsorption of some molecules takes place. |
Important points
1. Movement of various
types can be taken as an indication of life.
2. The maintenance of life
requires processes like nutrition, respiration, transport of materials within
the body and excretion of waste products.
3. Autotrophic nutrition
involves the intake of simple inorganic materials from the environment and
using an external energy source like the sun to synthesis complex high energy
organic materials.
4. Heterotrophic nutrition
involves the intake of complex materials prepared by other organisms.
5. In human beings, the
food eaten is broken down by various steps along the alimentary canal and the
digested food is absorbed in the small intestine to be sent to all cells in the
body.
6. During the process of respiration,
complex organic compounds such as glucose are broken down to provide energy in
the form of ATP. ATP is used to provide energy from other reactions in the
cell.
7. Respiration may be
aerobic or anaerobic. Aerobic respiration makes more energy available to the
organism.
8. In human beings, the
transport of materials such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, food, and excretory
products is a function of the circulatory system. The circulatory system
consists of the heart and blood vessels.
9. In highly
differentiated plants, transport of water, mineral, food, and other materials are
a function of the vascular tissues which consists of xylem and phloem.
Here you will find extra questions – answers to chapter 6 Life Process which will help you a lot. These questions have been prepared by our teachers.
1. What are life processes?
Ans. - The basic processes
which are performed by a living organism to keep themselves alive are known as
life processes.
2. What is the sources of energy in living organisms?
Ans. –Food is the main
source of energy in living organisms and food is also known as fuel.
3. What is nutrition? Or Define nutrition.
Ans. - Nutrition is a
physiological process in which living organisms get nutrients. These nutrients
are necessary for activities in living organisms so nutrition is the
process of obtaining and utilizing food.
4. What is the mode of nutrition in – (a) Fungi (b) Plasmodium?
Ans. - (a) Fungi-
Saprotrophic nutrition
(b) Plasmodium- parasitic
nutrition
5. Why energy is required by an organism at the time of sleeping?
Ans. - As at the time of sleeping,
various biological processes keep on occurring in the body so energy is
required at the time of sleeping.
6. Name the factors which affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Ans. - following factors
affect the rate of photosynthesis-
a. Sunlight
b. water
c. Temperature
d. Carbon dioxide
7. What is light reaction? Or define light reaction.
Ans. - A chemical reaction
that takes place in the presence of light is called a light reaction. It takes
place in grana of chlorophyll.
8. What is a dark reaction?
Ans. - A chemical reaction
which takes place even in the absence of light and it takes place in the stroma
of chloroplast.
9. Name the process by which plants make food.
Ans. Photosynthesis
10.What is chlorophyll?
Ans. Chlorophyll is a
green pigment found in the leaves of plants and green parts of the plant. It
traps the sunlight. It is found in the chloroplast in plant cells.
11.Where is the light reaction occur in the plants?
Ans. The light reaction takes place in the thylakoids
(grana) in the chloroplast.
12. Name the two cells of xylem in plants.
Ans. - (i). Tracheids
(ii). Vessels
13. Name the tissue which transport water and mineral in
plants.
Ans. - Xylem tissue
14. Which is the largest glans in human beings?
Ans. - Liver
15. What is the name tiny projections on the inner surface of
small intestine which helps in absorption of digested food?
Ans.- Villi
16. What is plasma?
Ans.- plasma is a colourless fluid and contains
water, proteins, and carbohydrates.
17.
What make red corpuscles red?
Ans. - Haemoglobin
18. Name the excretory unit of a kidney?
Ans. - Nephron
19. How many chambers are found in human heart?
Ans. - Four chambers- two
upper auricles and two lower ventricles.
20. Name the system responsible for transportation of
materials in human beings.
Ans. - Circulatory system
21. List the components of blood.
Ans. - Blood contains
RBCs, WBCs, Platelets, and Plasma.
22. Why do the walls of trachea not collapse when there is
less air in it?
Ans. Trachea is supported
by C shaped cartilage rings so trachea do not collapse when there is no air in
it.
23. Name the two phases of photosynthesis.
Ans. - (i). Light reaction
(ii). Dark reaction
24. Which part of the alimentary canal receives bile from the
liver?
Ans. - Small intestine
25. What is the function of pancreatic juice?
Ans. - In pancreatic juice
Trypsin, amylase, and lipase enzymes are found. Trypsin digest protein, lipase
emulsified fats and amylase digest carbohydrates present in food.
26. Where does the exchange of gases take place during
respiration?
Ans.- The exchange of
gases take place in alveoli in the lungs.
27. What is the source of oxygen in the process of photosynthesis?
Ans.-Oxygen is a byproduct
in the process of photosynthesis and water absorbed from the soil is the source
of this oxygen.
28.What is the peristaltic movements?
Ans.- The contraction and
expansion of the wall of food pipe is
called peristaltic movement and due to this process, food moves forward in the
alimentary canal.
29. What will happen when xylem is removed from plant?
Ans.- Xylem transports
water and minerals from the soil to the other parts of plant, and when it is
removed the process of transportation will stop and ultimately plant will die.
30.What is chyme?
Ans.- When food enters
into stomach where it is mixed with gastric juices and churned into a semisolid
paste, it is called chyme.
These NCERT solutions and
study material will help you good marks for your CBSE Board and Other state board exams.
Remedial
Education Point.com provides you
complete study material for class 10 absolutely free. Now you can get accurate
NCERT Book Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Life Processes prepared by
our expert teachers.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science All Chapters below
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Chapter 2 Acids, Bases, and Salts
- Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
- Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
- Chapter 6 Life Processes
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science PDf free download
- MCQs Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 1
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 2
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 3
- MCQ Questions for Class 10Science Chemistry Chapter 4
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Chemistry Chapter 5
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter6
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 11
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 8
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 10
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 12
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Physics Chapter 13
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter 15
Here you have been provided Online MCQ Quiz Test- Click the link below
MCQ Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Online Quiz- Set A
MCQ Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reaction and Equations Online Quiz - Set B
Extra Questions Class 10 Science
Click the link given below-
1. Chemical Reactions and Equations Extra Questions
2. Acids.Bases and Salts Extra Questions
3. Metals and Non-Metals Extra Questions
5. Periodic Classification of Elements
10.Light- Reflection and Refraction
11. The Human Eye and The Colourful World
12. Electricity
13. Magnetic Effects of Electric Current
15. Our Environment
16. Management of Natural Resources
If you find any difficulty, please do comment.
Hoping for progress with Remedial Classes
NCERT Solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 in Hindi medium
को अनुभवी शिक्षकों द्वारा तैयार किया गया है और इसमें बहुत ही आसान भाषा का प्रयोग किया गया है , जिससे NCERT solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 in Hindi medium को समझना इतना आसान है। कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 6 का एनसीईआरटी समाधान आपको बोर्ड परीक्षा 2021-22 में अधिकतम अंक प्राप्त करने देता है।
इस लेख में NCERT Solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 in Hindi medium में आपको महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु मिलेंगे जो अध्याय
6 जैव प्रक्रम को बेहतर ढंग से समझने में
आपकी मदद करेंगे। आप ऑफ़लाइन उपयोग के लिए NCERT
solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 in Hindi medium
को pdf प्रारूप में डाउनलोड कर सकते हैं। कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 6 के
एनसीईआरटी समाधान सीबीएसई बोर्ड परीक्षा 2021-22 का पूरा
पाठ्यक्रम उपलब्ध करवाया गया है |
NCERT Solutions for class 10 science chapter 6 in Hindi medium
1.जैव प्रक्रम क्या है ?
2.पोषण
i.स्वपोषी पोषण
ii.विषम पोषी पोषण
3.जीव अपना पोषण कैसे करते हैं?
i.मनुष्य में पोषण
3.श्वशन
4.वहन
i.मानव में वहन
ii.पादपों में परिवहन
5.उत्सर्जन – मानव में उत्सर्जन पादपों में
उत्सर्जन
NCERT, RBSE और राजस्थान, उत्तर प्रदेश, एमपी, गुजरात और अन्य सभी राज्यों के अन्य राज्य बोर्डों के छात्र कक्षा 10 के लिए NCERT विज्ञान के अध्याय 6 जीवन प्रक्रियाओं के समाधान अंग्रेजी माध्यम और हिंदी माध्यम में PDF प्रारूप में free डाउनलोड कर सकते हैं। आप कक्षा 10 के NCERTविज्ञान के अध्याय 6 जीवन प्रक्रियाओं के समाधान के वीडियो ऑनलाइन भी देख सकते हैं। समाधान CBSE 2021-22 के नवीनतम पाठ्यक्रम पर आधारित हैं।
पाठ्य पुस्तक प्रश्न:
पृष्ठ -105
प्र .1 हमारे जैसे बहुकोशिकीय जीवों में ऑक्सीजन आवश्यकता पूरी करने में लिए विसरण क्योंअपर्याप्त
है?
उत्तर- मनुष्य जैसे बहुकोशिकीय जीवों के शरीर की जटिल संरचनाएँ होती हैं।
शरीर की सभी कोशिकाएं आसपास के वातावरण के सीधे संपर्क में नहीं होती हैं। उनके
पास शरीर के विभिन्न आवश्यक कार्यों को करने के लिए विशेष कोशिकाएँ और ऊतक होते
हैं इसलिए, शरीर की
प्रत्येक कोशिका को वातावरण से विसरण की प्रक्रिया द्वारा आवश्यकता के अनुसार
ऑक्सीजन नहीं मिलेगी। इसलिए बहुकोशिकीय जीवों की ऑक्सीजन आवश्यकताओं को पूरा करने
के लिए विसरण अपर्याप्त है।
प्र .2 कोई वस्तु सजीव है , इसका निर्धारण करने
के लिए हम किस मानदंड का उपयोग करेंगे ?
उत्तर- कोई वस्तु सजीव है या नहीं यह तय करने के लिए आणविक गति के मानदंड
का उपयोग करेंगे । जीवित प्राणी वृद्धि और गति दिखाते हैं
प्र .3 किसी जीव द्वारा किन कच्ची सामग्रियों का उपयोग किया जाता है?
उत्तर- एक जीव बाहरी कच्चे माल का उपयोग ज्यादातर भोजन और ऑक्सीजन के रूप
में करता है। पृथ्वी पर जीवन कार्बन आधारित अणुओं पर निर्भर करता है। इसलिए एक जीव
द्वारा कार्बन आधारित कच्चे माल का उपयोग किया जाता है। जीव की जटिलता और उसके
पर्यावरण के आधार पर एक जीव द्वारा आवश्यक कच्ची सामग्री बहुत अलग अलग हो सकती हैं।
प्र .4 जीवन के अनुरक्षण के लिए आप किन प्रक्रमों
को आवश्यक मानेंगे।
उत्तर- जीवन को बनाए रखने के लिए पोषण, श्वसन, परिवहन, उत्सर्जन आदि जैसी जीवन प्रक्रियाएं आवश्यक हैं।
प्र .1 स्वपोषी पोषण और विषमपोषी पोषण में
क्या अंतर हैं?
उत्तर-
|
स्वपोषी पोषण |
विषमपोषी पोषण |
|
(i) वे
सरल अकार्बनिक कच्चे माल जैसे कार्बन डाइ ऑक्साइड और जल से भोजन का संश्लेषण कर सकते हैं। |
(i) वे
भोजन प्रत्यक्ष या अप्रत्यक्ष रूप से स्वपोषी से प्राप्त करते हैं। यह भोजन
एंजाइमों की सहायता से टूट जाता है। |
|
(ii) हरे
वर्णक (क्लोरोफिल) की उपस्थिति आवश्यक है। |
(ii) इस
प्रकार के पोषण में किसी वर्णक की आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। |
|
(iii) भोजन सामान्य
रूप से दिन के समय तैयार किया जाता है |
(iii) भोजन
हर समय तैयार किया जा सकता है | |
प्र .2 प्रकाश
संश्लेषण के लिए आवश्यक कच्ची सामग्री पौधा कहाँ से प्राप्त करता हैं ? उत्तर- पौधों में प्रकाश संश्लेषण के
लिए निम्नलिखित कच्चे माल की आवश्यकता होती है - कार्बन डाइ ऑक्साइड रंध्र के माध्यम से वातावरण
से प्रवेश करता है। पौधों की जड़ों द्वारा मिट्टी से पानी अवशोषित किया जाता है।
सूर्य का प्रकाश, भोजन के
निर्माण के लिए आवश्यक घटक है, क्लोरोफिल और पौधों के अन्य हरे भागों द्वारा अवशोषित किया जाता है।
प्र .3 हमारे आमाशय में अम्ल की भूमिका क्या है?
उत्तर- पेट की दीवार में मौजूद जठर ग्रंथियां हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल का स्त्रवणकरती हैं। यह निम्नलिखित दो कार्य
करता है।
(i)हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल का स्त्रवन जठर में होता है यह पाचन के लिए अम्लीय माध्यम प्रदान करता है। एंजाइम पेप्सिन
प्रोटीन को पचाता है और यह एंजाइम अम्लीय माध्यम में ही कार्य करता है।
(ii)भोजन के साथ आने वाले हानिकारक रोगाणु (रोगाणु) भी हाइड्रोक्लोरिक अम्ल द्वारा मारे जाते हैं।
प्र .4 पाचक एंजाइमों का क्या कार्य है?
उत्तर- पाचन एंजाइम जटिल खाद्य पदार्थों को सरल अणुओं में तोड़ते हैं।
एमाइलेज, लाइपेज, पेप्सिन, ट्रिप्सिन आदि जैसे एंजाइम जटिल खाद्य
कणों को सरल कणों में तोड़ने में मदद करते हैं। प्रोटीन को अमीनोअम्ल में, वसा को वसा अम्ल में और जटिल कार्बोहाइड्रेट को ग्लूकोज में
परिवर्तित करते हैं ।
प्र .5 पचे हुए भोजन को अवशोषित करने के लिए क्षुदान्त्र
को कैसे अभिकल्पित किया गया है ?
उत्तर- छोटी आंत में लाखों छोटी उंगली
जैसे अति वृद्धि होती हैं जिन्हें विली
कहा जाता है। इनके कारण अवशोषण के लिए सतह का क्षेत्रफल बहुत अधिक बढ़ जाता है। विली में कई रक्त वाहिकाएं मौजूद
होती हैं जो पचे हुए भोजन को अवशोषित कर रक्त प्रवाह में ले जाती हैं। रक्त प्रवाह
से, अवशोषित
भोजन शरीर की प्रत्येक कोशिका तक पहुँचाया जाता है।
प्र .1 श्वसन के लिए ऑक्सीजन प्राप्त करने की दिशा
में एक जलीय जीव पर स्थलीय जीव किस प्रकार लाभप्रद है?
उत्तर- स्थलीय जीव हवा से ऑक्सीजन लेते हैं जबकि जलीय जानवरों को पानी में
मौजूद ऑक्सीजन का उपयोग करने की आवश्यकता होती है। चूंकि हवा में ऑक्सीजन की
मात्रा अधिक होती है, इसलिए
स्थलीय जानवरों को अधिक ऑक्सीजन प्राप्त करने के लिए तेजी से सांस लेने की
आवश्यकता नहीं होती है। दूसरी ओर जलीय जीव जल में घुली ऑक्सीजन को ग्रहण करते हैं और जल में ऑक्सीजन की मात्रा बहुत कम होती है। जलीय
जंतु स्थलीय जंतुओं की तुलना में अधिक ऊर्जा खर्च करते हैं।
प्र .2 ग्लूकोज के ऑक्सीकरण से भिन्न जीवों में ऊर्जा प्राप्त करने के विभिन्न पथ क्या हैं?
उत्तर- सबसे पहले ग्लूकोज कोशिका कोशिका
द्रव्य में तीन कार्बन अणु वाले यौगिक पाइरूवेट में टूट जाता है। पाइरूवेट को
ऊर्जा प्रदान करने के विभिन्न तरीकों से तोड़ा जाता है। विभिन्न मार्गों से
ग्लूकोज के टूटने को निम्नानुसार दर्शाया जा सकता है।
चित्र -
प्र .3 मनुष्यों
में ऑक्सीजन और कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड का परिवहन
कैसे होता है? उत्तर-
मनुष्य में ऑक्सीजन और कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड का परिवहन निम्न प्रकार से होता है-
हीमोग्लोबिन कोशिकीय श्वसन के लिए ऑक्सीजन अणु को शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं तक
पहुँचाता है। रक्त में मौजूद हीमोग्लोबिन वर्णक ऑक्सीजन के अणुओं से जुड़ जाता है
और ऑक्सीहीमोग्लोबिन बनाता है। यह ऑक्सीजन युक्त रक्त हृदय द्वारा शरीर की सभी
कोशिकाओं में वितरित किया जाता है। कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड पानी में घुलनशील है इसलिए
श्वसन के दौरान उत्पादित अधिकांश कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड रक्त में घुले हुए रूप में फेफड़ों तक पहुचायी जाती है जहां से उसका उत्सर्जन कर दिया जाता है ।
प्र .4 गैसों के विनिमय के लिए मानव फुफ्फुस में
अधिकतम क्षेत्रफल को कैसे अभिकल्पित किया गया
हैं ?
उत्तर- मनुष्यों में, गैसों के आदान-प्रदान के लिए क्षेत्र को अधिकतम करने के लिए, फेफड़ों की आंतरिक सतह में छोटी और छोटी नलिकाएं होती हैं जो अंत में गुब्बारे जैसी संरचनाओं में समाप्त हो जाती हैं जिन्हें एल्वियोली(वायु कूपिकाएँ) कहा जाता है। इस प्रकार, एल्वियोली गैसों के आदान-प्रदान का स्थान है। एल्वियोली की दीवारों में रक्त वाहिकाओं (केशिकाओं) का व्यापक जाल होता है। प्रत्येक फेफड़े में लाखों एल्वियोली होते हैं। ये असंख्य एल्वियोली श्वसन की प्रक्रिया को और अधिक सुगम बनाने के लिए गैसीय विनिमय के लिए सतह क्षेत्र को बढ़ाते हैं। साँस लेने की प्रक्रिया के दौरान फेफड़े हवा से भर जाते हैं क्योंकि पसलियाँ ऊपर उठ जाती हैं और डायाफ्राम चपटा हो जाता है। फेफड़ों के अंदर जो हवा चलती है, वह फेफड़ों में मौजूद असंख्य एल्वियोली को भर देती है।
प्र .1 मानव में वहन तन्त्र के घटक कौनसे हैं? इन घटकों के क्या कार्य हैं? उत्तर- परिवहन के मुख्य घटक मनुष्य में
प्रणाली इस प्रकार है:
(i) रक्त (ii) रक्त वाहिकाएं (iii) ह्रदय
घटकों के कार्य-
(i)रक्त:- यह एक तरल संयोजी ऊतक है और रक्त
ऑक्सीजन, पोषक
तत्वों, CO2, और नाइट्रोजनयुक्त अपशिष्टों के परिवहन में मदद करता है।
(ii) रक्त वाहिकाएं: रक्त वाहिकाएं दो प्रकार की होती हैं: धमनियां और शिराएं
धमनियां रक्त को हृदय से शरीर के विभिन्न अंगों तक ले जाती हैं और शिराएं रक्त
को हृदय में वापस लाती हैं।
(iii) हृदय: यह एक पेशीय अंग है जो ऑक्सीजन
युक्त रक्त को धमनियों में पंप करता है और वाहिकाओं के माध्यम से शरीर के विभिन्न अंगों से ऑक्सीजन
रहित रक्त प्राप्त करता है।
प्र .2 स्तनधारी और पक्षियों में ऑक्सीजनित और
विऑक्सीजनित रुधिर को अलग करना क्यों
आवश्यक है?
उत्तर- गर्म रक्त वाले जानवर जैसे पक्षी
और स्तनधारी शरीर के तापमान को स्थिर बनाए रखते हैं। इसलिए इन जानवरों को अधिक
कोशिकीय श्वसन के लिए अधिक ऑक्सीजन (O2) की आवश्यकता होती है ताकि वे अपने शरीर
के तापमान को बनाए रखने के लिए अधिक ऊर्जा का उत्पादन कर सकें। स्तनधारियों और
पक्षियों में ऑक्सीजन युक्त और ऑक्सीजन रहित रक्त को अलग करना आवश्यक है, क्योंकि उन्हें अधिक ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता
होती है | ऑक्सीजन युक्त और ऑक्सीजन रहित रक्त को अलग करने से अंगों को उच्च
ऑक्सीजन की आपूर्ति होती है।
प्र .3 उच्च संगठित पादप में वहन तंत्र के घटक
क्या हैं ?
उत्तर- अत्यधिक संगठित पौधों में परिवहन
प्रणाली के घटक इस प्रकार हैं:
(i)जाइलम
(ii)फ्लाएम
(i)जाइलम- जड़ों द्वारा अवशोषित जल और खनिजों को
पौधे के विभिन्न भागों में पहुँचाता है।
(ii) फ्लोएम- तैयार भोजन को पत्तियों से पौधे के
विभिन्न भागों तक पहुंचाता है।
प्र .4 पादप में
जल और खनिज लवण का वहन कैसे होता है?
उत्तर- क्षैतिज वाष्पोत्सर्जन पौधों में जल और खनिजों के परिवहन में
महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका निभाता है। जड़ों, तनों और पत्तियों के जाइलम ऊतक
(ट्रेकिड्स और वाहिकाओं) के घटक आपस में जुड़े होते हैं, जिससे जल-संचालन चैनलों की एक सतत
प्रणाली बनती है जो पौधे के सभी भागों तक पहुँचती है।
वाष्पोत्सर्जन से एक चूषण दबाव बनता है, जिसके कारण जल को
जड़ों की जाइलम कोशिकाओं में प्रवेश करता
है। जड़ों में मूल रोम पाए जाते है, ये मिट्टी और जल के संपर्क में रहते हैं । ये मूल रोम जल और खनिज
को अवशोषित करते हैं। पत्तियों से वाष्पोत्सर्जन जड़ों से पत्तियों तक पानी का एक
स्थिर स्तंभ बनाए रखता है।इसके साथ जड़ में
जाइलम से पौधों के सभी भागों में परस्पर जुड़े जल-संचालन चैनलों के माध्यम से पानी
की एक स्थिर गति होती है।
प्र .5 पादप में भोजन का स्थानातंरण कैसे होता है?
उत्तर- पौधे की हरी पत्तियों में भोजन तैयार होता है। पौधों के सभी भागों
में भोजन का परिवहन फ्लोएम द्वारा किया
जाता है। फ्लोएम खाद्य पदार्थों को पत्तियों से पौधे के शरीर के विभिन्न भागों में
पहुंचाता है।
फ्लोएम में भोजन का परिवहन एटीपी से ऊर्जा का उपयोग करके प्राप्त किया जाता है। इसके परिणामस्वरूप, ऊतक मे परासरण दबाव बढ़ जाता है, खाद्य अणु फ्लोएम कोशिकाओं में प्रवेश करते हैं और ऊपर और नीचे ले जाते हैं। भोजन के इस संचलन को स्थानान्तरण के रूप में जाना जाता है।
प्र .1 वृक्काणु (नेफ्रॉन) की रचना और क्रिया विधि का वर्णन कीजिये ।
उत्तर- प्रत्येक गुर्दे में असंख्य महीन नलिकाएँ पायी जाती हैं इन नलिका (ट्यूब)
जैसी संरचना जिसे नेफ्रॉन कहा जाता है। नेफ्रॉन गुर्दे की एक संरचनात्मक और
कार्यात्मक इकाई है। प्रत्येक नेफ्रॉन में एक कटोरे जैसी संरचना होती है जिसे बोमन
सम्पुट कहा जाता है। बोमन सम्पुट के अंदर
केशिकाओं का नेटवर्क होता है जिसे ग्लोमेरुली कहा जाता है। प्रत्येक नेफ्रॉन एक
ट्यूब में खुलता है जिसे कलेक्टिंग डक्टया संग्रह वाहिनी कहते हैं। संग्रह वाहिनी के चारों ओर रक्त
वाहिकाओं का एक जाल होता है। ट्यूब U आकार की हो जाती है जिसे हेनले लूप कहा जाता है|
नेफ्रॉन की कार्यविधि - संचार प्रणाली में पोषक तत्व के साथ-साथ
अपशिष्ट पदार्थ भी होते हैं। बोमन कैप्सूल में प्रवेश करने वाली धमनी का व्यास
बड़ा होता है जबकि बाहर आने वाली धमनी का व्यास छोटा होता है। ग्लोमेरुलस के अंदर
दबाव बढ़ जाता है और अपशिष्ट के साथ-साथ उपयोगी पदार्थों को भी छान लिया जाता है।
इसे प्रारंभिक निस्पंदन कहा जाता है। ग्लूकोज, अमीनो एसिड, लवण और पानी मुख्य रूप से पुनः अवशोषित होते हैं , जब मूत्र संग्रह नलिका में बहता है। अब यूरिन को यूरेटर के जरिए
यूरिनरी ब्लैडर में भेजा जाता है। जहां से उसे उत्सर्जित कर दिया जाता हैं |
प्र .2 उत्सर्जी उत्पाद से छुटकारा पाने के
लिए पादप किन विधियों का उपयोग करते हैं ?
उत्तर- पौधों में कोई उत्सर्जन अंग नहीं होते हैं। वे निम्नलिखित विधियों
का उपयोग करते हैं-
रेजिन, लेटेक्स और अन्य पदार्थों को लेन्टीकल द्वारा बाहर निकाला जाता हैं ।
पत्तियों में रंध्रों द्वारा गैसों का आदान-प्रदान होता है।
मृत ऊतक कॉर्क , छाल आदि
में जमा हो जाते हैं।
अतिरिक्त पानी पत्तियों द्वारा वाष्पित होता है।
उत्तर- उत्पादित मूत्र की मात्रा शरीर में मौजूद अतिरिक्त पानी और घुले हुए अपशिष्ट की मात्रा पर निर्भर करती है। नेफ्रॉन में प्रतिदिन लगभग 180 लीटर द्रव एकत्र किया जाता है, लेकिन अधिकांश पानी नलिका द्वारा पुन: अवशोषित कर लिया जाता है। मूत्र एक लंबी ट्यूब में प्रवेश करता है, जिसे मूत्रवाहिनी कहा जाता है, जो मूत्राशय तक जाती है। इसमें मूत्र जमा होता है और जरूरत पड़ने पर इसे बाहर निकाल दिया जाता है।
अभ्यास प्रश्न
प्र .1 मनुष्य में वृक्क एक तंत्र का भाग हैं जो सम्बंधित है -
(a) पोषण
(b) श्वसन
(c) उत्सर्जन
(d) परिवहन
उत्तर- (c) उत्सर्जन
प्र .2 पौधों में जाइलम उत्तरदायी है
(a) जल का वहन
(b) भोजन का वहन
(c) अमीनो अम्ल का वहन
(d) ऑक्सीजन का वहन
उत्तर- (a) जल का वहन
प्र .3 स्वपोषी पोषण के लिए आवश्यक है
(a) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड और जल
(b) क्लोरोफिल
(c) सूर्य का प्रकाश
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
उत्तर- (c) उपरोक्त सभी
प्र .4 पाइरूवेट के विखंडन से यह कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड,जल और ऊर्जा देता है और यह क्रिया होती है
-
(a) कोशिका द्रव्य
(b) माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया
(c) हरित लवक
(d) नाभिक
उत्तर- (c) माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया
प्र .5 हमारे शरीर में वसा का पाचन कैसे होता
है? यह प्रक्रम
कहाँ होता है? उत्तर-वसा का पाचन छोटी आंत में होता है।
वसा छोटी आंत में बड़ी गोलिकाओं के रूप में मौजूद होती है। छोटी आंत को स्राव
क्रमशः यकृत और अग्न्याशय से पित्त रस और अग्नाशयी रस के रूप में प्राप्त होता है।
वसा का पाचन निम्नलिखित चरणों में पूरा होता है:
पित्त लवण बड़े ग्लोब्यूल्स को छोटे ग्लोब्यूल्स में तोड़ते हैं।
अग्न्याशय द्वारा स्रावित अग्नाशयी रस में एंजाइम लाइपेज होता है जो
इमल्सीफाइड वसा को तोड़ता है।
छोटी आंत की दीवारों से स्रावित एंजाइम अंत में वसा को वसा अम्ल में परिवर्तित करते हैं ।
प्र .6 भोजन के पाचन में लार की भूमिका क्या है?
उत्तर- लार पानी जैसा तरल पदार्थ है जिसमें लार एमाइलेज एंजाइम और श्लेष्मा
होता है। भोजन के पाचन में लार निम्नलिखित भूमिका निभाती है।
लार भोजन को नम और नरम करती है।
लार में एंजाइम एमाइलेज होता है जिसे टायलिन भी कहा जाता है जो स्टार्च (एक जटिल अणु) को
माल्टोस (चीनी का एक साधारण अणु) में तोड़
देता है।
लार एमाइलेज
स्टार्च------------------→ माल्टोस
उत्तर- स्वपोषी पोषण के लिए आवश्यक इस प्रकार हैं: (i)क्लोरोफिल (ii) पानी (iii) कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड (iv) सूर्य का प्रकाश
ऑक्सीजन उप उत्पाद है |
प्र .8 वायवीय तथा अवायवीय श्वसन में क्या अंतर हैं? कुछ जीवों के नाम लिखिए जिनमे अवायवीय श्वसन
होता है।
उत्तर-
|
वायवीय श्वसन |
अवायवीय श्वसन |
|
अवायवीय
श्वसन यह O2 की उपस्थिति में होता है। |
यह O2 की अनुपस्थिति
में होता है । |
|
गैसों
का आदान-प्रदान होता है। |
गैसों
का आदान-प्रदान अनुपस्थित है। |
|
यह
साइटोप्लाज्म और माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया में होता है। |
यह
केवल साइटोप्लाज्म में होता है। |
|
ग्लूकोज
पूरी तरह से कार्बन डाई ऑक्साइड, पानी
और ऊर्जा में ऑक्सीकृत हो जाता है। |
ग्लूकोज
को लैक्टिक एसिड और एथिल अल्कोहल में ऑक्सीकृत किया जाता है। |
|
यह 36 एटीपी
पैदा करता है। |
यह
केवल 2 एटीपी उत्पन्न करता है। |
प्र .9 गैसों के अधिकतम विनिमय के लिए कूपिकाएं
किस प्रकार अभिकल्पित है?
उत्तर- कूपिकाएँ (एल्वियोली) फेफड़ों में मौजूद छोटी गुब्बारे जैसी
संरचनाएं होती हैं जो गैसों के आदान-प्रदान के लिए क्षेत्र को अधिकतम करती हैं।
एल्वियोली की दीवारों में रक्त वाहिकाओं का विस्तृत नेटवर्क होता है। प्रत्येक
फेफड़े में 300-350 मिलियन वायु
कुपिकाएँ होती हैं। यह बड़ा सतह क्षेत्र गैसीय विनिमय बढ़ा देता है।
प्र .10 हमारे शरीर में हीमोग्लोबिन की कमी के
क्या परिणाम हो सकते हैं ?
उत्तर-हीमोग्लोबिन श्वसन वर्णक है जो
कोशिकीय श्वसन के लिए ऑक्सीजन को शरीर की कोशिकाओं तक पहुंचाता है। हमारे शरीर में
हीमोग्लोबिन की कमी से ऊतकों और कोशिकाओं को ऑक्सीजन की आपूर्ति प्रभावित होती है।
इससे एनीमिया(रक्ताल्पता )नामक रोग भी हो सकता है । इसके परिणामस्वरूप सांस की
तकलीफ, कड़ी
मेहनत करने में थकान आदि होगी।
प्र .11 मनुष्य में दोहरा परिसंचरणकी व्याख्या कीजिए। यह क्यों आवश्यक है?
उत्तर। प्रत्येक हृदय चक्र में रक्त हृदय से दो बार प्रवाहित होता है। शरीर
के अंगों से ऑक्सीजन रहित रक्त दाएं आलिंद और दाएं निलय में ले जाया जाता है। जब दायां वेंट्रिकल
सिकुड़ता है, तो
फुफ्फुसीय धमनी द्वारा रक्त फेफड़ों में ले जाया जाता है।
अब ऑक्सीजन युक्त रक्त को फुफ्फुसीय शिरा द्वारा बाएं आलिंद और बाएं निलय
में ले जाया जाता है। जब बायां निलय सिकुड़ता है, तो रक्त शरीर के सभी अंगों में वितरित हो
जाता है। इसलिए रक्त एक हृदय चक्र में दो बार बहता है, इसे’दोहरा परिसंचरण ' कहा जाता है।
दोहरा परिसंचरण का महत्व: दोहरा परिसंचरण ऑक्सीजन युक्त और डीऑक्सीजनेटेड रक्त को अलग रखता है ताकि रक्त मिश्रित न हो। यह शरीर के सभी अंगों और कोशिकाओं को ऑक्सीजन की अत्यधिक कुशल आपूर्ति करता है। मानव और पक्षियों जैसे गर्म रक्त वाले जानवरों को शरीर का तापमान स्थिर बनाए रखना होता है, इसलिए शरीर के तापमान को बनाए रखने के लिए उन्हें अधिक ऑक्सीजन की आवश्यकता होती है, दोहरा परिसंचरण शरीर के अंगों को ऑक्सीजन की अधिक आपूर्ति करता है।
प्र. 12 जाइलम
और फ्लोएम में पदार्थों के वहन में क्या अंतर है?
उत्तर- जाइलम और फ्लोएम में पदार्थों परिवहन के बीच अंतर
|
जायलम |
फ्लोएम |
|
(i) जाइलम
ऊतक खनिजों का परिवहन करता है| |
(i) फ्लोएम
द्वारा पत्तियों द्वारा तैयार भोजन का परिवहन होता है। |
|
(ii) परिवहन
ऊपर की दिशा में होता है। |
(ii) यह परिवहन
पत्तियों से अन्य भागों जैसे जड़ों, फलों और बीजों तक होता है। |
|
(iii) यह मुख्य रूप से
वाष्पोत्सर्जन जैसे साधारण भौतिक बलों का उपयोग करके होता है। |
(iii)इस परिवहन
में एटीपी के रूप में ऊर्जा का उपयोग किया जाता है
|
उत्तर-
|
वायु कुपिका (एल्वियोली) |
नेफ्रॉन |
|
(i) एल्वियोली(कूपिकाएँ ) फेफड़ों की महीन नलियों के अंत में गुब्बारे जैसी
संरचना होती है। |
(i) नेफ्रॉन गुर्दे में मौजूद ट्यूबलर संरचनाएं हैं।
|
|
(ii) एल्वियोली श्वसन तंत्र की इकाई है। |
(ii) नेफ्रॉन उत्सर्जन तंत्र की
इकाई है। |
|
(iii)। एल्वियोली की दीवारें एक कोशिका मोटी होती हैं और इसमें रक्त का एक व्यापक
नेटवर्क होता है केशिकाएं। |
(iii)नेफ्रॉन ग्लोमेरुलस, बोमन कैप्सूल और एक लंबी
वृक्क नली से बने होते हैं। इसमें पतली दीवारों वाली केशिकाओं का एक समूह भी
होता है। |
|
(iv) कूपिकाओं में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान होता है।
|
(iv)नेफ्रॉन में, अपशिष्ट उत्पादों को फ़िल्टर
किया जाता है और कुछ अणुओं का चयनात्मक पुन: अवशोषण होता है। |
महत्वपूर्ण बिंदु
1. विभिन्न प्रकार की गति को जीवन के सूचक माना जा सकता है।
2. जीवन के अनुरक्षण के लिए पोषण, श्वसन, शरीर के अंदर पदार्थों का संवहन तथा
अपशिष्ट उत्पादों का उत्सर्जन आदि प्रक्रियाएँ आवश्यक होती है।
3. स्वपोषी पोषण में पर्यावरण से सरल
अकार्बनिक पदार्थों का सेवन और सूर्य जैसे बाहरी ऊर्जा स्रोत का उपयोग करके जटिल
उच्च ऊर्जा कार्बनिक पदार्थों को संश्लेषित करना शामिल है।
4. विषमपोषी
पोषण में अन्य जीवों द्वारा तैयार किए गए जटिल पदार्थों का सेवन शामिल है।
5. मनुष्यों
में, खाया
गया भोजन आहारनाल में विभिन्न चरणों में टूट जाता है और पचाया हुआ भोजन छोटी आंत
में अवशोषित होकर शरीर की सभी कोशिकाओं में भेज दिया जाता है।
6. श्वसन
की प्रक्रिया के दौरान, जटिल
कार्बनिक यौगिक जैसे ग्लूकोज क टूट कर एटीपी के रूप में ऊर्जा प्रदान करते हैं। कोशिकाओं
में अन्य प्रतिक्रियाओं से ऊर्जा प्रदान करने के लिए एटीपी का उपयोग किया जाता है।
7. श्वसन वायवीय
या अवायवीय हो सकता है। वायवीय श्वसन में जीव को अधिक ऊर्जा प्राप्त होती है।
8. मनुष्यों
में, ऑक्सीजन, कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड, भोजन और उत्सर्जन उत्पादों जैसे पदार्थों
का वहन परिसंचरण तंत्र का एक कार्य है। परिसंचरण तंत्र में हृदय और रक्त वाहिकाएं
होती हैं।
9. उच्च विभेदित पौधों में, जल, खनिज, भोजन और अन्य सामग्रियों का परिवहन
संवहनी ऊतकों का एक कार्य है जिसमें जाइलम और फ्लोएम होते हैं।
यहां आपको अध्याय 6 जैव प्रक्रम के अतिरिक्त
प्रश्न - उत्तर मिलेंगे जो परीक्षा की दृष्टि से आपके लिए बहुत उपयोगी होंगे । ये प्रश्न हमारे शिक्षकों
द्वारा तैयार किए गए हैं।
Class 10
science chapter 6 extra questions
-
Extra Questions
कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 6 अतिरिक्त प्रश्न –
1. जैव प्रक्रम
क्या हैं?
उत्तर - जीवित जीवों द्वारा स्वयं को जीवित रखने के लिए की जाने वाली आधार्हूट
प्रक्रियाओं को जैव प्रक्रम के रूप में जाना जाता है।
2. जीवों
में ऊर्जा के स्रोत क्या हैं?
उत्तर - जीवों में भोजन ऊर्जा का मुख्य स्रोत है और भोजन को ईंधन के रूप
में भी जाना जाता है।
उत्तर - पोषण एक शारीरिक प्रक्रिया है जिसमें जीव पोषक तत्व प्राप्त करते हैं । ये पोषक तत्व
जीवित जीवों में गतिविधियों के लिए आवश्यक हैं इसलिए पोषण भोजन प्राप्त करने और
उपयोग करने की प्रक्रिया है।
4. निम्न में पोषण की
विधि क्या है –
(a) कवक
(b) प्लास्मोडियम
उत्तर - (a) कवक- मृतपोषी पोषण
(b) प्लास्मोडियम- परजीवी पोषण
5. किसी
जीव को सोते समय ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता क्यों होती है?
उत्तर - सोते समय शरीर में विभिन्न
जैविक प्रक्रियाएं होती रहती हैं, इसलिए सोते समय ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होती है।
6. उन कारकों के नाम लिखिए जो प्रकाश
संश्लेषण की दर को प्रभावित करते हैं|
उत्तर - निम्नलिखित कारक प्रकाश संश्लेषण की दर को प्रभावित करते हैं-
(a).सूरज की रोशनी
(b). पानी
(c).तापमान
(d).कार्बन डाइऑक्साइड
7.प्रकाश अभिक्रिया क्या है? अथवा प्रकाश अभिक्रिया को परिभाषित कीजिए।
उत्तर
- प्रकाश की उपस्थिति में होने वाली रासायनिक अभिक्रिया प्रकाश अभिक्रिया कहलाती
है। यह क्लोरोफिल के कणिका(ग्रेना) में होती है।
8. अप्रकाशिक अभिक्रिया क्या है?
उत्तर - एक रासायनिक अभिक्रिया जो प्रकाश की अनुपस्थिति में होती है और क्लोरोप्लास्ट के स्ट्रोमा में होती
है।
9. उस प्रक्रिया का नाम बताइए जिसके
द्वारा पौधे भोजन बनाते हैं।
उत्तर - प्रकाश संश्लेषण
10. हरित लवक (क्लोरोफिल) क्या है?
उत्तर- हरित लवक (क्लोरोफिल) एक हरे रंग का वर्णक होता है जो पौधों की पत्तियों और पौधे के हरे भागों
में पाया जाता है। यह सूर्य के प्रकाश को ग्रहण करता है। यह पादप कोशिका में क्लोरोप्लास्ट पाया जाता
है।
11. पौधों में प्रकाश अभिक्रिया कहाँ होती
है?
उत्तर-पौधों में प्रकाश अभिक्रिया क्लोरोप्लास्ट में थायलाकोइड्स (ग्रेना) में
होती है।
12. पौधों
में जाइलम की दो कोशिकाओं के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर - ट्रेकिड्स(वाहिनिका) (ii)। वाहिकाएं
13. उस
ऊतक का नाम लिखिए जो पौधों में जल और खनिज का परिवहन करता है|
उत्तर - जाइलम ऊतक
14. मनुष्य में सबसे बड़ी ग्रंथि कौन सी है?
उत्तर – यकृत
उत्तर- विली
16. प्लाज्मा
क्या है?
उत्तर- प्लाज्मा एक रंगहीन द्रव है और इसमें पानी, प्रोटीन और कार्बोहाइड्रेट होते हैं।
17. लाल
कणिकाओं को क्या लाल बनाता है?
उत्तर - हीमोग्लोबिन
18. वृक्क
की उत्सर्जी इकाई का नाम बताइए?
उत्तर - नेफ्रॉन
19. मानव
हृदय में कितने कक्ष पाए जाते हैं?
उत्तर - चार कक्ष- दो ऊपरी आलिंद और दो निचले निलय।
20. मानव में पदार्थों के परिवहन के लिए
उत्तरदायी तंत्र का नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर- रक्त परिसंचरण
21. रक्त
के प्रमुख घटक कौनसे हैं ।
उत्तर - रक्त में लाल रुधिर कणिकाएँ, श्वेतरुधिर कणिकाए , प्लेटलेट्स(बिम्बाणु) और प्लाज्मा होते
हैं।
22. श्वासनली
की दीवारें कम हवा होने पर सिकुड़ती क्यों नहीं हैं ?
उत्तर- श्वासनली में C आकार के उपास्थि के छल्ले पायें जाते है, जो इसके
आकार को निश्चित बनाते है ,इसलिए जब इसमें हवा नहीं होती है तो श्वासनली सिकुड़ती नहीं हैं ।
23. प्रकाश
संश्लेषण की दो अवस्थाओं के नाम लिखिए।
उत्तर - (i) प्रकाशिक अभिक्रिया (ii) अप्रकाशिक अभिक्रिया
24. आहार
नाल का कौन सा भाग यकृत से पित्त प्राप्त करता है?
उत्तर - छोटी आंत
25. अग्नाशयी रस का क्या कार्य है?
उत्तर - अग्नाशयी रस में ट्रिप्सिन, एमाइलेज और लाइपेज एंजाइम पाए जाते हैं।
ट्रिप्सिन प्रोटीन का पाचन , लाइपेज वसा का इमल्सीकरण और एमाइलेज भोजन
में मौजूद कार्बोहाइड्रेट का पाचन करता
है।
26. श्वसन
के दौरान गैसों का आदान-प्रदान कहाँ होता है?
उत्तर- फेफड़ों में वायुकोशिकाओं में गैसों का आदान-प्रदान होता है।
27. प्रकाश संश्लेषण की प्रक्रिया में
ऑक्सीजन का स्रोत क्या है?
उत्तर - प्रकाश संश्लेषण की प्रक्रिया में ऑक्सीजन एक उपोत्पाद के रूप में प्राप्त
होता हैं और मिट्टी से अवशोषित पानी इस
ऑक्सीजन का स्रोत है।
28. क्रमाकुंचन
गति क्या है?
उत्तर- भोजन नली की दीवार के संकुचन और विस्तार को क्रमाकुंचन गति कहते हैं
और इस प्रक्रिया के कारण भोजन आहार नाल में आगे बढ़ता है।
29. क्या
होगा जब पौधे में जाइलम हटा दिया जाएगा?
उत्तर .- जाइलम
पानी और खनिजों को मिट्टी से पौधे के अन्य भागों तक पहुँचाता है, और जब यह हटा दिया जाता है तो परिवहन की
प्रक्रिया रुक जाएगी और अंततः पौधा मर जाएगा।
30. काइम(चाइम
) क्या है?
उत्तर- जब भोजन पेट में प्रवेश करता है जहां उसे जठर रस के साथ मिलाकर एक
अर्ध-ठोस पेस्ट बनाया जाता है, तो इसे काइम(चाइम ) कहा जाता है।
Remedial Education Point.com आपको कक्षा 10 के लिए पूरी अध्ययन सामग्री बिल्कुल मुफ्त प्रदान करता है। ये NCERT समाधान और अध्ययन सामग्री आपके CBSE बोर्ड और अन्य राज्य बोर्ड परीक्षाओं के लिए अच्छे अंक लाने में आपकी मदद करेगी। अब आप हमारे विशेषज्ञ शिक्षकों द्वारा तैयार सटीक NCERT कक्षा 10 विज्ञान अध्याय 6 जैव प्रक्रम प्राप्त कर सकते हैं।
- Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
- Chapter 8 How Do Organisms Reproduce?
- Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution
- Chapter 14 Sources of Energy
- Chapter 16 Management of Natural Resources
- MCQ Questions for Class 10 Science Biology Chapter6
- Life Processes Extra Questions
If you find any difficulty, please do comment.
Hoping for progress with Remedial Classes



.jpg)


No comments:
Post a Comment